mlforecast


Install
PyPI
pip install mlforecast
conda-forge
conda install -c conda-forge mlforecast
For more detailed instructions you can refer to the installation
page.
Quick Start
Get Started with this quick
guide.
Follow this end-to-end
walkthrough
for best practices.
Videos
Sample notebooks
Why?
Current Python alternatives for machine learning models are slow,
inaccurate and don’t scale well. So we created a library that can be
used to forecast in production environments.
MLForecast
includes efficient feature engineering to train any machine learning
model (with fit and predict methods such as
sklearn) to fit millions of time
series.
Features
- Fastest implementations of feature engineering for time series
forecasting in Python.
- Out-of-the-box compatibility with pandas, polars, spark, dask, and
ray.
- Probabilistic Forecasting with Conformal Prediction.
- Support for exogenous variables and static covariates.
- Familiar
sklearn syntax: .fit and .predict.
Missing something? Please open an issue or write us in

Examples and Guides
📚 End to End
Walkthrough:
model training, evaluation and selection for multiple time series.
🔎 Probabilistic
Forecasting:
use Conformal Prediction to produce prediciton intervals.
👩🔬 Cross
Validation:
robust model’s performance evaluation.
🔌 Predict Demand
Peaks:
electricity load forecasting for detecting daily peaks and reducing
electric bills.
📈 Transfer
Learning:
pretrain a model using a set of time series and then predict another one
using that pretrained model.
🌡️ Distributed
Training:
use a Dask, Ray or Spark cluster to train models at scale.
How to use
The following provides a very basic overview, for a more detailed
description see the
documentation.
Data setup
Store your time series in a pandas dataframe in long format, that is,
each row represents an observation for a specific serie and timestamp.
from mlforecast.utils import generate_daily_series
series = generate_daily_series(
n_series=20,
max_length=100,
n_static_features=1,
static_as_categorical=False,
with_trend=True
)
series.head()
| 0 | id_00 | 2000-01-01 | 17.519167 | 72 |
| 1 | id_00 | 2000-01-02 | 87.799695 | 72 |
| 2 | id_00 | 2000-01-03 | 177.442975 | 72 |
| 3 | id_00 | 2000-01-04 | 232.704110 | 72 |
| 4 | id_00 | 2000-01-05 | 317.510474 | 72 |
Note: The unique_id serves as an identifier for each distinct time
series in your dataset. If you are using only single time series from
your dataset, set this column to a constant value.
Models
Next define your models, each one will be trained on all series. These
can be any regressor that follows the scikit-learn API.
import lightgbm as lgb
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
models = [
lgb.LGBMRegressor(random_state=0, verbosity=-1),
LinearRegression(),
]
Forecast object
Now instantiate an
MLForecast
object with the models and the features that you want to use. The
features can be lags, transformations on the lags and date features. You
can also define transformations to apply to the target before fitting,
which will be restored when predicting.
from mlforecast import MLForecast
from mlforecast.lag_transforms import ExpandingMean, RollingMean
from mlforecast.target_transforms import Differences
fcst = MLForecast(
models=models,
freq='D',
lags=[7, 14],
lag_transforms={
1: [ExpandingMean()],
7: [RollingMean(window_size=28)]
},
date_features=['dayofweek'],
target_transforms=[Differences([1])],
)
Training
To compute the features and train the models call fit on your
Forecast object.
fcst.fit(series)
MLForecast(models=[LGBMRegressor, LinearRegression], freq=D, lag_features=['lag7', 'lag14', 'expanding_mean_lag1', 'rolling_mean_lag7_window_size28'], date_features=['dayofweek'], num_threads=1)
Predicting
To get the forecasts for the next n days call predict(n) on the
forecast object. This will automatically handle the updates required by
the features using a recursive strategy.
predictions = fcst.predict(14)
predictions
| 0 | id_00 | 2000-04-04 | 299.923771 | 311.432371 |
| 1 | id_00 | 2000-04-05 | 365.424147 | 379.466214 |
| 2 | id_00 | 2000-04-06 | 432.562441 | 460.234028 |
| 3 | id_00 | 2000-04-07 | 495.628000 | 524.278924 |
| 4 | id_00 | 2000-04-08 | 60.786223 | 79.828767 |
| ... | ... | ... | ... | ... |
| 275 | id_19 | 2000-03-23 | 36.266780 | 28.333215 |
| 276 | id_19 | 2000-03-24 | 44.370984 | 33.368228 |
| 277 | id_19 | 2000-03-25 | 50.746222 | 38.613001 |
| 278 | id_19 | 2000-03-26 | 58.906524 | 43.447398 |
| 279 | id_19 | 2000-03-27 | 63.073949 | 48.666783 |
280 rows × 4 columns
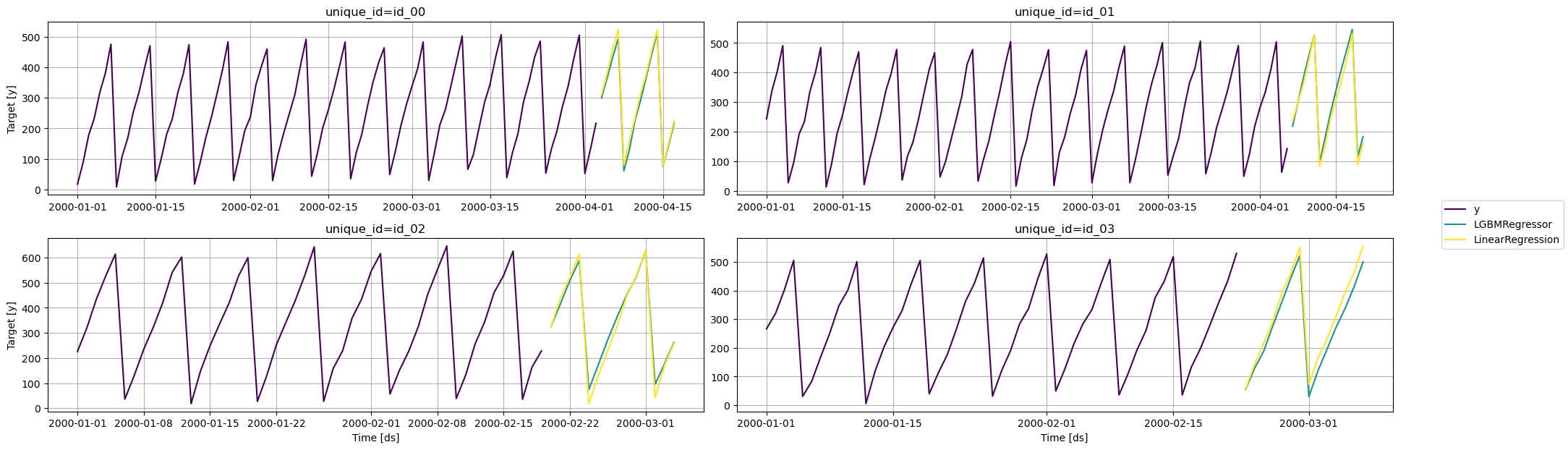
Visualize results
from utilsforecast.plotting import plot_series
fig = plot_series(series, predictions, max_ids=4, plot_random=False)
How to contribute
See
CONTRIBUTING.md.