
Research
PyPI Package Disguised as Instagram Growth Tool Harvests User Credentials
A deceptive PyPI package posing as an Instagram growth tool collects user credentials and sends them to third-party bot services.
Commandline tool for visualizing data distribution on your storage volumes.
It can be difficult to create a mental picture of where your bytes are, especially when you have a lot of them. Thin provisioning, copy-on-write, deduplication and compression can help you pack more bytes into your raw storage, but can also make it even harder to understand what's really consuming your storage.
This becomes really important when you're trying to cherrypick the most critical data from a 9TB filesystem that will still fit on a 640GB USB disk. It also would have been useful a year ago when I was trying to keep track of 100TB+ on a nearline backup system.
It also particularly helps when you're using a tool like zfs-auto-snapshot and you're wondering if deleting any of your old snapshots would gain you back a significant amount of space, or if they're mostly just referencing the same data that's in the live filesystem.
Volviz tries to help.
If you've ever used WinDirStat or Baobab (Gnome's Disk Usage Analyzer), you're familiar with the basic idea. Those tools, however, map the size of files in a hierarchy of directories.
Volviz maps the size of filesystems, snapshots, and volumes. It shows the actual space used on disk, not just the reported size.
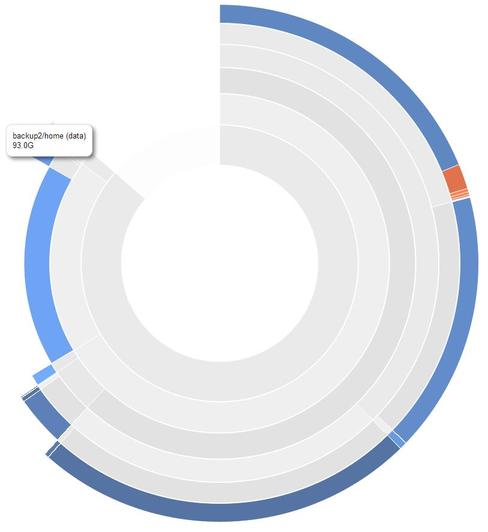
Barely alpha. This was hacked together in a day. The HTML/JavaScript/CSS is the sort of mess you expect when cutting and pasting from a bunch of different examples.
But safe! It's completely read-only in its default mode. If you ask it to, it'll write a JSON file and an HTML file where you tell it to.
Only ZFS is currently supported. It shouldn't be too hard to refactor and add adapters for LVM and others.
Only Linux has been tested.
Volviz gets all its visualization magic from D3.js. D3.js is awesome.
Installation should be simple with RubyGems. If you don't already have it, your package manager can install everything you need.
sudo apt-get install rubygems || sudo yum install rubygems
Once that's done, you can install the latest release:
sudo gem install volume_visualizer
Volviz's default mode will query the first volume it finds, discover where all the bytes are, launch an HTTP server and display a URL on the console. Navigate to this URL to see the visualization.
Note: Volviz needs root privileges to get volume information, and will run sudo if necessary. If you don't want to trust Volviz with root, there are other ways to run it. Keep reading.
In Automatic Mode, Volviz scans the first volume it finds and starts a web server to show you the output. Volviz will output a URL on the console.
> vv
This is a shortcut for the instaweb command.
> vv instaweb
You can specify the volume you want to visualize.
> vv --volume backup2
Volviz only needs root when querying your volumes. If you don't like that, you can ask Volviz to parse a text file. First, ask volviz for the correct command.
> vv show-command
You can figure it out yourself easily enough, but you can specify a volume if you like.
> vv show-command --volume backup2
Once you're satisfied that the command Volviz suggests is safe, you can run it as root yourself and pipe the output into Volviz.
> sudo zfs list -t all -H -r \
-o name,available,used,referenced,usedbysnapshots,usedbydataset,\
usedbychildren,compressratio,type \
tank | vv --parse-file -
Or:
> sudo zfs list -t all -H -r \
-o name,available,used,referenced,usedbysnapshots,usedbydataset,\
usedbychildren,compressratio,type \
tank > /tmp/zfsdata
> vv --parse-file /tmp/zfsdata
Volviz's built-in web server is meant for convenience only. You might instead want to generate static output that can be served by a webserver of your choice.
> mkdir /var/www/volviz
> vv generate --output-path /var/www/volviz
You can use a non-default name for the datafile if you like:
> vv generate --output-path /var/www/volviz --data-name backup2
You can load alternate datafiles in the Volviz UI by appending
?data=backup2 to the URL.
This might make particular sense if you want to update your data regularly from cron.
You can combine untrusted and static mode if you like.
> vv generate --output-path /var/www/volviz --parse-file /tmp/zfsdata
Maybe you have a bunch of hosts and you don't want to install Volviz on
each one. Generate data to parse and ship it to a central host that has
Volviz installed, and then use Static Mode to generate the output.
Assuming you've put all your volume dumps in /var/lib/volviz/, here's
some Bash that might be a good starting point.
OUTDIR=/var/www/volviz
DIR=$OUTDIR/directory.html
echo "<h1>Volviz</h1><ul>" > $DIR
for DATAFILE in /var/lib/volviz/*; do
NAME=`basename $DATAFILE`
vv generate --output-path $OUTDIR --data-name $NAME --parse-file $DATAFILE
echo "<li><a href="index.html?data=$NAME">$NAME</a></li>" >> $DIR
done
echo "</ul>" > $DIR
echo Processing complete. The following URL might work.
echo http://`hostname`/volviz/directory.html
> vv help
You probably figured that out on your own.
Volviz ignores any volume, filesystem, or snapshot with a reported size of 0 bytes.
I'd be thrilled to get your pull request. Boilerplate follows.
git checkout -b my-new-feature)git commit -am 'Add some feature')git push origin my-new-feature)FAQs
Unknown package
We found that volume_visualizer demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
A deceptive PyPI package posing as an Instagram growth tool collects user credentials and sends them to third-party bot services.

Product
Socket now supports pylock.toml, enabling secure, reproducible Python builds with advanced scanning and full alignment with PEP 751's new standard.

Security News
Research
Socket uncovered two npm packages that register hidden HTTP endpoints to delete all files on command.