
Research
/Security News
npm Malware Campaign Uses Adspect Cloaking to Deliver Malicious Redirects
Malicious npm packages use Adspect cloaking and fake CAPTCHAs to fingerprint visitors and redirect victims to crypto-themed scam sites.


Ax Sharma
October 24, 2022
Last week, when reviewing multiple packages flagged by Socket’s sleek GitHub App, a finding that stood out was an npm package called, ‘state-counter’ which, at the time of writing, has received almost 1000 downloads.

We’ve previously seen various statistical tools written in NodeJS including simple “visit” counters but a “state-counter,” you say?
In addition to containing obfuscated code, the package hits several red flags that warranted us to take a closer look:
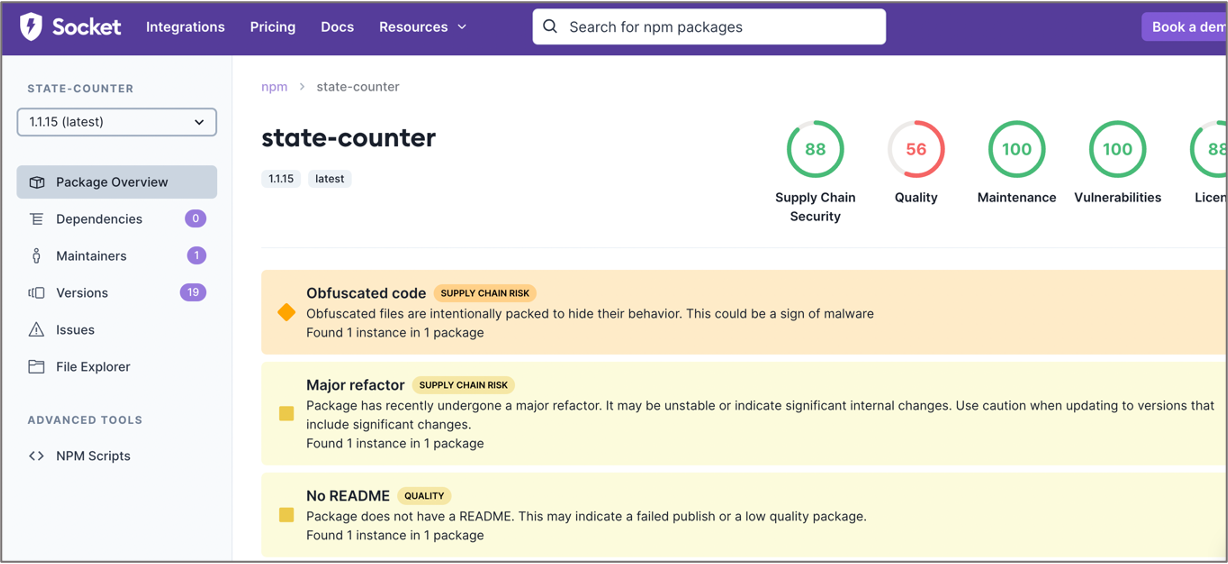
Nearly all versions of ‘state-counter’ contain tightly packed obfuscated code in the “counter.js” file. Interestingly, comments left by the package author in the JavaScript file mislead you to believe the package is indeed a “stat” counter—or related to the legitimate StatCounter.com operation:
A classic technique exhibited by malicious open source packages leveraging brandjacking and typosquatting techniques.
Moreover, the copyright banner attributing the code to Twitter is even flimsier as neither the code contained in the package nor the company StatCounter have anything to do with Twitter.
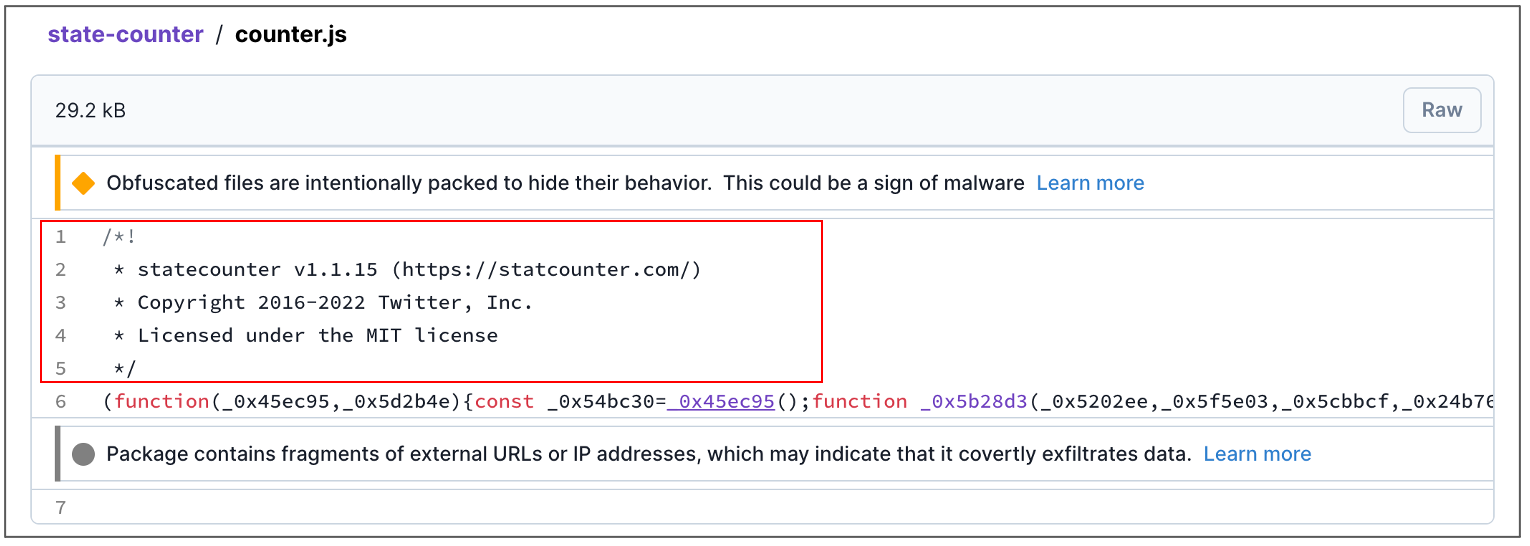
The obfuscation contained in later versions of “state-counter” is quite complex with most plaintext strings scrambled haphazardly. Analyzing earlier versions, now unpublished from npm by the author but preserved by Socket, helped us better understand the true nature of the package during static analysis.
A quick glance at the (plaintext) string array alone showed fragments of several URLs, including one starting with https://t.co/ - Twitter’s URL shortener:
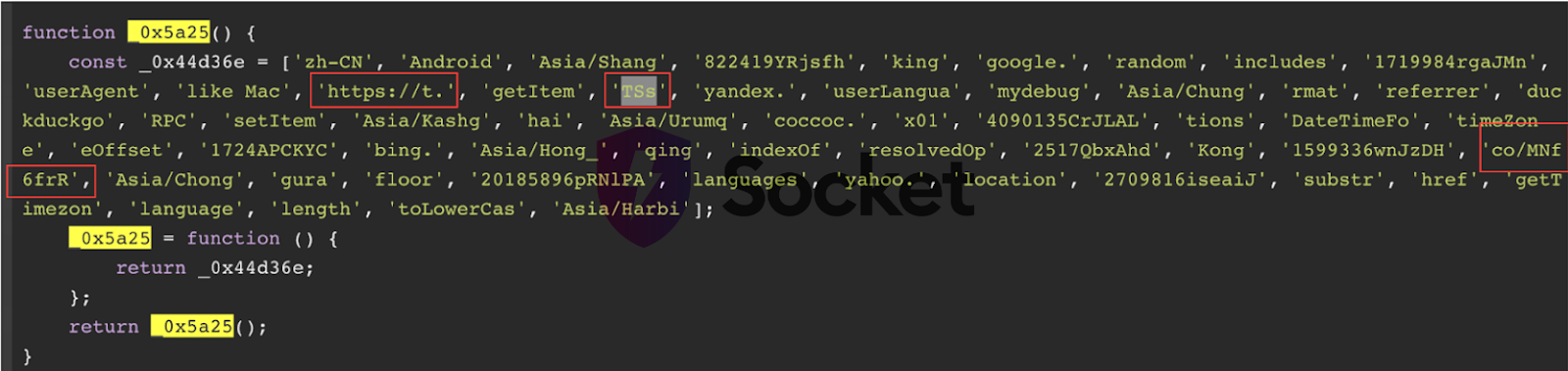
This fragmented URL, hxxps://t(.)co/MNf6frRTSs redirects to an adult love doll and toy store:
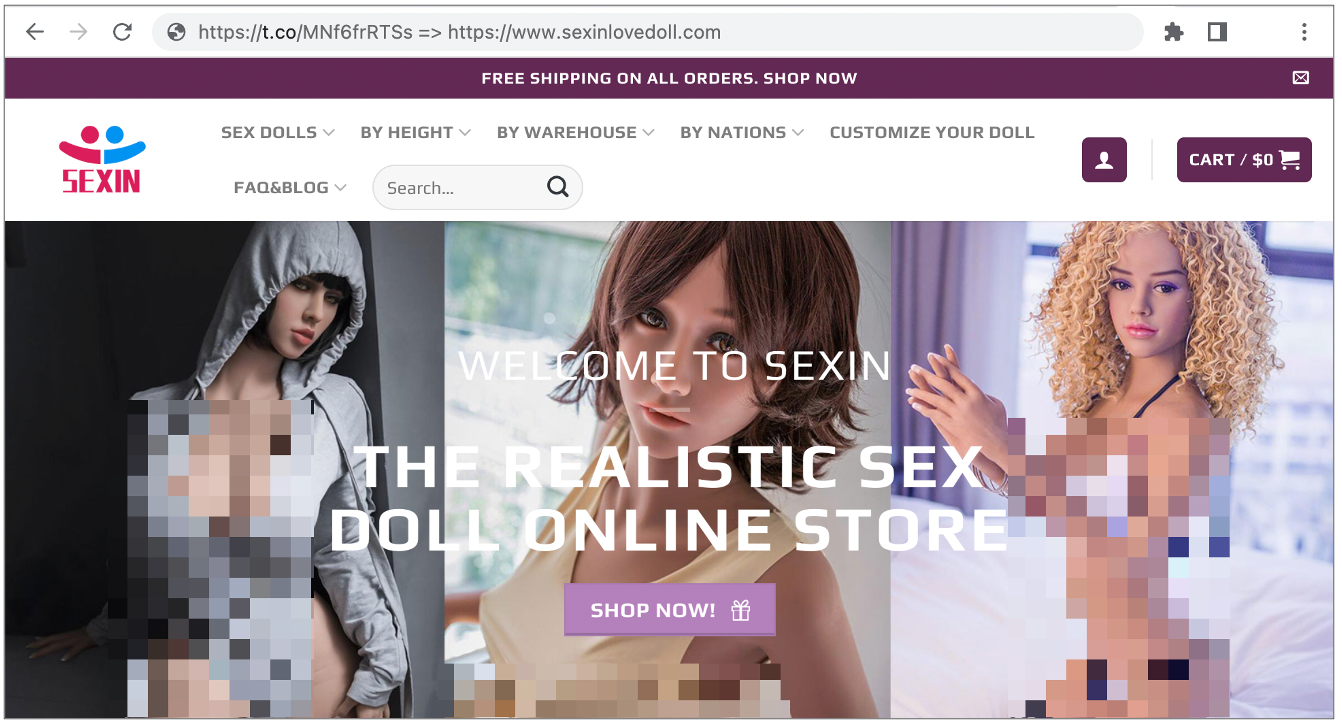
Other references in the code point to specific sections of the online store, as well as ascertaining the user’s timezone, language as well as search engine settings. On meeting the specified criteria, the adware launches the NSFW URL on a user’s system.
Based on the criteria specified, “state-counter” appears to target China-based developers and users.
Granted, this typosquat isn’t nearly as sinister as malicious npm packages previously caught launching cryptominers, password stealers, and even ransomware scripts. But, it still counts as a counterfeit component posing risk to the overall security, integrity, and hygiene of the open source software ecosystem.
Ongoing threats to the software supply chain include package hijacks and dependency confusion PoCs, such as 'surveyoptic’ and ‘wormhole-chain-sdk’—the latter targeting an actual internal dependency of Wormhole Foundation’s SDK. These are just a few examples of unwanted components identified by Socket this week.
We reported “state-counter” to npm prior to publishing and it was taken down shortly by GitHub’s security team.
Developers can install Socket’s free GitHub app which can detect malicious uses of obfuscated code among other supply chain risks in your npm packages.
Subscribe to our newsletter
Get notified when we publish new security blog posts!
Try it now

Research
/Security News
Malicious npm packages use Adspect cloaking and fake CAPTCHAs to fingerprint visitors and redirect victims to crypto-themed scam sites.

Research
/Security News
A malicious Chrome extension posing as an Ethereum wallet steals seed phrases by encoding them into Sui transactions, enabling full wallet takeover.

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers discovered nine malicious NuGet packages that use time-delayed payloads to crash applications and corrupt industrial control systems.