Product
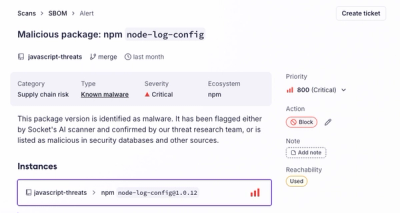
Introducing the Alert Details Page: A Better Way to Explore Alerts
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
To facilitate the implementation of standard func(http.Handler) http.Handler
middleware, the MiddlewareFunc interface and the NewMiddleware() factory
were created.
type MiddlewareFunc func(rw http.ResponseWriter, req *http.Request,
next http.Handler)
The next argument is never nil, and a do-nothing NoMiddleware middleware
was introduced. When the NoMiddleware() is called without a handler, it will
return a 404 handler.
Alternatively there is MiddlewareErrorFunc and NewMiddlewareError() that
allows the handler to return an error that is then passed to HandleError()
and then to the registered ErrorHandler.
We call Resolver a function that will give us the Path our resource should be
handling, and for this task darvaza.org/x/web provides four helpers.
WithResolver() to attach a dedicated Resolver to the request's context.NewResolverMiddleware() to attach one to every request.Resolver(), to retrieve a previously attached Resolver from the request's
context.Resolve() helper that will use the above and call the specified
Resolver, or take the request's URL.Path, and then clean it to make sure
its safe to use.CleanPath() cleans and validates the path for URL.Path handling.The darvaza.org/x/web/resource sub-package offers a Resource[T] wrapper to
implement a RESTful interface to a particular resource.
Using respond.WithRequest() we compute our options and
PreferredContentType() tells one how to encode the data.
The QualityList parser allows choosing the best option during Content
Negotiation, e.g. accepted Content-Types.
qlist offers two helpers to choose the best option from a QualityList and a
list of supported options, BestQuality() and BestQualityWithIdentity().
Identity is an special option we consider unless it's explicitly forbidden.
qlist.BestEncoding() is a special case of BestQualityWithIdentity()
using the Accept header, and falling back to "identity" as magic type.
Helper functions for manipulating HTTP headers:
SetHeader(hdr, key, value, args...) — Sets a header value, with
optional fmt.Sprintf formatting.SetHeaderUnlessExists(hdr, key, value, args...) — Sets a header
value only if not already present.SetCache(hdr, duration) — Sets the Cache-Control header based on
the duration.SetNoCache(hdr) — Sets the Cache-Control header to "no-cache".SetRetryAfter(hdr, duration) — Sets the Retry-After header in
seconds, rounded up (minimum 1 second for non-zero durations).SetLastModifiedHeader(hdr, time) — Sets the Last-Modified header
in HTTP-date format if not already set (uses current time if zero).CheckIfModifiedSince(req, time) — Checks the If-Modified-Since
header for HTTP 304 caching support (per RFC 7232). Returns true if
the resource has been modified since the client's cached time, false
otherwise (uses second precision for comparison).Cache-Control duration conventions:
"private""no-cache""max-age=<seconds>"For development guidelines, architecture notes, and AI agent instructions, see AGENTS.md.
HTTPErrorHTTPError{} is an http.Handler that is also an error and can be used to
build HTTP errors.
darvaza.org/x/web provides a mechanism to hook an HTTP error handler to the
request Context.
WithErrorHandler() to attach a
func(http.ResponseWriter, *http.Request, error)NewErrorHandlerMiddleware() to attach it to every request,ErrorHandler() to read it back.We also provide a basic implementation called HandleError which will first
attempt to get a better handler for the context, via
ErrorHandler(req.Context()) and hand it over.
If there is no ErrorHandlerFunc in the context it will test if the error
itself via the http.Handler interface and invoke it.
As last resort HandleError() will check if the error provides an
HTTPStatus() int method to infer the HTTP status code of the error, and if
negative or undefined it will assume it's a 500, compose a web.HTTPError and
serve it.
AsError() that will do the same as HandleError() to ensure the given
error, if any, is http.Handler-ableAsErrorWithCode() to suggest an HTTP status code to be used
instead of 500 when it can't be determined.There are also web.HTTPError factories to create new errors, from a generic:
NewHTTPError() and NewHTTPErrorf() and a companion ErrorText(code)
helper.redirect factories (with Location header):
NewStatusMovedPermanently(loc, ...) (301)NewStatusFound(loc, ...) (302)NewStatusSeeOther(loc, ...) (303)NewStatusTemporaryRedirect(loc, ...) (307)NewStatusPermanentRedirect(loc, ...) (308)error wrappers (preserve underlying error):
NewStatusBadRequest(err) (400)NewStatusUnsupportedMediaType(err) (415)NewStatusUnprocessableEntity(err) (422)NewStatusInternalServerError(err) (500)NewStatusBadGateway(err) (502)retry helpers (with Retry-After header):
NewStatusTooManyRequests(duration) (429)NewStatusServiceUnavailable(duration) (503)and simple status responses:
NewStatusNotModified() (304)NewStatusUnauthorized() (401)NewStatusForbidden() (403)NewStatusNotFound() (404)NewStatusMethodNotAllowed(allowed...) (405)NewStatusNotAcceptable() (406)NewStatusConflict() (409)NewStatusGone() (410)NewStatusPreconditionFailed() (412)NewStatusNotImplemented() (501)NewStatusGatewayTimeout() (504)FAQs
Unknown package
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.
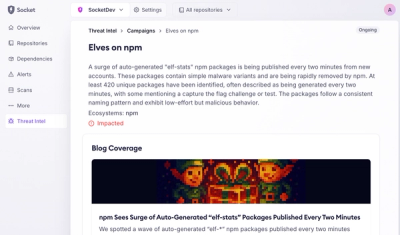
Product
Campaign-level threat intelligence in Socket now shows when active supply chain attacks affect your repositories and packages.

Research
Malicious PyPI package sympy-dev targets SymPy users, a Python symbolic math library with 85 million monthly downloads.