
Product
Introducing Socket Fix for Safe, Automated Dependency Upgrades
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.
To install, run either npm install --save @ayc0/std or yarn add @ayc0/std, and then:
const std = require('@ayc0/std');
const multiplyBy2 = std.map(x => x * 2);
// OR
const map = require('@ayc0/std/map');
const multiplyBy2 = map(x => x * 2);
// And then you can use it:
const input = [1, 2];
const output = multiplyBy2(input);
For all of the functions listed below, you can either do std.<function> or import them from @ayc0/std/<function>:
function* range([from,] to[, step]) {
// yield every steps
}
function* zip(iterables) {
// yield [currentValues, indexes, iterables]
}
for (const [currentValues, indexes, iterables] of zip([
'123',
[1, 2, 3],
{ a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 },
])) {
console.log(currentValues);
// [ '1', 1, 1 ]
// [ '2', 2, 2 ]
// [ '3', 3, 3 ]
console.log(indexes);
// [ 0, 0, 'a' ]
// [ 1, 1, 'b' ]
// [ 2, 2, 'c' ]
}
function len(iterable) {
// return length of iterable
}
function map(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
// return new iterable of the input iterable type
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// return new element of iterable
}
map(x => x * 2)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// { a: 2, b: 4 }
map(x => x * 2)([1, 2]);
// [ 2, 4 ]
map(x => x * 2)(new Set([1, 2]));
// Set(2) {2, 4}
map(x => x * 2)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// Map(2) {"a" => 2, "b" => 4}
map(x => x.repeat(2))('ab');
// 'aabb'
function forEach(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
}
forEach(x => console.log(x * 2))({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// 2
// 4
forEach(x => console.log(x * 2))([1, 2]);
// 2
// 4
forEach(x => console.log(x * 2))(new Set([1, 2]));
// 2
// 4
forEach(x => console.log(x * 2))(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// 2
// 4
forEach(x => console.log(x.repeat(2)))('ab');
// aa
// bb
function filter(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
// return new iterable of the input iterable type
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// return if you should keep this element of not
}
filter(x => x % 2)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// { a: 1 }
filter(x => x % 2)([1, 2]);
// [ 1 ]
filter(x => x % 2)(new Set([1, 2]));
// Set(1) {1}
filter(x => x % 2)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// Map(1) {"a" => 1}
filter(x => x % 2)('12');
// '1'
function reduce(callback, initialValue, thisArg) {
return function (iterable) {
// return reduced value
};
}
function callback(accumulator, currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// returns the value that results from the reduction
}
reduce((acc, x) => acc + x, 0)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// { a: 1 }
reduce((acc, x) => acc + x, 0)([1, 2]);
// [ 1 ]
reduce((acc, x) => acc + x, 0)(new Set([1, 2]));
// Set(1) {1}
reduce(
(acc, x) => acc + x,
0,
)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// Map(1) {"a" => 1}
reduce((acc, x) => acc + Number(x), 0)('12');
// '1'
function take(limit) {
return function (iterable) {
// return new iterable with only the <limit> first items
};
}
take(1)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// { a: 1 }
take(1)([1, 2]);
// [ 1 ]
take(1)(new Set([1, 2]));
// Set(1) {1}
take(1)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// Map(1) {"a" => 1}
take(1)('ab');
// 'a'
function drop(limit) {
return function (iterable) {
// return new iterable with <limit> first item trimmed
};
}
drop(1)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// { b: 2 }
drop(1)([1, 2]);
// [ 2 ]
drop(1)(new Set([1, 2]));
// Set(1) {2}
drop(1)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// Map(1) {"b" => 2}
drop(1)('ab');
// 'b'
function find(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
// return the element and its key or undefined
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// return if you it matches your element or not
}
find(x => x % 2)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// [ 1, 'a' ]
find(x => x % 2)([1, 2]);
// [ 1, 0 ]
find(x => x % 2)(new Set([1, 2]));
// [ 1, 0 ]
find(x => x % 2)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// [ 1, 'a' ]
find(x => x % 2)('12');
// [ '1', 0 ]
function every(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
// return true if all elements match the callback
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// return if you it matches your element or not
}
every(x => x <= 2)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// true
every(x => x <= 2)([1, 2]);
// true
every(x => x <= 2)(new Set([1, 2]));
// true
every(x => x <= 2)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// true
every(x => x === '1')('12');
// false
function some(callback[, thisArg]) {
return function (iterable) {
// return true if at least 1 element matches the callback
}
}
function callback(currentValue[, index[, iterable]]) {
// return if you it matches your element or not
}
some(x => x <= 2)({ a: 1, b: 2 });
// true
some(x => x <= 2)([1, 2]);
// true
some(x => x <= 2)(new Set([1, 2]));
// true
some(x => x <= 2)(
new Map([
['a', 1],
['b', 2],
]),
);
// true
some(x => x === '1')('12');
// true
Iterator allows you to chain operations more easily. It supports all these methods:
droptakemapfiltereverysomereducefindlenforEachYou can also use the method build() to reconstruct an iterable (either from the same type as the input, or you can transform it).
const iterable = Iterable.from([1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]);
iterable
.drop(1)
.filter(x => x % 2 === 0)
.map(x => x * 3)
.take(2)
.build();
// [6, 12]
build() accepts an optional parameter type:
const iterable = Iterable.from([1, 2, 3]);
iterable.build(type.Set);
// Set([1, 2, 3])
FAQs
Standard JS functions
We found that @ayc0/std demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.

Security News
CISA denies CVE funding issues amid backlash over a new CVE foundation formed by board members, raising concerns about transparency and program governance.
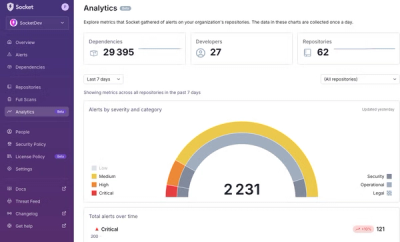
Product
We’re excited to announce a powerful new capability in Socket: historical data and enhanced analytics.