
Security News
Deno 2.6 + Socket: Supply Chain Defense In Your CLI
Deno 2.6 introduces deno audit with a new --socket flag that plugs directly into Socket to bring supply chain security checks into the Deno CLI.
@njmaeff/math-euclidean-algorithm
Advanced tools
In mathematics, the Euclidean algorithm, or Euclid's algorithm, is an efficient method for computing the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers, the largest number that divides both of them without leaving a remainder.
The Euclidean algorithm is based on the principle that the
greatest common divisor of two numbers does not change if
the larger number is replaced by its difference with the
smaller number. For example, 21 is the GCD of 252 and
105 (as 252 = 21 × 12 and 105 = 21 × 5), and the same
number 21 is also the GCD of 105 and 252 − 105 = 147.
Since this replacement reduces the larger of the two numbers,
repeating this process gives successively smaller pairs of
numbers until the two numbers become equal.
When that occurs, they are the GCD of the original two numbers.
By reversing the steps, the GCD can be expressed as a sum of
the two original numbers each multiplied by a positive or
negative integer, e.g., 21 = 5 × 105 + (−2) × 252.
The fact that the GCD can always be expressed in this way is
known as Bézout's identity.
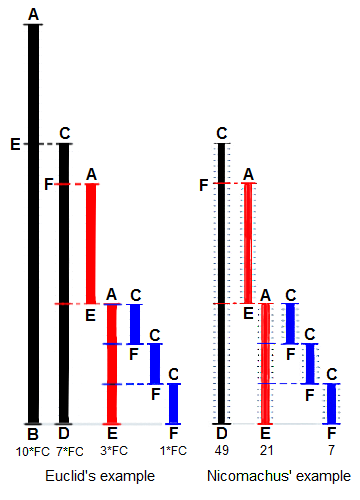
Euclid's method for finding the greatest common divisor (GCD)
of two starting lengths BA and DC, both defined to be
multiples of a common "unit" length. The length DC being
shorter, it is used to "measure" BA, but only once because
remainder EA is less than DC. EA now measures (twice)
the shorter length DC, with remainder FC shorter than EA.
Then FC measures (three times) length EA. Because there is
no remainder, the process ends with FC being the GCD.
On the right Nicomachus' example with numbers 49 and 21
resulting in their GCD of 7 (derived from Heath 1908:300).
A 24-by-60 rectangle is covered with ten 12-by-12 square
tiles, where 12 is the GCD of 24 and 60. More generally,
an a-by-b rectangle can be covered with square tiles of
side-length c only if c is a common divisor of a and b.

Subtraction-based animation of the Euclidean algorithm.
The initial rectangle has dimensions a = 1071 and b = 462.
Squares of size 462×462 are placed within it leaving a
462×147 rectangle. This rectangle is tiled with 147×147
squares until a 21×147 rectangle is left, which in turn is
tiled with 21×21 squares, leaving no uncovered area.
The smallest square size, 21, is the GCD of 1071 and 462.
FAQs
Unknown package
The npm package @njmaeff/math-euclidean-algorithm receives a total of 1 weekly downloads. As such, @njmaeff/math-euclidean-algorithm popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @njmaeff/math-euclidean-algorithm demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Deno 2.6 introduces deno audit with a new --socket flag that plugs directly into Socket to bring supply chain security checks into the Deno CLI.

Security News
New DoS and source code exposure bugs in React Server Components and Next.js: what’s affected and how to update safely.

Security News
Socket CEO Feross Aboukhadijeh joins Software Engineering Daily to discuss modern software supply chain attacks and rising AI-driven security risks.