
Security News
npm Adopts OIDC for Trusted Publishing in CI/CD Workflows
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.
@thi.ng/hiccup
Advanced tools
HTML/SVG/XML serialization of nested data structures, iterables & closures
[!NOTE] This is one of 210 standalone projects, maintained as part of the @thi.ng/umbrella monorepo and anti-framework.
🚀 Please help me to work full-time on these projects by sponsoring me on GitHub. Thank you! ❤️
HTML/SVG/XML serialization of nested data structures, iterables & closures.
Inspired by Hiccup and Reagent for Clojure/ClojureScript, this package provides key infrastructure for a number of other related libraries.
Forget all the custom toy DSLs for templating and instead use the full power of modern JavaScript to directly define fully data-driven, purely functional and easily composable components for static serialization to HTML & friends.
This library is suitable for any SGML-style (HTML/XML/SVG/RSS/Atom etc.) serialization, including static website/asset generation, server side rendering etc. For interactive use cases, please see companion packages @thi.ng/rdom (or the older, now unmaintained @thi.ng/hdom) and their various support packages.
style attribute objects(*) Lazy composition here means that functions are only executed at serialization time. Examples below...
.innerHTML body generationUsing only vanilla language features simplifies the development, removes need for extra tooling, improves composability, reusability, transformation and testing of components. No custom template parser (a la JSX or Handlebars etc.) is required and you're only restricted by the expressiveness of the language / environment, not by your template engine.
Components can be defined as simple arrays and/or functions returning arrays or can be dynamically generated or loaded via JSON...
For many years, Hiccup has been the de-facto standard to encode HTML/XML datastructures in Clojure (and many years before that, the overall idea was introduced in Scheme by Oleg Kiselyov and Kirill Lisovsky in 1999). This library brings & extends this convention into ES6. A valid Hiccup tree is any flat (though, usually nested) array of the following possible structures. Any functions embedded in the tree are expected to return values of the same structure. Please see examples & API further explanations...
["tag", ...]
["tag#id.class1.class2", ...]
["tag", {other: "attrib", ...}, ...]
["tag", {...}, "body", 23, function, [...]]
[function, arg1, arg2, ...]
[{render: (ctx, ...args) => [...]}, args...]
iterable
STABLE - used in production
Search or submit any issues for this package
yarn add @thi.ng/hiccup
ESM import:
import * as h from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
Browser ESM import:
<script type="module" src="https://esm.run/@thi.ng/hiccup"></script>
For Node.js REPL:
const h = await import("@thi.ng/hiccup");
Package sizes (brotli'd, pre-treeshake): ESM: 2.24 KB
Note: @thi.ng/api is in most cases a type-only import (not used at runtime)
11 projects in this repo's /examples directory are using this package:
| Screenshot | Description | Live demo | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
 | Heatmap visualization of this mono-repo's commits | Source | |
 | Filterable commit log UI w/ minimal server to provide commit history | Demo | Source |
 | Applying thi.ng/hdiff to generate static HTML diff output | Demo | Source |
 | Various hdom-canvas shape drawing examples & SVG conversion / export | Demo | Source |
 | Generating pure CSS image transitions | Demo | Source |
| Hiccup / hdom DOM hydration example | Demo | Source | |
 | Markdown to Hiccup to HTML parser / transformer | Demo | Source |
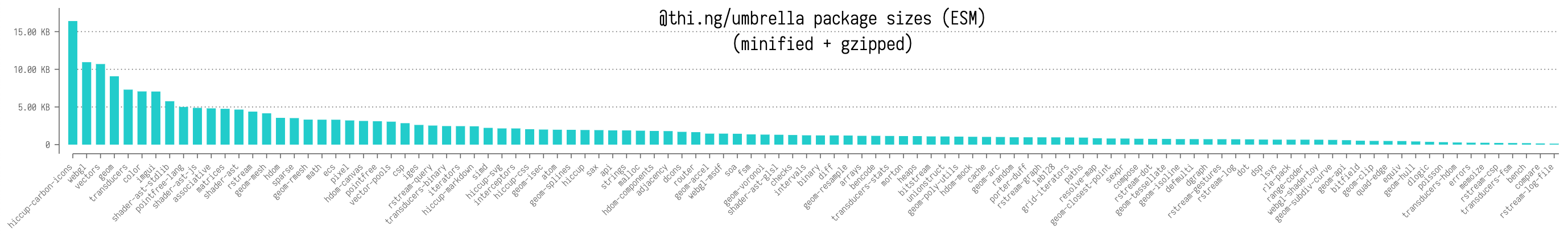 | CLI util to visualize umbrella pkg stats | Source | |
 | Generate SVG using pointfree DSL | Source | |
 | Basic usage of the declarative rdom-forms generator | Demo | Source |
 | Interactive grid generator, SVG generation & export, undo/redo support | Demo | Source |
Tag names support Emmet/Zencoding style ID & class attribute expansion:
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
serialize(
["div#yo.hello.world", "Look ma, ", ["strong", "no magic!"]]
);
<div id="yo" class="hello world">Look ma, <strong>no magic!</strong></div>
Arbitrary attributes can be supplied via an optional 2nd array element.
style attributes can be given as CSS string or as an object. Boolean
attributes are serialized in HTML5 syntax (i.e. present or not, but no
values).
If the 2nd array element is not a plain object, it's treated as normal child node (see previous example).
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
serialize(
["div.notice",
{
selected: true,
style: {
background: "#ff0",
border: "3px solid black"
}
},
"WARNING"]
);
<div class="notice" selected style="background:#ff0;border:3px solid black">WARNING</div>
If an attribute specifies a function as value, the function is called with the
entire attribute object as argument (incl. any id or class attribs derived
from an Emmet-style tag name). This allows for the dynamic generation of
attribute values, based on existing ones. The result MUST be a string.
["div#foo", { bar: (attribs) => attribs.id + "-bar" }]
<div id="foo" bar="foo-bar"></div>
Function values for event attributes (any attrib name starting with "on") WILL BE OMITTED from output:
["div#foo", { onclick: () => alert("foo") }, "click me!"]
<div id="foo">click me!</div>
["div#foo", { onclick: "alert('foo')" }, "click me!"]
<div id="foo" onclick="alert('foo')">click me!</div>
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
const thumb = (src) => ["img.thumb", { src, alt: "thumbnail" }];
serialize(
["div.gallery", ["foo.jpg", "bar.jpg", "baz.jpg"].map(thumb)]
);
<div class="gallery">
<img class="thumb" src="foo.jpg" alt="thumbnail"/>
<img class="thumb" src="bar.jpg" alt="thumbnail"/>
<img class="thumb" src="baz.jpg" alt="thumbnail"/>
</div>
Every component function will receive an arbitrary user defined context object
as first argument. This context object can be passed to
serialize()
via its options argument and is then passed as arg to every component function
call.
The context object should contain any global component configuration, e.g. for theming purposes.
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
const header = (ctx, body) =>
["h1", ctx.theme.title, body];
const section = (ctx, title, ...body) =>
["section", ctx.theme.section, [header, title], ...body];
// theme definition (here using Tachyons CSS classes,
// but could be any attributes)
const theme = {
section: { class: "bg-black moon-gray bt b--dark-gray mt3" },
title: { class: "white f3" }
};
serialize(
[section, "Hello world", "Easy theming"],
// pass context object via options
{ ctx: { theme } }
);
// <section class="bg-black moon-gray bt b--dark-gray mt3"><h1 class="white f3">Hello world</h1>Easy theming</section>
Note: Of course the context is ONLY auto-injected for lazily embedded
component functions (like the examples shown above), i.e. if the functions are
wrapped in arrays and only called during serialization. If you call such a
component function directly, you MUST pass the context (or null) as first arg
yourself. Likewise, if a component function doesn't make use of the context you
can use either:
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
// skip the context arg and require direct invocation
const div = (attribs, body) => ["div", attribs, body];
serialize(div({id: "foo"}, "bar"));
// <div id="foo">bar</div>
Or...
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
// ignore the first arg (context) and support both direct & indirect calls
const div = (_, attribs, body) => ["div", attribs, body];
// direct invocation of div (pass `null` as context)
serialize(div(null, {id: "foo"}, "bar"));
// <div id="foo">bar</div>
// lazy invocation of div
serialize([div, {id: "foo"}, "bar"]);
// <div id="foo">bar</div>
Also see @thi.ng/hiccup-svg and @thi.ng/geom for related (and more advanced) functionality.
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
import { repeatedly } from "@thi.ng/transducers";
import { writeFileSync } "node:fs";
// creates an unstyled SVG circle element
// we ignore the first arg (an auto-injected context arg)
// context handling is described further below
const circle = (_, x, y, r) => ["circle", { cx: ~~x, cy: ~~y, r: ~~r }];
// note how this next component lazily composes `circle`.
// This form delays evaluation of the `circle` component
// until serialization time.
// since `circle` is in the head position of the returned array
// all other elements are passed as args when `circle` is called
const randomCircle = () => [
circle,
Math.random() * 1000,
Math.random() * 1000,
Math.random() * 100
];
// generate 100 random circles and write serialized SVG to file
// `randomCircle` is wrapped
import { XML_SVG } from "@thi.ng/prefixes";
const doc = [
"svg", { xmlns: XML_SVG, width: 1000, height: 1000 },
["g", { fill: "none", stroke: "red" },
repeatedly(randomCircle, 100)]];
writeFileSync("export/circles.svg", serialize(doc));
Resulting example output:
<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="1000" height="1000">
<g fill="none" stroke="red">
<circle cx="182" cy="851" r="66"/>
<circle cx="909" cy="705" r="85"/>
<circle cx="542" cy="915" r="7"/>
<circle cx="306" cy="762" r="88"/>
...
</g>
</svg>
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
// data
const glossary = {
foo: "widely used placeholder name in computing",
bar: "usually appears in combination with 'foo'",
hiccup: "de-facto standard format to define HTML in Clojure",
toxi: "author of this fine library",
};
// mapping function to produce single definition list item (pair of <dt>/<dd> tags)
const dlItem = (index, key) => [["dt", key], ["dd", index[key]]];
// Helper function: takes a function `f` and object `items`,
// executes fn for each key (sorted) in object and returns array of results
const objectList = (f, items) => Object.keys(items).sort().map((k)=> f(items, k));
// full definition list component
const dlList = (_, attribs, items) => ["dl", attribs, objectList(dlItem, items)];
// finally the complete widget
const widget = [
"div.widget",
["h1", "Glossary"],
[dlList, { id: "glossary" }, glossary]];
// serialize with enforced HTML entity encoding (off by default)
console.log(serialize(widget, { escape: true }));
(Re)formatted output (generated HTML will always be dense, without intermittent white space):
<div class="widget">
<h1>Glossary</h1>
<dl id="glossary">
<dt>bar</dt>
<dd>usually appears in combination with 'foo'</dd>
<dt>foo</dt>
<dd>widely used placeholder name in computing</dd>
<dt>hiccup</dt>
<dd>de-facto standard format to define HTML in Clojure</dd>
<dt>toxi</dt>
<dd>author of this fine library</dd>
</dl>
</div>
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
// stateful component to create hierarchically
// indexed & referencable section headlines:
// e.g. "sec-1.1.2.3"
const indexer = (prefix = "sec") => {
let counts = new Array(6).fill(0);
return (_, level, title) => {
counts[level - 1]++;
counts.fill(0, level);
return [
["a", { name: "sec-" + counts.slice(0, level).join(".") }],
["h" + level, title]
];
};
};
const TOC = [
[1, "Document title"],
[2, "Preface"],
[3, "Thanks"],
[3, "No thanks"],
[2, "Chapter"],
[3, "Exercises"],
[4, "Solutions"],
[2, "The End"]
];
// create new indexer instance
const section = indexer();
console.log(
serialize([
"div.toc",
TOC.map(([level, title]) => [section, level, title])
])
);
Re-formatted HTML output:
<div class="toc">
<a name="sec-1"></a><h1>Document title</h1>
<a name="sec-1.1"></a><h2>Preface</h2>
<a name="sec-1.1.1"></a><h3>Thanks</h3>
<a name="sec-1.1.2"></a><h3>No thanks</h3>
<a name="sec-1.2"></a><h2>Chapter</h2>
<a name="sec-1.2.1"></a><h3>Exercises</h3>
<a name="sec-1.2.1.1"></a><h4>Solutions</h4>
<a name="sec-1.3"></a><h2>The End</h2>
</div>
The sibling library
@thi.ng/hdom
supports components with basic life cycle methods (init, render, release). To
support serialization of hdom component trees, hiccup too supports such
components since version 2.0.0. For static serialization only the render
method is of interest and others are ignored.
const component = {
render: (ctx, title, ...body) => ["section", ["h1", title], ...body]
};
serialize([component, "Hello world", "Body"]);
The following attributes can be used to control the serialization behavior of individual elements / tree branches:
__escape - boolean flag to enable/disable entity escaping__skip - if true, skips serialization (also used by
@thi.ng/hdom)__serialize - if false, skips serialization (hiccup only)serialize(["div.container", ["div", { __skip: true }, "ignore me"]]);
// <div class="container"></div>
Single or multiline comments can be included using the special COMMENT
tag (or __COMMENT__, always WITHOUT attributes!).
import { COMMENT } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
[COMMENT, "Hello world"]
// serializes to:
// <!-- Hello world -->
[COMMENT, "Hello", "world"]
// <!--
// Hello
// world
// -->
Pre-serialized markup can be inlined without any further processing using the
special INLINE tag (or __INLINE__, always WITHOUT attributes!):
import { INLINE, serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
serialize(
["div", {}
[INLINE, "<h3>Inlined & Embedded</h3><p>Lorem ipsum...</p>"]
]
);
// <div><h3>Inlined & Embedded</h3><p>Lorem ipsum...</p></div>
Currently, the only processing / DTD instructions supported are:
?xml!DOCTYTPE!ELEMENT!ENTITY!ATTLISTThese are used as follows (attribs are only allowed for ?xml, all
others only accept a body string which is taken as is):
["?xml", { version: "1.0", standalone: "yes" }]
// <?xml version="1.0" standalone="yes"?>
["!DOCTYPE", "html"]
// <!DOCTYPE html>
Emitted processing instructions are always succeeded by a newline character.
The library exposes these two functions:
Signature: serialize(tree: any, ctx?: any, escape = false): string
Recursively normalizes and serializes given tree as HTML/SVG/XML string. Expands any embedded component functions with their results. Each node of the input tree can have one of the following input forms:
["tag", ...]
["tag#id.class1.class2", ...]
["tag", {other: "attrib"}, ...]
["tag", {...}, "body", function, ...]
[function, arg1, arg2, ...]
[{render: (ctx,...) => [...]}, args...]
iterable
Tags can be defined in "Zencoding" convention, e.g.
["div#foo.bar.baz", "hi"]
// <div id="foo" class="bar baz">hi</div>
The presence of the attributes object (2nd array index) is optional. Any attribute values, incl. functions are allowed. If the latter, the function is called with the full attribs object as argument and the return value is used for the attribute. This allows for the dynamic creation of attrib values based on other attribs. The only exception to this are event attributes, i.e. attribute names starting with "on".
["div#foo", { bar: (attribs) => attribs.id + "-bar" }]
// <div id="foo" bar="foo-bar"></div>
The style attribute can ONLY be defined as string or object.
["div", { style: { color: "red", background: "#000" } }]
// <div style="color:red;background:#000;"></div>
Boolean attribs are serialized in HTML5 syntax (present or not). null or empty string attrib values are ignored.
Any null or undefined array values (other than in head position) will be
removed, unless a function is in head position.
A function in head position of a node acts as a mechanism for component composition & delayed execution. The function will only be executed at serialization time. In this case the optional global context object and all other elements of that node / array are passed as arguments when that function is called. The return value the function MUST be a valid new tree (or undefined).
import { serialize } from "@thi.ng/hiccup";
const foo = (ctx, a, b) => ["div#" + a, ctx.foo, b];
serialize([foo, "id", "body"], { foo: { class: "black" } })
// <div id="id" class="black">body</div>
Functions located in other positions are called ONLY with the global context arg and can return any (serializable) value (i.e. new trees, strings, numbers, iterables or any type with a suitable .toString() implementation).
Please also see list of supported behavior control attributes.
If this project contributes to an academic publication, please cite it as:
@misc{thing-hiccup,
title = "@thi.ng/hiccup",
author = "Karsten Schmidt",
note = "https://thi.ng/hiccup",
year = 2016
}
© 2016 - 2025 Karsten Schmidt // Apache License 2.0
FAQs
HTML/SVG/XML serialization of nested data structures, iterables & closures
We found that @thi.ng/hiccup demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.

Research
/Security News
A RubyGems malware campaign used 60 malicious packages posing as automation tools to steal credentials from social media and marketing tool users.

Security News
The CNA Scorecard ranks CVE issuers by data completeness, revealing major gaps in patch info and software identifiers across thousands of vulnerabilities.