
Security News
npm Adopts OIDC for Trusted Publishing in CI/CD Workflows
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.
@tsmx/express-jwt-validator
Advanced tools
Simple express middleware for validating JWT bearer tokens.
Simple express middleware for validating JWT bearer tokens.
Stop writing boilerplate code to protect express routes with JWT bearer tokens in your projects.
Supports optional log output using winston, log4js or any other compatible logger. For details refer to the log configuration section
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'YOUR_JWT_SECRET'
});
app.get('/secret', verifyToken, (req, res) => {
// token payload available in req.authData
res.send('Only accessible with a valid JWT bearer token.');
});
For further customizing please refer to the configuration options.
This module exports a middleware function for express to check a request for a valid JSON Web token authorization. The token must be provided as a bearer token in the HTTP request header according to the RFC standard.
Requests with a failed JWT validation will be rejected with HTTP status 401 by default. If the validations succeeds, the verified JWT payload will be added to the request and it will be passed to the next element of the middleware chain.
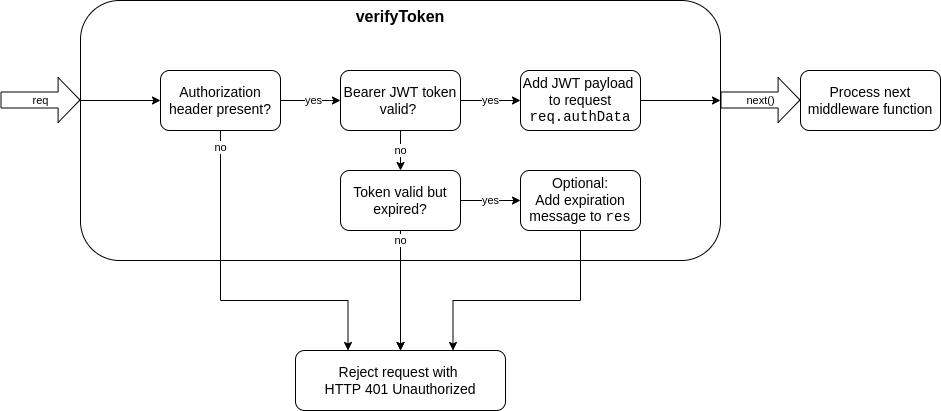
When requiring in the middleware with...
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
/* configuration object */
});
...the passed configuration object supports the following properties.
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| secret | The JWT validation secret |
| header | Custom header HTTP name |
| strictBearerValidation | Enable/disable strict validation |
| rejectHttpStatus | Custom HTTP response status for failed validations |
| sendExpiredMessage | Enable/disable error message for expired tokens |
| requestAuthProp | Custom property name to store token data in req |
| logger | An optional logger to receive log output |
Type: String
Default: undefined
Mandatory: yes
The sceret used to verify the JWT bearer token. Must be present, otherwise an exception will be thrown.
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456'
});
Type: String
Default: authorization
Mandatory: no
Can be used if the bearer token will be supplied in another header field than authorization (Note: HTTP header field names are case-insensitive).
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
header: 'auth'
});
Type: Boolean
Default: false
Mandatory: no
If set to true, the authorization header is strictly validated against the schema Bearer <JWT> (including the whitespace), like Bearer eyJhb.... If set to false (default), it is sufficient if the header consists of two strings separated by a whitespace whereas the second entry is considered to be the JWT.
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
strictBearerValidation: true
});
Type: Number
Default: 401
Mandatory: no
The HTTP status to be sent back to the client if the bearer token validation fails. Defaults to 401 for Unauthorized, could also be set to 403 Forbidden for example. Please note that although any status is possible here you should use an appropriate HTTP client error code.
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
rejectHttpStatus: 403
});
Type: Boolean
Default: true
Mandatory: no
If set to true, the rejection response will contain a JSON body with one property error and value TokenExpiredError indicating the client that the token has expired. This can be useful to allow the client to check that the token must be refreshed.
If set to false, an expired token will be rejected without any response body.
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
sendExpiredMessage: false
});
Type: String
Default: authData
Mandatory: no
The name of the property in req where the JWT bearer token payload should be stored for further processing. Can be changed to any property name, please make sure it is unique and no other properties are overwritten.
Example:
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
requestAuthProp: 'tokenPayload'
});
Token data would now be accessible with req.tokenPayload instead of req.authData in following middleware functions.
Type: Object
Default: undefined
Mandatory: no
You can pass a winston or log4js logger instance (or any compatible) to get log output from the middleware. Compatible means that the logger must provide info, warn and error functions receiving a string to be logged.
Note: the package contains tests for winston and log4js.
The following events will be logged:
| Event | Log level |
|---|---|
| Rejected - No auth header present | WARN |
| Rejected - No valid 'Bearer TOKEN' entry in auth header | WARN |
| Rejected - Strict Bearer validation failed | WARN |
| Rejected - Expired token was sent | WARN |
| Rejected - Invalid token was sent (potential attack) | ERROR |
| Passed - Valid Bearer token was sent | INFO |
Example for winston:
const winston = require('winston');
winstonLogger = winston.createLogger({ /*... winston options ...*/ });
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
logger: winstonLogger
});
Example for log4js:
const log4js = require('log4js');
log4js.configure({ /*... log4js options ...*/ });
log4jsLogger = log4js.getLogger();
const verifyToken = require('@tsmx/express-jwt-validator')({
secret: 'MySecretKey-123456',
logger: log4jsLogger
});
FAQs
Simple express middleware for validating JWT bearer tokens.
We found that @tsmx/express-jwt-validator demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
npm now supports Trusted Publishing with OIDC, enabling secure package publishing directly from CI/CD workflows without relying on long-lived tokens.

Research
/Security News
A RubyGems malware campaign used 60 malicious packages posing as automation tools to steal credentials from social media and marketing tool users.

Security News
The CNA Scorecard ranks CVE issuers by data completeness, revealing major gaps in patch info and software identifiers across thousands of vulnerabilities.