compromise

modest natural language processing
npm install compromise


don't you find it strange,


compromise
tries its best to turn text into data.

it makes limited and sensible decisions.
 it's not as smart as you'd think.
it's not as smart as you'd think.


import nlp from 'compromise'
let doc = nlp('she sells seashells by the seashore.')
doc.verbs().toPastTense()
doc.text()

don't be fancy, at all:
if (doc.has('simon says #Verb')) {
return true
}

grab parts of the text:
let doc = nlp(entireNovel)
doc.match('the #Adjective of times').text()

and get data:
import plg from 'compromise-speech'
nlp.extend(plg)
let doc = nlp('Milwaukee has certainly had its share of visitors..')
doc.compute('syllables')
doc.places().json()

avoid the problems of brittle parsers:
let doc = nlp("we're not gonna take it..")
doc.has('gonna')
doc.has('going to')
doc.contractions().expand()
doc.text()

and whip stuff around like it's data:
let doc = nlp('ninety five thousand and fifty two')
doc.numbers().add(20)
doc.text()

-because it actually is-
let doc = nlp('the purple dinosaur')
doc.nouns().toPlural()
doc.text()

Use it on the client-side:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/compromise"></script>
<script>
var doc = nlp('two bottles of beer')
doc.numbers().minus(1)
document.body.innerHTML = doc.text()
</script>
or likewise:
import nlp from 'compromise'
var doc = nlp('London is calling')
doc.verbs().toNegative()


compromise is ~250kb (minified):
it's pretty fast. It can run on keypress:
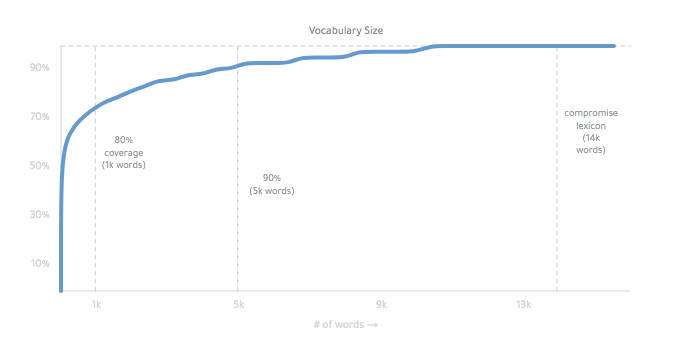
it works mainly by conjugating all forms of a basic word list.
The final lexicon is ~14,000 words:
you can read more about how it works, here. it's weird.

okay -
compromise/one
A tokenizer of words, sentences, and punctuation.

import nlp from 'compromise/one'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let data = doc.json()
compromise/one splits your text up, wraps it in a handy API,

/one is quick - most sentences take a 10th of a millisecond.
It can do ~1mb of text a second - or 10 wikipedia pages.
Infinite jest takes 3s.

compromise/two
A part-of-speech tagger, and grammar-interpreter.

import nlp from 'compromise/two'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let str = doc.match('#Possessive #Noun').text()

compromise/two automatically calculates the very basic grammar of each word.
this is more useful than people sometimes realize.
Light grammar helps you write cleaner templates, and get closer to the information.

compromise has 83 tags, arranged in a handsome graph.
#FirstName → #Person → #ProperNoun → #Noun
you can see the grammar of each word by running doc.debug()
you can see the reasoning for each tag with nlp.verbose('tagger').
if you prefer Penn tags, you can derive them with:
let doc = nlp('welcome thrillho')
doc.compute('penn')
doc.json()

compromise/three
Phrase and sentence tooling.

import nlp from 'compromise/three'
let doc = nlp("Wayne's World, party time")
let str = doc.people().normalize().text()
compromise/three is a set of tooling to zoom into and operate on parts of a text.
.numbers() grabs all the numbers in a document, for example - and extends it with new methods, like .subtract().
When you have a phrase, or group of words, you can see additional metadata about it with .json()
let doc = nlp('four out of five dentists')
console.log(doc.fractions().json())
let doc = nlp('$4.09CAD')
doc.money().json()

API
Compromise/one
Output
- .text() - return the document as text
- .json() - return the document as data
- .debug() - pretty-print the interpreted document
- .out() - a named or custom output
- .html({}) - output custom html tags for matches
- .wrap({}) - produce custom output for document matches
Utils
- .found [getter] - is this document empty?
- .docs [getter] get term objects as json
- .length [getter] - count the # of characters in the document (string length)
- .isView [getter] - identify a compromise object
- .compute() - run a named analysis on the document
- .clone() - deep-copy the document, so that no references remain
- .termList() - return a flat list of all Term objects in match
- .cache({}) - freeze the current state of the document, for speed-purposes
- .uncache() - un-freezes the current state of the document, so it may be transformed
- .freeze({}) - prevent any tags from being removed, in these terms
- .unfreeze({}) - allow tags to change again, as default
Accessors
Match
(match methods use the match-syntax.)
- .match('') - return a new Doc, with this one as a parent
- .not('') - return all results except for this
- .matchOne('') - return only the first match
- .if('') - return each current phrase, only if it contains this match ('only')
- .ifNo('') - Filter-out any current phrases that have this match ('notIf')
- .has('') - Return a boolean if this match exists
- .before('') - return all terms before a match, in each phrase
- .after('') - return all terms after a match, in each phrase
- .union() - return combined matches without duplicates
- .intersection() - return only duplicate matches
- .complement() - get everything not in another match
- .settle() - remove overlaps from matches
- .growRight('') - add any matching terms immediately after each match
- .growLeft('') - add any matching terms immediately before each match
- .grow('') - add any matching terms before or after each match
- .sweep(net) - apply a series of match objects to the document
- .splitOn('') - return a Document with three parts for every match ('splitOn')
- .splitBefore('') - partition a phrase before each matching segment
- .splitAfter('') - partition a phrase after each matching segment
- .join() - merge any neighbouring terms in each match
- .joinIf(leftMatch, rightMatch) - merge any neighbouring terms under given conditions
- .lookup([]) - quick find for an array of string matches
- .autoFill() - create type-ahead assumptions on the document
Tag
- .tag('') - Give all terms the given tag
- .tagSafe('') - Only apply tag to terms if it is consistent with current tags
- .unTag('') - Remove this term from the given terms
- .canBe('') - return only the terms that can be this tag
Case
Whitespace
- .pre('') - add this punctuation or whitespace before each match
- .post('') - add this punctuation or whitespace after each match
- .trim() - remove start and end whitespace
- .hyphenate() - connect words with hyphen, and remove whitespace
- .dehyphenate() - remove hyphens between words, and set whitespace
- .toQuotations() - add quotation marks around these matches
- .toParentheses() - add brackets around these matches
Loops
- .map(fn) - run each phrase through a function, and create a new document
- .forEach(fn) - run a function on each phrase, as an individual document
- .filter(fn) - return only the phrases that return true
- .find(fn) - return a document with only the first phrase that matches
- .some(fn) - return true or false if there is one matching phrase
- .random(fn) - sample a subset of the results
Insert
Transform
Lib
(these methods are on the main nlp object)

compromise/two:
Contractions

compromise/three:
Nouns
- .nouns() - return any subsequent terms tagged as a Noun
Verbs
- .verbs() - return any subsequent terms tagged as a Verb
Numbers
Sentences
- .sentences() - return a sentence class with additional methods
Adjectives
Misc selections

.extend():
This library comes with a considerate, common-sense baseline for english grammar.
You're free to change, or lay-waste to any settings - which is the fun part actually.
the easiest part is just to suggest tags for any given words:
let myWords = {
kermit: 'FirstName',
fozzie: 'FirstName',
}
let doc = nlp(muppetText, myWords)
or make heavier changes with a compromise-plugin.
import nlp from 'compromise'
nlp.extend({
tags: {
Character: {
isA: 'Person',
notA: 'Adjective',
},
},
words: {
kermit: 'Character',
gonzo: 'Character',
},
irregulars: {
get: {
pastTense: 'gotten',
gerund: 'gettin',
},
},
api: View => {
View.prototype.kermitVoice = function () {
this.sentences().prepend('well,')
this.match('i [(am|was)]').prepend('um,')
return this
}
},
})
Docs:
gentle introduction:
Documentation:
Talks:
Articles:
Some fun Applications:
Comparisons
Plugins:
These are some helpful extensions:
Dates
npm install compromise-dates
Stats
npm install compromise-stats
Speech
npm install compromise-syllables
Wikipedia
npm install compromise-wikipedia
Typescript
we're committed to typescript/deno support, both in main and in the official-plugins:
import nlp from 'compromise'
import stats from 'compromise-stats'
const nlpEx = nlp.extend(stats)
nlpEx('This is type safe!').ngrams({ min: 1 })
Limitations:
-
slash-support:
We currently split slashes up as different words, like we do for hyphens. so things like this don't work:
nlp('the koala eats/shoots/leaves').has('koala leaves') //false
-
inter-sentence match:
By default, sentences are the top-level abstraction.
Inter-sentence, or multi-sentence matches aren't supported without a plugin:
nlp("that's it. Back to Winnipeg!").has('it back')//false
-
nested match syntax:
the danger beauty of regex is that you can recurse indefinitely.
Our match syntax is much weaker. Things like this are not (yet) possible:
doc.match('(modern (major|minor))? general')
complex matches must be achieved with successive .match() statements.
-
dependency parsing:
Proper sentence transformation requires understanding the syntax tree of a sentence, which we don't currently do.
We should! Help wanted with this.
FAQ
☂️ Isn't javascript too...
yeah it is!
it wasn't built to compete with NLTK, and may not fit every project.
string processing is synchronous too, and parallelizing node processes is weird.
See here for information about speed & performance, and
here for project motivations
💃 Can it run on my arduino-watch?
Only if it's water-proof!
Read quick start for running compromise in workers, mobile apps, and all sorts of funny environments.
🌎 Compromise in other Languages?
✨ Partial builds?
we do offer a tokenize-only build, which has the POS-tagger pulled-out.
but otherwise, compromise isn't easily tree-shaken.
the tagging methods are competitive, and greedy, so it's not recommended to pull things out.
Note that without a full POS-tagging, the contraction-parser won't work perfectly. ((spencer's cool) vs. (spencer's house))
It's recommended to run the library fully.
See Also:

MIT