Product
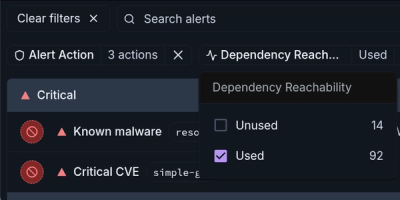
Introducing Module Reachability: Focus on the Vulnerabilities That Matter
Module Reachability filters out unreachable CVEs so you can focus on vulnerabilities that actually matter to your application.
context-state
Advanced tools
React state management solution with Context Like unstated-next, but Pro
npm i context-state
If you are using v3, please refer to here to upgrade to v4
React Context and useContext have some performance issues. When the context changes, all components that use the context will re-render. With context-state, developers don't need to worry about context penetration issues.
import React from 'react';
import { createStore } from 'context-state';
function useCounter() {
const [count, setCount] = React.useState(0);
const increment = () => setCount((c) => c + 1);
return {
count,
increment,
};
}
const CounterStore = createStore(useCounter);
function CounterDisplay() {
const { count, increment } = CounterStore.usePicker(['count', 'increment']);
return (
<div>
{count}
<button
type='button'
onClick={increment}
>
ADD
</button>
</div>
);
}
function App() {
return (
<CounterStore.Provider>
<CounterDisplay />
</CounterStore.Provider>
);
}
render(<App />, document.getElementById('root'));
createContainer(useHook, options)import { createStore, useMemoizedFn } from 'context-state';
function useCustomHook(props: {
initialValue: string;
}) {
const [value, setInput] = useState(props.initialValue);
const onChange = useMemoizedFn((e) => setValue(e.currentTarget.value));
return {
value,
onChange,
};
}
const Store = createStore(useCustomHook, {
// middlewares, used to listen to store changes
middlewares: [{
onInit: () => {},
onChange: () => {}
}]
});
// Store === { Provider, useStore }
If useCustomHook has parameters, they can be passed through Store.Provider.
<Container.Provider>const Container = createContainer(useCustomHook);
function ParentComponent({ children }) {
return <Container.Provider>{children}</Container.Provider>;
}
<Store.Provider>const Store = createStore(useCustomHook);
function ParentComponent({ children }) {
return <Store.Provider initialValue={'value'}>{children}</Store.Provider>;
}
Store.useStore()useStore is used to get the return value from the Provider.
useStore accepts 3 types of parameters:
function App() {
const { count } = Store.useStore(['count']);
}
function App() {
const count = Store.useStore((store) => store.count);
}
function App() {
const store = Store.useStore();
}
For best performance, it is recommended to use 1 and 2, which can avoid unnecessary rendering.
FAQs
Like unstated-next, but Pro
The npm package context-state receives a total of 63 weekly downloads. As such, context-state popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that context-state demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Module Reachability filters out unreachable CVEs so you can focus on vulnerabilities that actually matter to your application.

Company News
Socket is bringing best-in-class reachability analysis into the platform — cutting false positives, accelerating triage, and cementing our place as the leader in software supply chain security.
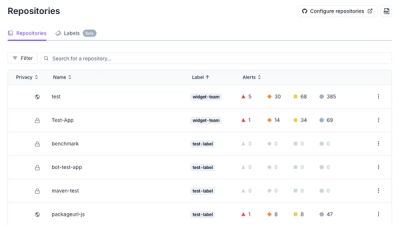
Product
Socket is introducing a new way to organize repositories and apply repository-specific security policies.