
What is FastText and FastText.js
FastText is a library for efficient learning of word representations and sentence classification. FastText is provided by Facebook Inc.
FastText.js is a JavaScript library that wraps FastText to run smoothly within node.
What's New
Added support for M1 Apple processor.
Table of Contents
FastText.js APIs
This version of FastText.js comes with the following JavaScript APIs
FastText.new(options)
FastText.load()
FastText.loadnn() [NEW API]
FastText.word2vec() [NEW API]
FastText.train()
FastText.test()
FastText.predict(string)
FastText.nn() [NEW API]
How to Install
git clone https://github.com/loretoparisi/fasttext.js.git
cd fasttext.js
npm install
Install via NPM
FastText.js is available as a npm module here. To add the package to your project
npm install --save fasttext.js
Install via Docker
Build the docker image
docker build -t fasttext.js .
This will update the latest FastText linux binaries from source to lib/bin/linux.
Now running the image on the docker host binding the port 3000 it is possibile to run the server example:
docker build -t fasttext.js .
docker run --rm -it -p 3000:3000 fasttext.js node fasttext.js/examples/server.js
To serve a different custom model a volume can be used and passing the MODEL environment variable
docker run -v /models/:/models --rm -it -p 3000:3000 -e MODEL=/models/my_model.bin fasttext.js node fasttext.js/examples/server.js
WASM
We provide a WASM compiled binary of FastText to be used natively NodeJS. Please check /wasm folder for library and examples. :new:
How to Use
Train
You can specify all the train parameters supported by fastText as a json object
train: {
thread: 8,
verbose: 4,
neg: 5,
loss: process.env.TRAIN_LOSS || 'ns',
lr: process.env.TRAIN_LR || 0.05,
lrUpdateRate: 100,
wordNgrams: process.env.TRAIN_NGRAM || 1,
minCount: 1,
minCountLabel: 1,
dim: process.env.TRAIN_DIM || 100,
ws: process.env.TRAIN_WS || 5,
epoch: process.env.TRAIN_EPOCH || 5,
bucket: 2000000,
minn: process.env.TRAIN_MINN || 3,
maxn: process.env.TRAIN_MAXN || 6,
t: 0.0001,
pretrainedVectors: process.env.WORD2VEC || ''
}
Train Supervised
To train the model you must specificy the training set as trainFile and the file where the model must be serialized as serializeTo. All the FastText supervised options are supported. See here for more details about training options. Note that serializeTo does not need to have the file extension in. A bin extension for the quantized model will be automatically added. You can use the pretrainedVectors option to load an unsupervised pre-trained model. Please use the word2vec api to train this model.
var fastText = new FastText({
serializeTo: './band_model',
trainFile: './band_train.txt'
});
fastText.train()
.then(done=> {
console.log("train done.");
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
})
Train Unsupervised
To train an unsupervised model use the word2vec api. You can specify the words representation to train using word2vec.model parameter set to skipgram or cbow and use the train parameters as usual:
fastText.word2vec()
.then(done => {
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("Train error", error);
})
Track Progress
It is possible to track the training progress using the callback parameters trainProgress in the options:
{
trainCallback: function(res) {
console.log( "\t"+JSON.stringify(res) );
}
}
This will print out the training progress in the following format:
{
"progress":17.2,
"words":174796,
"lr":0.041382,
"loss":1.232538,
"eta":"0h0m",
"eta_msec":0
}
that is the parsed JSON representation of fasttext output
Progress: 17.2% words/sec/thread: 174796 lr: 0.041382 loss: 1.232538 ETA: 0h 0m
where eta_msec represents the ETA (estimated time of arrival) in milliseconds.
So a typical progress will fire the trainCallback several times like
{"progress":0.6,"loss":4.103271,"lr":0.0498,"words":21895,"eta":"0h9m","eta_msec":540000}
{"progress":0.6,"loss":3.927083,"lr":0.049695,"words":21895,"eta":"0h6m","eta_msec":360000}
{"progress":0.6,"loss":3.927083,"lr":0.049695,"words":21895,"eta":"0h6m","eta_msec":360000}
{"progress":0.6,"loss":3.676603,"lr":0.049611,"words":26813,"eta":"0h5m","eta_msec":300000}
{"progress":0.6,"loss":3.676603,"lr":0.049611,"words":26813,"eta":"0h5m","eta_msec":300000}
{"progress":0.6,"loss":3.345654,"lr":0.04949,"words":33691,"eta":"0h4m","eta_msec":240000}
{"progress":1.2,"loss":3.345654,"lr":0.04949,"words":39604,"eta":"0h4m","eta_msec":240000}
Until the progress will reach 100%:
{"progress":99,"loss":0.532964,"lr":0.000072,"words":159556,"eta":"0h0m","eta_msec":0}
{"progress":99,"loss":0.532964,"lr":0.000072,"words":159556,"eta":"0h0m","eta_msec":0}
{"progress":99,"loss":0.532392,"lr":-0.000002,"words":159482,"eta":"0h0m","eta_msec":0}
{"progress":100,"loss":0.532392,"lr":0,"words":159406,"eta":"0h0m","eta_msec":0}
{"progress":100,"loss":0.532392,"lr":0,"words":159406,"eta":"0h0m","eta_msec":0}
NOTE. Please note that some approximation errors may occur in the output values.
Test
To test your model you must specificy the test set file as testFile and the model file to be loaded as loadModel. Optionally you can specificy the precision and recall at k (P@k and R@k) passing the object test: { precisionRecall: k }.
var fastText = new FastText({
loadModel: './band_model.bin',
testFile: './band_test.txt'
});
fastText.test()
.then(evaluation=> {
console.log("test done.",evaluation);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
})
The evaluation will contain the precision P, recall R and number of samples N as a json object { P: '0.278', R: '0.278' }.
If a train is called just before test the evaluation will contain the number of words W and the number of labels L as well as a json object: { W: 524, L: 2, N: '18', P: '0.278', R: '0.278' }:
fastText.train()
.then(done=> {
return fastText.test();
})
.then(evaluation=> {
console.log("train & test done.",evaluation);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("train error",error);
})
Test-Labels
:new: The api testLabels evaluate labels F1-Score, Recall and Precision for each label in the model.
var fastText = new FastText({
loadModel: './band_model.bin',
testFile: './band_test.txt'
});
fastText.testLabels()
.then(evaluation=> {
console.log("test-labels:",evaluation);
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
})
This will print out the values F1, P and R for each label.
[
{
"ham": {
"F1": "0.172414",
"P": "0.094340",
"R": "1.000000"
}
},
{
"spam": {
"F1": "0.950495",
"P": "0.905660",
"R": "1.000000"
}
}
]
Predict
To inference your model with new data and predict the label you must specify the model file to be loaded as loadModel. You can then call the load method once, and predict(string) to classify a string. Optionally you can specify the k most likely labels to print for each line as predict: { precisionRecall: k }
var sample="Our Twitter run by the band and crew to give you an inside look into our lives on the road. Get #FutureHearts now: http://smarturl.it/futurehearts";
fastText.load()
.then(done => {
return fastText.predict(sample);
})
.then(labels=> {
console.log("TEXT:", sample, "\nPREDICT:",labels );
sample="LBi Software provides precisely engineered, customer-focused #HRTECH solutions. Our flagship solution, LBi HR HelpDesk, is a SaaS #HR Case Management product.";
return fastText.predict(sample);
})
.then(labels=> {
console.log("TEXT:", sample, "\nPREDICT:",labels );
fastText.unload();
})
.catch(error => {
console.error(error);
});
Multi-Label
A multi-label example will have a list of columns of labels marked by __label__ prefix
__label__sauce __label__cheese How much does potato starch affect a cheese sauce recipe?
FastText.js will automatically handle multiple labels in the dataset for training and testing, please run the multilabel.js example to test it out:
cd examples/
node multilabel.js
The train() and test() will print out:
N 3000
P@1 0.000333
R@1 0.000144
Number of examples: 3000
exec:fasttext end.
exec:fasttext exit.
{ N: '3000', P: '0.000333', R: '0.000144' }
while the testLabels api will print out the labels array:
[ '__label__equipment',
'__label__cast',
'__label__oven',
'__label__sauce',
'__label__indian',
'__label__breakfast',
'__label__chili',
'__label__spicy',
'__label__bread',
'__label__eggs',
'__label__baking',
...
and by labels scores:
F1-Score : 0.175182 Precision : 0.096000 Recall : 1.000000 __label__baking
F1-Score : 0.150432 Precision : 0.081333 Recall : 1.000000 __label__food-safety
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__substitutions
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__equipment
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__bread
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__chicken
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__storage-method
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__eggs
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__meat
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__sauce
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__cake
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__flavor
F1-Score : -------- Precision : -------- Recall : 0.000000 __label__freezing
...
Nearest Neighbor
To get the nearest neighbor words for a given term use the nn api:
fastText.loadnn()
.then(labels=> {
return fastText.nn(text)
})
.then(labels=> {
console.log("Nearest Neighbor\n", JSON.stringify(labels, null, 2));
})
.catch(error => {
console.error("predict error",error);
});
Tools
We provide some support tools and script.
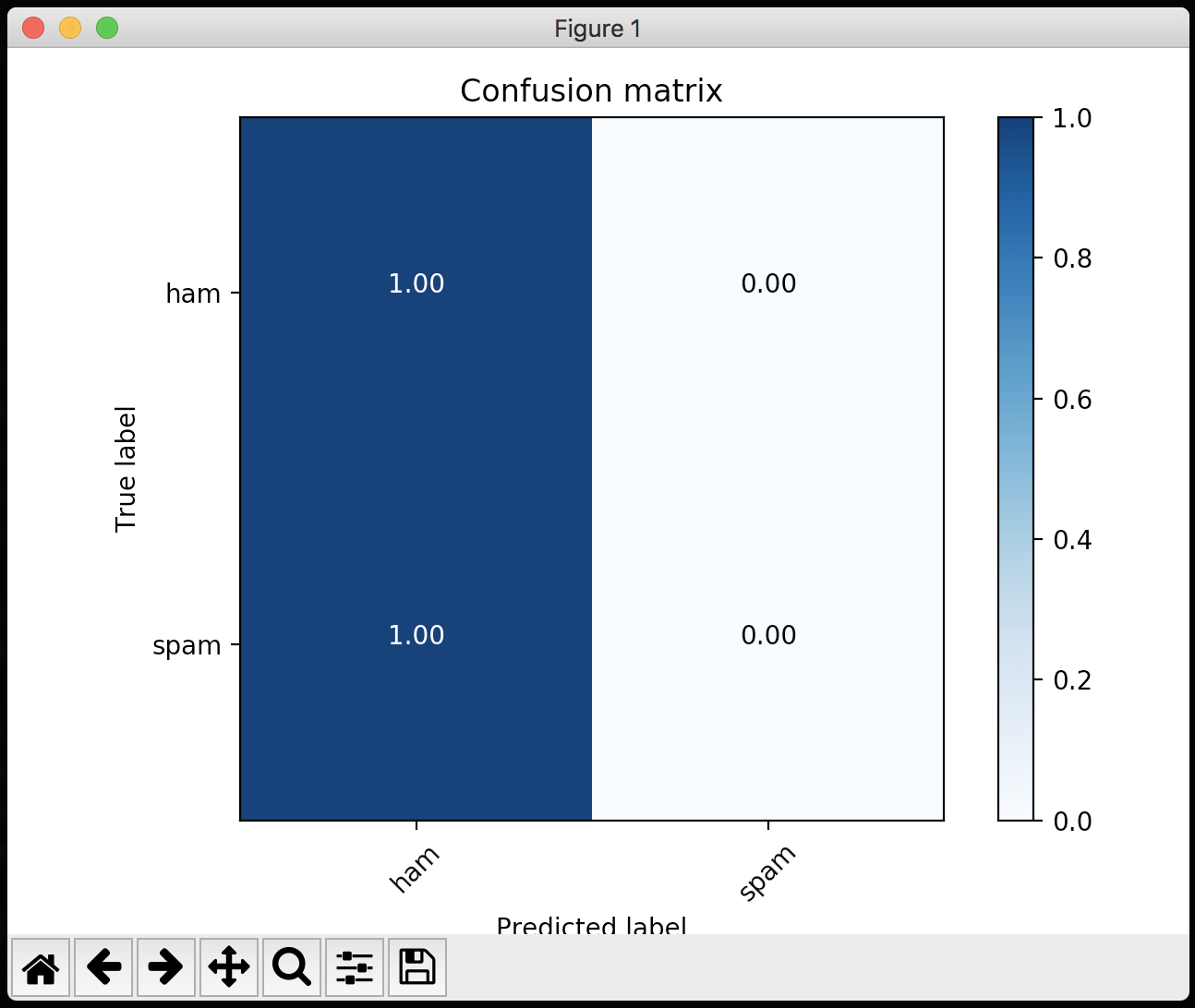
Confusion Matrix
To evaluate the Confusion Matrix of a model, please use the confusion.sh script provided in the tools/ folder. The script requires sklearn and matplotlib installed on the system:
$ cd tools/
$ ./confusion.sh
Usage: ./confusion.sh DATASET_FILE MODEL_FILE [LABEL_COLUMS, def:1] [LABEL_NORMALIZED, default|normalize, def:default] [PLOT, 0|1, def:0]
You must specify the dataset file path that has been used to train the model and the model file path. If the label golumn is different than the first column, plese specify the LABEL_COLUMN column index. If the dataset must be normalized, having a different label prefix or no one, please use the value normalize:
cd examples/
node train
cd ..
cd tools/
./confusion.sh ../examples/dataset/sms.tsv ../examples/models/sms_model.bin 1 normalize 1
If the dataset has the fasttext label prefix i.e. __label__, please set the parameter NORMALIZE_LABEL to default:
./confusion.sh ../examples/dataset/sms.tsv ../examples/models/sms_model.bin 1 default
The script will calculate the predictions against the dataset and build confusion matrix using sklearn
./confusion.sh ../examples/dataset/sms.tsv ../examples/models/sms_model.bin 1
Platform is Darwin
Normalizing dataset ../examples/dataset/sms.tsv...
Splitting 1 label colums...
Calculating predictions...
Calculating confusion matrix...
Test labels:1324 (sample)
['spam']
labels:{'ham', 'spam'}
Predicted labels:1324 (sample)
['ham']
Accuracy: 0.756797583082
[[1002 0]
[ 322 0]]
Confusion matrix
[[ 1. 0.]
[ 1. 0.]]
and and visualize it using matplotlib:
Examples
A folder examples contains several usage examples of FastText.js.
Train
$ cd examples/
$ node train.js
train [ 'supervised',
'-input',
'/var/folders/_b/szqwdfn979n4fdg7f2j875_r0000gn/T/trainfile.csv',
'-output',
'./data/band_model',
'-dim',
10,
'-lr',
0.1,
'-wordNgrams',
2,
'-minCount',
1,
'-bucket',
10000000,
'-epoch',
5,
'-thread',
4 ]
Read 0M words
Number of words: 517
Number of labels: 2
Progress: 100.0% words/sec/thread: 1853435 lr: 0.000000 loss: 0.681683 eta: 0h0m -14m
exec:fasttext end.
exec:fasttext exit.
train done.
task:fasttext pid:41311 terminated due to receipt of signal:null
Test
$ cd examples/
$ node test.js
test [ 'test',
'./data/band_model.bin',
'/var/folders/_b/szqwdfn979n4fdg7f2j875_r0000gn/T/trainfile.csv',
1 ]
Number of examples: 18
exec:fasttext end.
exec:fasttext exit.
test done.
task:fasttext pid:41321 terminated due to receipt of signal:null
Predict
$ cd examples/
$ node predict.js
TEXT: our twitter run by the band and crew to give you an inside look into our lives on the road . get
TEXT: lbi software provides precisely engineered , customer-focused
Run a Prediction Server
We run a model and serve predictions via a simple node http api. We first download the example hosted models:
cd examples/models
./models.sh
We now run the server.js example that will create a http server. We can export the MODEL env that will point to the local pretrained model, and a optional PORT parameter were the server is going to listen (default PORT is 3000):
$ cd examples/
$ export MODEL=models/lid.176.ftz
$ node server.js
model loaded
server is listening on 3000
Try this simple server api passing a text parameter like:
http://localhost:3000/?text=LBi%20Software%20provides%20precisely%20engineered,%20customer-focused%20#HRTECH
http://localhost:3000/?text=Our%20Twitter%20run%20by%20the%20band%20and%20crew%20to%20give%20you%20an%20inside%20look%20into%20our%20lives%20on%20the%20road.%20Get%20#FutureHearts
The server api will response in json format
{
"response_time": 0.001,
"predict": [{
"label": "BAND",
"score": "0.5"
},
{
"label": "ORGANIZATION",
"score": "0.498047"
}
]
}
Run a Prediction CLI
To run a prediction Command Line Interface, please specify the env MODEL of the model file to run and use the example script cli:
cd examples/
export MODEL=models/langid_model.bin
node cli
Loading model...
model loaded.
Welcome to FastText.js CLI
Type exit or CTRL-Z to exit
> hello how are you?
> [ { label: 'EN', score: '0.988627' },
{ label: 'BN', score: '0.000935369' } ]
> das is seher gut!
> [ { label: 'DE', score: '0.513201' },
{ label: 'EN', score: '0.411016' } ]
rien ne va plus
> [ { label: 'FR', score: '0.951547' },
{ label: 'EO', score: '0.00760891' } ]
exit
> model unloaded.
Language Identificaton Server
In this example we use the fastText compressed languages model (176 languages) we host.
cd examples/
export MODEL=./data/lid.176.ftz
export PORT=9001
node server
and then
http://localhost:9001/?text=%EB%9E%84%EB%9E%84%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%B0%A8%EC%B0%A8%EC%B0%A8%20%EB%9E%84%EB%9E%84%EB%9D%BC\n%EB%9E%84%EB%9E%84%EB%9D%BC%20%EC%B0%A8%EC%B0%A8%EC%B0%A8%20%EC%9E%A5%EC%9C%A4%EC%A0%95%20%ED%8A%B8%EC%9C%84%EC%8A%A4%ED%8A%B8%20%EC%B6%A4%EC%9D%84%20%EC%B6%A5%EC%8B%9C%EB%8B%A4
that will be correctly detected as KO:
{
"response_time": 0.001,
"predict": [{
"label": "KO",
"score": "1"
},
{
"label": "TR",
"score": "1.95313E-08"
}
]
}
Train Language Identification Model
We train a langauge identification model from scratch. Please see in the examples/models folder.
Training set and Test set format
The trainFile and testFile are a TSV or CSV file where the fist column is the label, the second column is the text sample. FastText.js will try to normalize the dataset to the FastText format using FastText.prepareDataset method. You do not have to call this method explicitly by the way, FastText.js will do for you. For more info see here.
Datasets
We host some example datasets in order to train, test and predict FastText models on the fly. For more info how to download and work with datasets, please see in the examples/datasets folder.
Models
We host some example pretrained models. For more info how to download and work with pretrained models, please see in the examples/models folder.
Other Versions
Supported Platforms
In this release FastText.js comes with precompiled binaries for linux, macOS and Windows in the lib/bin/ folder. The Windows version is a 64-bit compiled version. It requires the Visual C++ Redistributable for Visual Studio 2015 components. See here for more info about the Windows version.
External Binary
To use an external binary version use the bin option to specify the executable absolute path:
var fastText = new FastText({
bin: '/usr/local/bin/fasttext'
loadModel: DATA_ROOT + '/sms_model.bin'
});
A executable not found in path error will be thrown if the executable has not been found in the specified path.
How It Works
Precompiled binaries runs FastText natively. A node child_process spawn will fork a new FastText native process tu run at OS speed, manage the state, the errors and the output of the process to the JavaScript API.
Disclaimer
For more info about FastText and FastText license see here.
Acknowledgments
I thank you the following devs that helped me to improve FastText.js





