
Security News
Potemkin Understanding in LLMs: New Study Reveals Flaws in AI Benchmarks
New research reveals that LLMs often fake understanding, passing benchmarks but failing to apply concepts or stay internally consistent.
A simple & minimal helpers for creating high performance gRPC microservices.
This package will simplify the creation of gRPC servers and services, you will just need to extend base GrpcService and implement remote functions, this library will turn your normal functions into gRPC callable functions, which makes it easy to create microservices in a clean way.
Basic microservice archticture using helpers in this library
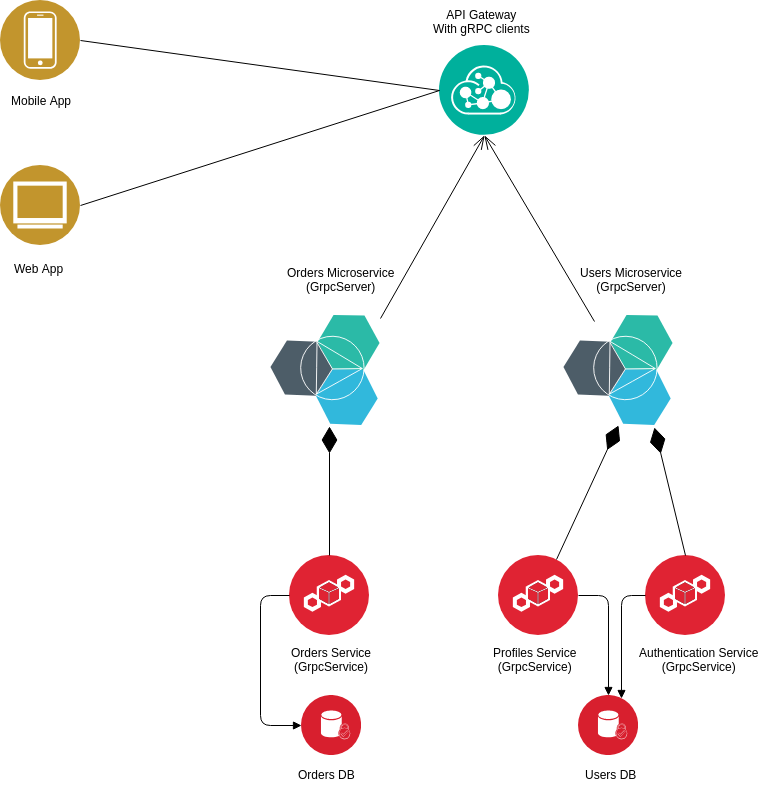
- You need to be familiar with gRPC and protocol buffers.
- Example in this package uses the proto3 version of the protocol buffers language.
- You can find out more about gRPC and proto3 in References section.
npm install grpc-core --save
You will need to create a new instance from GrpcServer with appropriate configurations then start your server.
You can register one or more gRPC services with the same server
Example:
const { GrpcServer } = require('grpc-core');
const UsersService = require('./UsersService');
const database = require('./database');
const server = new GrpcServer({
host: 'localhost',
port: 3000,
services: [
UsersService
],
onStart: async () => {
return database.connect();
},
onConnected: () => {
console.log('Users service is up');
}
});
server.start();
GrpcService constructor(config)
| Name | Type | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| host | string | Server host | |
| port | number | Server port | |
| services | Array.<GrpcService> | Array of GrpcService derived classes to be exposed | |
| onConnected | function | Function to be executed after server connection | Optional |
| onStart | function | Function to be executed before server start (ex. db connection) | Optional |
| onClose | function | Function to be executed before server shutdown (ex. close db connection) | Optional |
You will need to create your own service class which extends GrpcService class, and normal class methods will ne callable from your GrpcClient.
- Async methods are supported.
- Methods starts with _
underscorewill be ignored and considered private, so it will not be exposed into your gRPC service, even if you expose it in your protobuf schema, so it will get missing implementation error.
Example:
const path = require('path');
const { GrpcService } = require('grpc-core');
const hooks = require('../grpc/serviceHooks');
const middlewares = require('../grpc/serviceMiddlewares');
const PROTO = path.join(__dirname, '../config/proto/users.proto');
const User = require('../database/models/user');
class UsersService extends GrpcService {
constructor(){
super({
proto: PROTO,
hooks: hooks,
middlewares: middlewares
});
}
// Private method (will not be callable)
async _getUserId(user) {
return user._id;
}
async getUsers(ctx) {
return User.find({});
}
async create(ctx){
try {
const body = ctx.request;
await ctx.validateParams(userCreateSchema, body);
return User.create(body);
} catch(err) {
throw err;
}
}
async update(ctx){
try {
const _id = ctx.request._id;
// Your update code
return { updated: true};
} catch(err) {
throw err;
}
}
async delete(ctx) {
try {
const _id = ctx.request._id;
// Your delete code
return { delete: true};
} catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
}
GrpcService Hooks
Hooks are simply helper functions to be attached to request context (ctx) object, which will be passed later to callee function.
Hooks are passed to GrpcService as an object which contains all hook functions
Ex. if we need the request context object to have our own validation function, we will need to define this in hooks:
// hooks.js
module.exports = {
validate: (body) => {
// Validation logic here
}
};
// Then use it in service definition
const { GrpcService } = require('grpc-core');
const hooks = require('./hooks');
const proto = path.join(__dirname, './users.proto');
class UsersService extends GrpcService {
constructor() {
super({
proto,
hooks
});
}
// within our remote function implementation,
// hook function will be attached to context object for convenience.
async create(ctx) {
try {
const user = ctx.request;
// validate function attached to context object
ctx.validate(user);
// add user logic
return user;
}
catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
}
module.exports = new UsersService();
GrpcService Middlewares
Middlewares are just functions that will be execute in order before service function and will have the request context as an argument, so inside middleware you can manipulate request data, or request context itself
Middlewares are passed to GrpcService as an array of functions
Ex. Adding middleware to parse request metadata and add it to params field:
// middlewares.js
module.exports = [
// Metadata parser
(ctx) => {
try {
const md = ctx.metadata.getMap();
if (md) {
ctx.params = md;
}
}catch (err) {
throw err;
}
}
];
// Then use it in service definition
const { GrpcService } = require('grpc-core');
const middlewares = require('./middlewares');
const proto = path.join(__dirname, './users.proto');
class UsersService extends GrpcService {
constructor() {
super({
proto,
middlewares
});
}
// within our remote function implementation,
// ctx object should contain [params] field if caller passed any metadata
async create(ctx) {
try {
const params = ctx.params;
return params;
}
catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
}
GrpcClient instance is required to call remote GrpcService functions, It has only one function "call" which enable a simple way call remote functions.
Creating new GrpcClient:
// usersClient.js
const path = require('path');
const { GrpcClient } = require('grpc-core');
const usersProto = path.join(__dirname, './users.proto');
module.exports = new GrpcClient({
proto: usersProto,
service: 'UsersService',
url: 'localhost:3000',
});
Using GrpcClient:
const client = require('./usersClient');
async function createUser() {
try {
const result = await client.call('create', {email: 'test@grpccore.com'});
} catch(err){
throw err;
}
}
TODO
MIT
FAQs
A simple & minimal helpers for creating gRPC microservices
The npm package grpc-core receives a total of 17 weekly downloads. As such, grpc-core popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that grpc-core demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
New research reveals that LLMs often fake understanding, passing benchmarks but failing to apply concepts or stay internally consistent.

Security News
Django has updated its security policies to reject AI-generated vulnerability reports that include fabricated or unverifiable content.

Security News
ECMAScript 2025 introduces Iterator Helpers, Set methods, JSON modules, and more in its latest spec update approved by Ecma in June 2025.