heap-ts



BinaryHeap data structure implemented in Typescript - https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Heap_(data_structure)
Goal
ts-heap provides a strongly typed and efficient Heap data structure implementation.
Introduction
A heap is a tree-based data structure in which all the nodes of the tree are in a specific order. A Binary Heap is a Heap where there are at most 2 children of a node.
For example, if X is the parent node of Y, then the value of X follows a specific order with respect to the value of Y and the same order will be followed across the tree.
In binary heap, if the heap is a complete binary tree with N nodes, then it has smallest possible height which is log2(N).
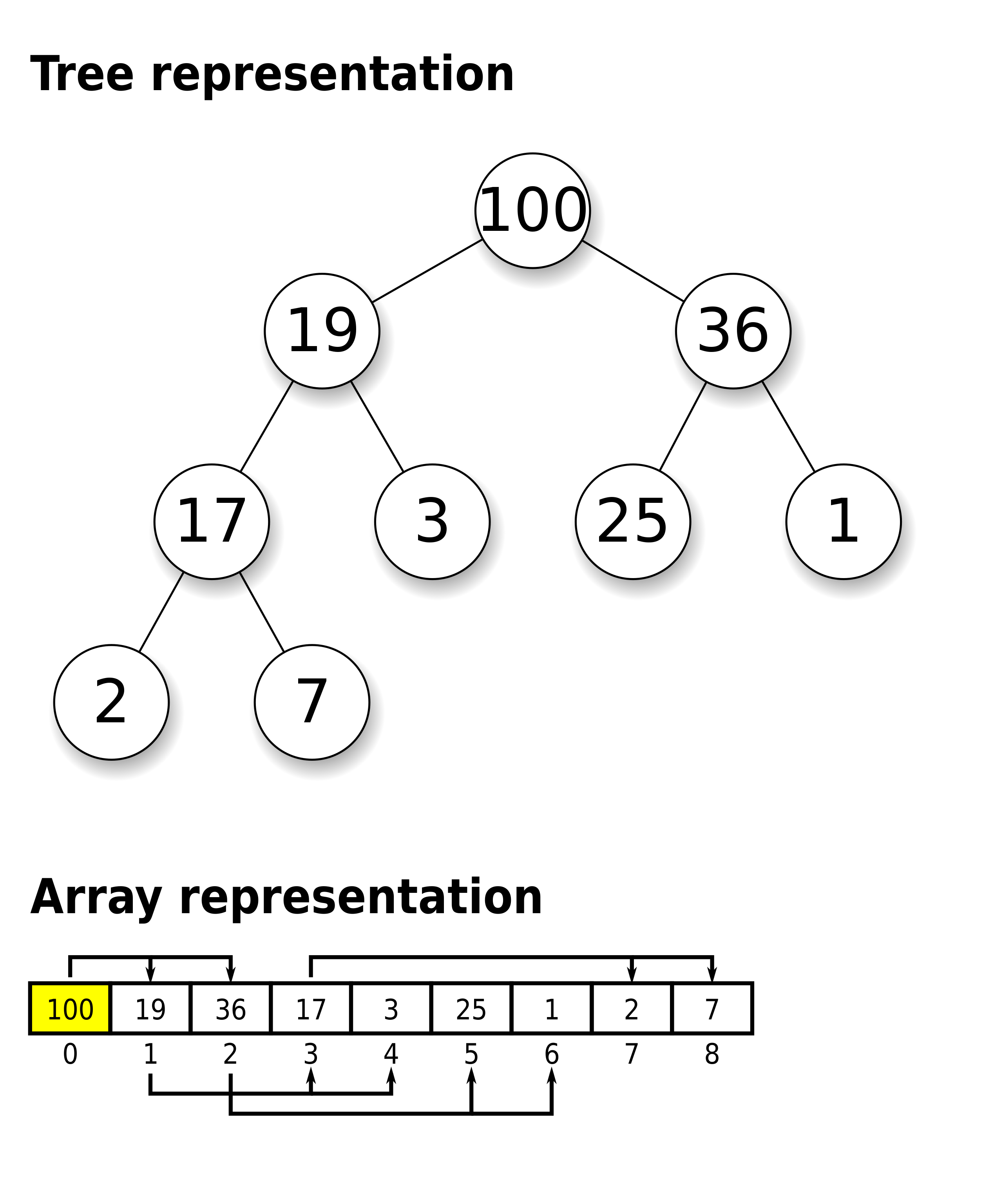
*Example of a binary max-heap with node keys being integers from 1 to 100*
The heap is one maximally efficient implementation of an abstract data type called a priority queue, and in fact, priority queues are often referred to as "heaps", regardless of how they may be implemented. In a heap, the highest (or lowest) priority element is always stored at the root. However, a heap is not a sorted structure; it can be regarded as being partially ordered. A heap is a useful data structure when it is necessary to repeatedly remove the object with the highest (or lowest) priority.
Installation
npm install heap-ts or yarn add heap-ts
Usage
First of all, we need to define a sorting function and an equality function.
const sortFunction: Sort<number> = (a, b) => a < b;
const equalityFunction: Equality<number> = (a, b) => a === b;
const items = [4, 5, 3, 8, 7, 23, 1, 456, 15, 9887, 3];
const heap = new BinaryHeap(sortFunction, equalityFunction, items);
Sorting function
The elements of the ts-heap are ordered by a Sort function provided at heap construction time.
export type Sort<T> = (a: T, b: T) => boolean;
Example of sorting function:
const sortFunction: Sort<number> = (a, b) => a < b;
Equality function
The elements of the ts-heap are compared by a Equality function provided at heap construction time.
export type Equality<T> = (a: T, b: T) => boolean;
Example of equality function:
const equalityFunction: Equality<number> = (a, b) => a === b;
Heap creation
We just need to create a new instance of BinaryHeap and pass the Sort and Equality functions:
const sortFunction: Sort<number> = (a, b) => a < b;
const equalityFunction: Equality<number> = (a, b) => a === b;
const heap = new BinaryHeap(sortFunction, equalityFunction);
Optionally, it is possible to create de heap with an array of initial values:
const sortFunction: Sort<number> = (a, b) => a < b;
const equalityFunction: Equality<number> = (a, b) => a === b;
const items = [4, 5, 3, 8, 7, 23, 1, 456, 15, 9887, 3];
const heap = new BinaryHeap(sortFunction, equalityFunction, items);
Operations
Binary heap operations are listed in the Heap.ts protocol:
export interface Heap<T> {
peek: () => T | undefined;
push: (item: T) => void;
pop: () => T | undefined;
remove: (item: T) => void;
length: () => number;
}
| Operation | Description | Time complexity (Big Oh) |
|---|
| peek() | Retrieves, but does not remove, the root of the heap, or returns undefined if the heap is empty. | O(1) |
| push(item: T) | Inserts the specified item into the heap. | O(log(n) |
| pop() | Retrieves and removes the root of the heap, or returns undefined if the heap is empty. | O(log(n) |
| remove(item: T) | Removes a single instance of the specified item from this heap, if it is present. | O(n + log(n)) |
| length() | Returns the number of elements in the heap. | O(1) |
| constructor with items (Building a heap from n elements) | Creates a new Heap with N elements | O(n * log(n)) |
Example
Imagine we have a list of orderes products, and we need to know what are the top 3 most sold products in an efficient time using a BinaryHeap.
import { Sort } from "../src/Sort";
import { Equality } from "../src/Equality";
import { BinaryHeap } from "../src/BinaryHeap";
const orders = [
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"Ultraboost 19",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Ultraboost 20",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"Superstar",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK",
"Superstar",
];
interface SoldProduct {
name: string;
timesSold: number;
}
function getKthMostSoldProducts(
k: number,
orderedProducts: string[]
): SoldProduct[] {
const soldProductsHash = getSoldProductsHash(orderedProducts);
const sortFunction: Sort<SoldProduct> = (a, b) => a.timesSold > b.timesSold;
const equalityFunction: Equality<SoldProduct> = (a, b) => a.name === b.name;
const heap = new BinaryHeap(sortFunction, equalityFunction);
Object.keys(soldProductsHash).forEach((name) => {
heap.push({
name,
timesSold: soldProductsHash[name],
});
});
let result: SoldProduct[] = [];
let index = k;
while (index > 0) {
const product = heap.pop();
if (product) {
result.push(product);
}
index--;
}
return result;
}
function getSoldProductsHash(
orderedProducts: string[]
): Record<string, number> {
const hash: Record<string, number> = {};
orderedProducts.forEach((product) => {
if (!hash[product]) {
hash[product] = 0;
}
hash[product] = hash[product] + 1;
});
return hash;
}
console.log(getKthMostSoldProducts(3, orders));
The console will print the following result:
[ { name: 'YEEZY BOOST 350 V2 ZEBRA', timesSold: 37 },
{ name: 'YEEZY BOOST 700 MNVN', timesSold: 32 },
{ name: 'YEEZY 500 UTILITY BLACK', timesSold: 17 } ]
Time complexity
Creating the hash map: O(p) where P is the number of orders.
Creating the heap: O(n * log(n)) where n is the number of different products.
Getting the Kth most sold products: O(k)
License
ts-heap is available under the MIT license. See the LICENSE file for more info.
Author
Ricardo Pallás






 *Example of a binary max-heap with node keys being integers from 1 to 100*
*Example of a binary max-heap with node keys being integers from 1 to 100*

