
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
ipld-vector
Advanced tools
An list / array-type data structure for very large, distributed data sets built on IPLD.
See also ipld-hashmap for an associative array Map-type data set for IPLD.
This JavaScript implementation conforms to the IPLD Vector specification.
The Vector in this implementation borrows from JavaScript's native Array object but uses asynchronous accessors rather than synchronous. Vector is also append-only (for now). When creating a new Vector or loading one with existing data, a backing store must be provided. The backing store is provided via a loader interface which should have a get() method that returns binary IPLD block data when provided a CID (content identifier) and a put() method that takes both a CID and binary block data that will store the IPLD block. This interface may connect to a P2P network, a block storage database or even a ZIP file.
The algorithm for this Vector is implemented in IAVector, you can read more about it there, or in the IPLD Vector specification. IAVector is serialization and storage agnostic and therefore does not contain any IPLD dependencies. IAVector is also immutable, where each mutation operation returns a new instance.
This implementation wraps IAVector with IPLD primitives, including the use of CIDs and the standard IPLD block encoding formats and presents a mutable interface. Each Vector object has its own root CID in the cid property. Whenever the Vector is mutated (push()), the cid property will change to the new root block CID.
You can create a new, empty, Vector with async Vector.create(loader[, options]). Loading a Vector from existing data can be done with async Vector.create(loader[, root][, options]).
Be aware that each mutation operation will create at least one new block, stored via loader.put(). Large numbers of mutations will create many extraneous intermediate blocks which will need to be garbage collected from the backing store if the intermediate states are not required.
class Vectorasync Vector#get(index)async Vector#size()async Vector#push(value)async Vector#values()async Vector#cids()async Vector.create(loader[, root][, options])class VectorAn IPLD Vector object. Create a new Vector or load an existing one with the asynchronous
Vector.create factory method.
This class serves mostly as a IPLD usability wrapper for
IAVector which implements the majority of the logic behind the
IPLD Vector specification, without being IPLD-specific. IAVector is immutable, in that each
mutation (delete or set) returns a new IAVector instance. Vector, however, is immutable, and
mutation operations may be performed on the same object but its cid property will change
with mutations.
Properties:
cid (CID): The current CID of this Vector. It is important to note that this CID
will change when successfully performing mutation a operation Vector#push.async Vector#get(index)Fetches the value of the provided key stored in this Vector, if it exists.
Parameters:
index (int): The index of the entry to look up in this Vector.Return value (*|CID|undefined): The value stored for the given index which may be any type serializable by IPLD, or a CID to
an existing IPLD object. This should match what was provided by Vector#set as the
value for this index. If the index is beyond the size of this Vector, undefined will be
returned.
async Vector#size()Count the number of entries stored in this Vector.
Return value (number): An integer greater than or equal to zero indicating the number of entries stored
in this Vector.
async Vector#push(value)Append an entry to this Vector. The value may be any object that can be serialized by
IPLD, or a CID to a more complex (or larger) object. Vector#get operations on the
index where this value is stored will retreve the value as it was set as long as
serialization and deserialization results in the same object.
As a mutation operation, performing a successful push() where a new entry, a new root node
will be generated so vector.cid will be a different CID. This CID should be used to refer
to this collection in the backing store where persistence is required.
Parameters:
value (*|CID): The value to store, either an object that can be serialized inline
via IPLD or a CID pointing to another object.async Vector#values()Asynchronously emit all values that exist within this Vector collection. This will cause a full traversal of all nodes that make up this collection so may result in many block loads from the backing store if the collection is large.
Return value (AsyncIterator.<(*|CID)>): An async iterator that yields values of the type stored in this collection, either inlined
objects or CIDs.
async Vector#cids()Asynchronously emit all CIDs for blocks that make up this Vector. This will cause a full traversal of all nodes that make up this collection so may result in many block loads from the backing store if the collection is large.
Return value (AsyncIterator.<CID>): An async iterator that yields CIDs for the blocks that comprise this Vector.
async Vector.create(loader[, root][, options])Create a new Vector instance, beginning empty, or loading from existing data in a
backing store.
A backing store must be provided to make use of a Vector, an interface to the store is given
through the mandatory loader parameter. The backing store stores IPLD blocks, referenced by
CIDs. loader must have two functions: get(cid) which should return the raw bytes (Buffer
or Uint8Array) of a block matching the given CID, and put(cid, block) that will store the
provided raw bytes of a block (block) and store it with the associated CID.
Parameters:
loader (Object): A loader with get(cid):block and put(cid, block) functions for
loading an storing block data by CID.root (CID, optional): A root of an existing Vector. Provide a CID if you want to load existing
data, otherwise omit this option and a new, empty Vector will be created.options (Object, optional): Options for the Vector. Defaults are provided but you can tweak
behavior according to your needs with these options.
options.blockCodec (string, optional, default='dag-json'): The IPLD codec used to encode the blocks.options.blockAlg (string, optional, default='sha2-256'): The hash algorithm to use when creating CIDs for
the blocks.options.width (string, optional, default=256): The width, or "artiy" of Vector nodes. Each constituent
block of this Vector will contain, at most, width elements or width elements to child nodes.
When a Vector exceeds width elements, a new level ("height") is added, where each element of
the upper level is used to refer to nodes of the lower level. When the Vector reaches 2^width
elements, another level is added, and so on. See
IPLD Vector specification
for more details on how this works.options.hasher (function, optional, default=murmur3.x86): A function that takes a byte array
(Uint8Array) and should return a byte representing a hash of the input. Supply this option if
you wish to override the default 'murmur3-32' hasher.options.expectedWidth (number, optional): When a root CID is provided, this option is used to
assert the expected width parameter that the existing Vector was created with.options.expectedHeight (number, optional): When a root CID is provided, this option is used to
assert the expected height of the existing Vector.Return value (Vector): - A Vector instance, either loaded from an existing root block CID, or a new,
empty Vector if no CID is provided.
Copyright 2019 Rod Vagg
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS, WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied. See the License for the specific language governing permissions and limitations under the License.
FAQs
A JavaScript implementation of the IPLD Vetor specification
We found that ipld-vector demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
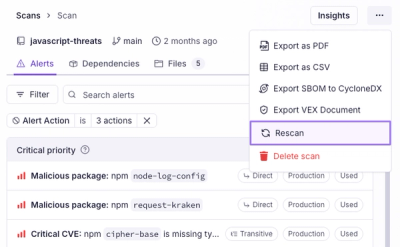
Product
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
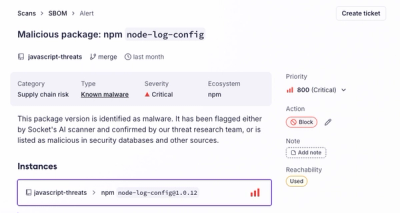
Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.