
Research
Malicious npm Packages Impersonate Flashbots SDKs, Targeting Ethereum Wallet Credentials
Four npm packages disguised as cryptographic tools steal developer credentials and send them to attacker-controlled Telegram infrastructure.
jsbaseclass
Advanced tools
A lightweight JavaScript base class for logging, event handling, and browser detection. Designed to simplify common tasks in frontend development.
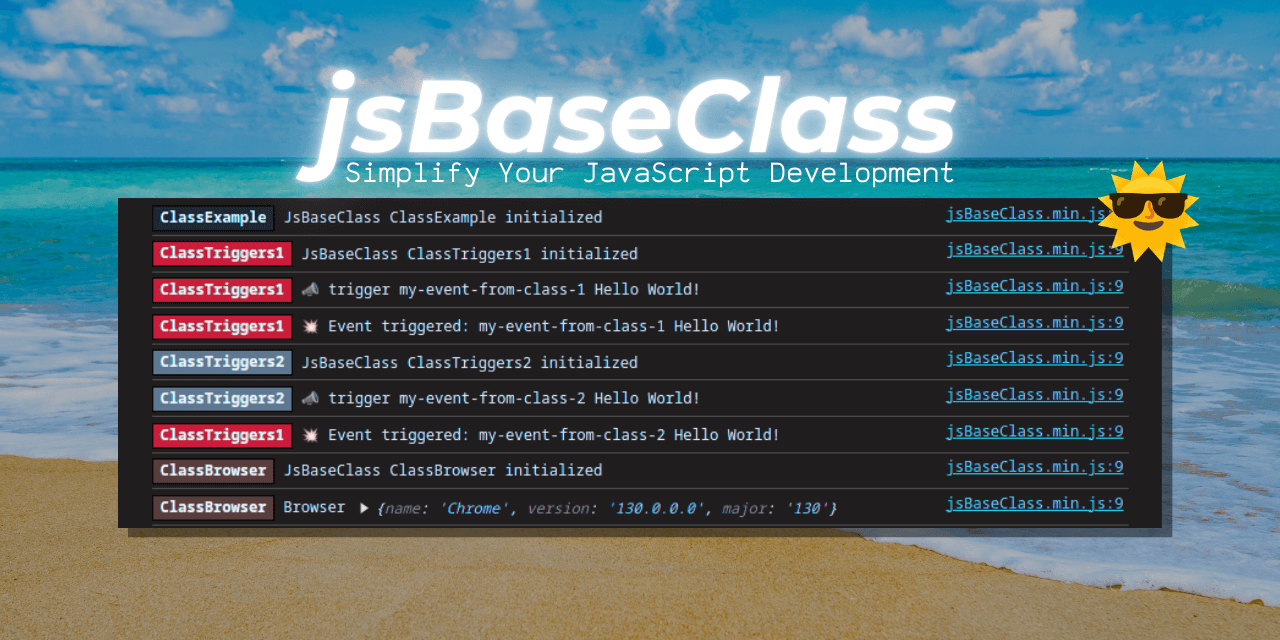

JsBaseClass is a versatile JavaScript base class designed to simplify common tasks such as logging, event handling, and browser detection. It provides a foundation for building modular and reusable components in your JavaScript applications. The class is lightweight, extensible, and easy to integrate into any project.
Looking for practical examples and ready-to-use snippets? Check out the JsBaseClass Wiki for a collection of guides and snippets to supercharge your development. 🚀
We also provide a pre-built reference specifically designed to instruct AI systems, available at: AI Reference. Use it to enhance your understanding and integration of JsBaseClass in AI-driven projects.
Custom Console Logging:
log, info, warn, error, and trace methods.Event Handling:
CustomEvent API.Browser Detection:
ua-parser-js.Lightweight and Extensible:
Include the library in your project using a script tag:
<!-- Development (with logging enabled) -->
<script src="path/to/jsBaseClass.min.js" data-silent="false"></script>
<!-- Production (with logging disabled) -->
<script src="path/to/jsBaseClass.min.js" data-silent="true"></script>
To use JsBaseClass, extend it in your own class and implement the handle method:
class MyApp extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Your initialization code here
this.console.log('Your code starts here...');
}
async onDomContentLoaded() {
// On DOM content loaded (page load)
this.console.log('DOM content loaded');
}
}
window.myApp = new MyApp();
myApp.init();
The JsBaseClass library integrates seamlessly with Axios, a popular HTTP client for making requests. Below is an example of how to use Axios within a class that extends JsBaseClass.
class ClassAxios extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
await this.getData(); // Fetch data from a valid API
await this.getNonExistsData(); // Attempt to fetch data from a non-existent API
}
async getData() {
try {
this.console.info(`1️⃣ Before Get Data`);
const response = await axios.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1');
this.console.log(`✅ Get Data`, response.data);
} catch (error) {
this.console.log(`🚨 ${error.message}`, error);
} finally {
this.console.log(`2️⃣ After Get Data`);
}
}
async getNonExistsData() {
try {
this.console.info(`1️⃣ Before Get Non Exists Data`);
const response = await axios.get('https://not-exists/json/1');
this.console.log(response.data);
} catch (error) {
this.console.log(`🚨 ${error.message}`, error);
} finally {
this.console.log(`2️⃣ After Get Non Exists Data`);
}
}
}
// Initialize the Axios example
window.objAxios = new ClassAxios();
await objAxios.init();
https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/1) and logs the response.https://not-exists/json/1) to demonstrate error handling.JsBaseClass to create your own class.axios to make HTTP requests within the handle method or other custom methods.this.console for structured logging and debugging.For more details on Axios, refer to the official documentation: Axios Documentation.
The JsBaseClass provides a built-in console object for logging. You can customize the log colors and styles:
class MyApp extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Set a custom color for logs
this.console.setColor('#3498db'); // Blue
// Log messages
this.console.log('This is a standard log message.');
this.console.info('This is an informational message.');
this.console.warn('This is a warning!');
this.console.error('This is an error!');
this.console.trace('This is a trace message.');
// Log with a random color
const randomColor = new JsBaseClassColors().get();
this.console.setColor(randomColor);
this.console.log(`This log has a random color: ${randomColor}`);
}
}
const app = new MyApp();
app.init();
Use the trigger and on methods to handle custom events. In this example, one class listens to an event, and another class triggers it:
// Class that listens to the event
class EventListener extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Listen to a custom event
this.on('my-event', (event) => {
this.console.log('Event received:', event.detail);
});
}
}
// Class that triggers the event
class EventTrigger extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Trigger the event
this.trigger('my-event', { message: 'Hello, World!' });
}
}
// Initialize both classes
const listener = new EventListener();
listener.init();
const trigger = new EventTrigger();
trigger.init();
The JsBaseClass provides browser detection capabilities:
class MyApp extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
this.console.log('Browser:', this.browser.name);
this.console.log('Browser Version:', this.browser.version);
this.console.log('Is Chrome?', this.is.chrome);
this.console.log('Is Firefox?', this.is.firefox);
}
}
const app = new MyApp();
app.init();
The JsBaseClass library provides built-in methods to manage cookies using the js-cookie library. Below is an example of how to set, get, and remove cookies, including advanced options like expires and domain. Additionally, the library includes helper methods for working with JSON data in cookies, making it easier to store and retrieve complex objects.
class ClassCookies extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Set a cookie with an expiration date (7 days from now)
this.setCookie('username', 'MarceloXP', { expires: 7 });
this.console.log('Username cookie set with expiration.');
// Set a cookie with a specific domain and path
this.setCookie('preferences', 'dark_mode', { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' });
this.console.log('Preferences cookie set with domain and path.');
// Get the value of a cookie
const username = this.getCookie('username');
this.console.log('Username cookie:', username);
const preferences = this.getCookie('preferences');
this.console.log('Preferences cookie:', preferences);
// Remove a cookie
this.removeCookie('username');
this.console.log('Username cookie removed.');
// Remove a cookie with domain and path
this.removeCookie('preferences', { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' });
this.console.log('Preferences cookie removed.');
// Check if the cookies were removed
const removedUsername = this.getCookie('username');
this.console.log('Username cookie after removal:', removedUsername);
const removedPreferences = this.getCookie('preferences');
this.console.log('Preferences cookie after removal:', removedPreferences);
// Example: Set and get a JSON cookie
const userSettings = {
theme: 'dark',
notifications: true,
language: 'en',
};
this.setJsonCookie('user_settings', userSettings, { expires: 7 });
this.console.log('User settings cookie set as JSON.');
const retrievedSettings = this.getJsonCookie('user_settings');
this.console.log('Retrieved user settings:', retrievedSettings);
}
}
// Initialize the cookies example
window.objCookies = new ClassCookies();
objCookies.init();
Set a Cookie:
this.setCookie(name, value, options) to set a cookie with a name, value, and optional settings like expires, domain, and path.this.setCookie('username', 'MarceloXP', { expires: 7 }) sets a cookie that expires in 7 days.this.setCookie('preferences', 'dark_mode', { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' }) sets a cookie for a specific domain and path.Get a Cookie:
this.getCookie(name) to retrieve the value of a cookie.this.getCookie('username').Remove a Cookie:
this.removeCookie(name, options) to delete a cookie. You can specify domain and path if needed.this.removeCookie('username').this.removeCookie('preferences', { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' }).Set a JSON Cookie:
this.setJsonCookie(name, value, options) to store a JSON object as a cookie. The object is automatically serialized to a string.this.setJsonCookie('user_settings', { theme: 'dark', notifications: true }, { expires: 7 }).Get a JSON Cookie:
this.getJsonCookie(name, defaultValue) to retrieve a JSON object from a cookie. The string is automatically parsed back into an object.this.getJsonCookie('user_settings', { theme: 'light', notifications: false }).🍪 Cookie set: username = MarceloXP { expires: 7 }
🍪 Cookie set: preferences = dark_mode { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' }
🍪 Cookie get: username = MarceloXP
🍪 Cookie get: preferences = dark_mode
🍪 Cookie removed: username {}
🍪 Cookie removed: preferences { domain: 'example.com', path: '/settings' }
🍪 Cookie get: username = undefined
🍪 Cookie get: preferences = undefined
🍪 Cookie set: user_settings = {"theme":"dark","notifications":true,"language":"en"} { expires: 7 }
🍪 Retrieved user settings: { theme: 'dark', notifications: true, language: 'en' }
Set a Cookie:
this.setCookie('username', 'MarceloXP', { expires: 7 });
Get a Cookie:
const username = this.getCookie('username');
Remove a Cookie:
this.removeCookie('username');
Set a JSON Cookie:
const userSettings = { theme: 'dark', notifications: true };
this.setJsonCookie('user_settings', userSettings, { expires: 7 });
Get a JSON Cookie:
const settings = this.getJsonCookie('user_settings', { theme: 'light', notifications: false });
setJsonCookie method automatically converts objects to strings, and getJsonCookie converts them back to objects.getJsonCookie method supports a default value, which is returned if the cookie doesn’t exist.expires: Always set an expiration date for cookies to avoid them persisting indefinitely.secure option for cookies that should only be transmitted over HTTPS.With these methods, you can easily manage cookies in your application, including storing and retrieving complex JSON data. For more details on cookie options, refer to the js-cookie documentation. 🍪🚀
expires to set an expiration date for the cookie.domain and path to control the scope of the cookie.Here’s a basic boilerplate to get started with JsBaseClass:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JsBaseClass Example</title>
<script src="path/to/jsBaseClass.min.js" data-silent="false"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JsBaseClass Example</h1>
<p>Open the browser console to see the logs.</p>
<script>
class MyApp extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
// Custom console logging
this.console.setColor('#3498db'); // Blue
this.console.log('This is a log message.');
this.console.info('This is an info message.');
this.console.warn('This is a warning!');
this.console.error('This is an error!');
// Event handling
this.on('my-event', (event) => {
this.console.log('Event triggered:', event.detail);
});
this.trigger('my-event', { message: 'Hello, World!' });
// Browser detection
this.console.log('Browser:', this.browser.name);
this.console.log('Browser Version:', this.browser.version);
}
}
window.myApp = new MyApp();
myApp.init();
</script>
</body>
</html>
The Brazil Plugin extends the functionality of JsBaseClass by adding utility methods specific to Brazil, such as CPF validation. This plugin is designed to simplify common tasks related to Brazilian data formats and regulations.
See more detailed information in the Wiki.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Brazil Plugin Example</title>
<script src="path/to/jsBaseClass.min.js"></script>
<script src="path/to/jsBaseClassPluginBrazil.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Brazil Plugin Example</h1>
<p>Open the browser console to see the validation results.</p>
<script>
class ClassBrazilValidator extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
const cpf = '111.111.111-11'; // Example CPF
const valid = this.brazil.isValidCpf(cpf);
if (valid) {
this.console.success(`🚀 ${cpf} is valid`);
} else {
this.console.error(`🚨 ${cpf} is invalid!!!`);
}
}
}
// Initialize the validator
window.objBrazilValidator = new ClassBrazilValidator();
objBrazilValidator.init();
</script>
</body>
</html>
To use the library with the latest version, you can use the jsDelivr CDN.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>JsBaseClass via jsDelivr</title>
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/gh/marceloxp/jsBaseClass@main/dist/jsBaseClass.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<h1>JsBaseClass via jsDelivr</h1>
<script>
class MyApp extends JsBaseClass {
async handle() {
this.console.log('JsBaseClass is working via jsDelivr!');
}
}
const app = new MyApp();
app.init();
</script>
</body>
</html>
JsBaseClass is licensed under the MIT License.
Contributions are welcome! Please open an issue or submit a pull request on the GitHub repository.
Enjoy using JsBaseClass! 🚀
FAQs
A lightweight JavaScript base class for logging, event handling, and browser detection. Designed to simplify common tasks in frontend development.
The npm package jsbaseclass receives a total of 10 weekly downloads. As such, jsbaseclass popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that jsbaseclass demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Four npm packages disguised as cryptographic tools steal developer credentials and send them to attacker-controlled Telegram infrastructure.

Security News
Ruby maintainers from Bundler and rbenv teams are building rv to bring Python uv's speed and unified tooling approach to Ruby development.

Security News
Following last week’s supply chain attack, Nx published findings on the GitHub Actions exploit and moved npm publishing to Trusted Publishers.