
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
ORM frontend for MySQL, uses JSON schema to define tables and relationships. This supports automatic table re-generation with indexes, default values, foreign keys, reference options, query logging and more.
For node.js: MySQL wrapper providing object mapping, automatic table generation via JSON schema, automatic foreign key generation and resolution, indexes, default values, reference options and more.
I'll write a proper README once all the basic functionality is in place, but for now use the documentation in the (hopefully) well-named .js files. Or more preferably, wait another week for me to get the first release of this together!
A test is given in the ./tests/ folder, which should demonstrate most of the core functionality. The components of this module (load.js, read.js, etc) are documented too, giving considerably more detail than this README.
/* Define a schema */
var schema = {
/* User-defined type aliases */
$types: {
/* Name begins with colon -> foreign key to some table */
'user': ':users',
'role': ':roles',
'string': 'varchar(64)',
'password': 'char(60)',
'boolean': 'bit',
/* A field of type "country" would be a foreign key to table "countries" */
'country': ':countries'
},
users: {
/* "id" field is generated automatically */
/* Dollar-prefix is used for metadata, e.g. default sort order */
$sort: '+username',
/* This field must have a unique value */
username: { type: 'string', unique: true },
password: { type: 'password' },
role: { type: 'role' },
lastactive: { type: 'timestamp' },
country: { type: 'country' }
},
roles: {
name: { type: 'string', unique: true },
rights: { type: 'string' }
},
posts: {
/* Prefix a sort field by + or - to explicitly set ascending or descending sort order */
$sort: '-date',
/* Set the ON UPDATE and ON DELETE actions for foreign key constraing */
user: { type: 'user', onDelete: 'cascade', onUpdate: 'cascade' },
/* Index this field */
title: { type: 'string', index: true },
content: { type: 'text' },
date: { type: 'timestamp' },
deleted: { type: 'boolean' }
},
countries: {
$sort: '+name',
name: { type: 'string', index: true }
}
};
/* Define the initial contents of the database (optional)
var data = {
roles: [
{ name: 'admin', rights: '*' },
{ name: 'ploom', rights: 'being a ploom' },
{ name: 'pleb', rights: 'lol' }
],
/* The auto_increment primary key `id` field is created automatically for each table */
countries: [
{ id: 44, name: 'United Kingdom' },
{ id: 372, name: 'Estonia' },
/* Lithuania was the largest country in Europe at one point */
{ id: 370, name: 'Lithuania' },
{ id: 7, name: 'Russia' }
],
users: [
/*
* We don't know what ID values the roles will have and we didn't explicitly specify them, but we can use the
* automatic foreign-key lookup to specify roles by name instead. Such search constraints must resolve to one
* and only one record in the parent table. Automatic lookup is also used for the country field. Easy!
*/
{ username: 'mark', password: Array(61).join('\0'), role: { name: 'admin' }, country: { name: 'Estonia' } },
{ username: 'marili', password: Array(61).join('\0'), role: { name: 'ploom' }, country: { name: 'Estonia' } }
],
posts: [
{ user: { username: 'mark' }, title: 'Test post', content: 'This is a test post', deleted: false }
]
};
/* See https://github.com/felixge/node-mysql for more information */
var mysql_params = {
host: 'localhost',
user: 'username',
password: 'password',
};
/* NOTE: The user must have SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE, etc rights to the database specified in the next section */
var orm_options = {
mysql: mysql_params,
/* Database name. User specified in previous section MUST have relevant rights to this database.* */
database: 'mysql-orm-test',
/* CAUTION: Setting this to true will drop the database then recreate it */
recreateDatabase: false,
/* CAUTION: Setting this to true will drop the tables mentioned in the schema then recreate them */
recreateTables: false,
/* Causes an annoying delay between each line output by ORM's logger */
debug: process.end.DEBUG
/* Log level (1,2,3=FAIL/WARN/INFO). See logging.js for more info. 2 (WARN) is default */
logLevel: 2
};
This will create the database if it does not exist and create the tables if they do not exist.
If recreateTables or recreateDatabase is specified, then the data will be added to the database.
Note that this will not occur if the tables/database are created but the recreate* parameters were not set.
CAUTION: recreateTables / recreateDatabase are for development purposes only, they WILL cause orm to drop the database and tables if they already exist.
var mysql_orm = require('../');
var orm = null;
mysql_orm.create(schema, data, orm_options, function (err, ormObject) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
orm = ormObject;
});
/* loadMany: Read multiple records from a table */
/* Specify the table by reference in the schema, or as a string e.g. 'countries' */
orm.loadMany(orm.schema.countries, null, function (err, countries) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
countries.forEach(function (country) { console.write(country.name });
});
/* load: Retrieve one record, return error if none were found or if several were found */
orm.load(orm.schema.users, 1, function (err, user) {
console.log(user.name + ' is in ' + user.country.name);
});
/* Oh did you notice that the `country` is automatically looked up there? Awesome! */
/* The second parameter of load / loadMany can also be an object containing search criteria */
orm.loadMany(orm.schema.users, { country: { name: 'Estonia' } }, callback);
/* We specified a value in a parent table as the search criteria :D */
Automatic lookups only go one level deep at the moment. TODO: Fix this. foreign-keys.js just needs a little tweak to enable recursive lookup.
/* Load a record, modify it, save it */
orm.load(orm.schema.users, { name: 'mark' }, function (err, user) {
if (err) throw err;
user.role = { name: 'pleb' };
orm.save(orm.schema.users, user, function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('User "mark" is now a pleb');
});
});
/*
* We could also do this instead, if we knew the user's ID. If the id is not
* specified, save() will create a new user and set the id field of the passed
* object to the new id returned from MySQL.
*/
orm.save(orm.schema.users, { id: 1, role: { name: 'pleb' } }, function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('User "mark" is now a pleb');
});
/*
* When inserting new items with no ID specified, the ID field of the passed
* object is set to the new row's ID in the database
*/
var guestRole = { name: 'guest', rights: 'read_posts,like_posts' };
orm.save(orm.schema.users, guestRole, function (err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('ID of guest role in roles table is ' + guestRole.id);
});
/*
* Save multiple records to a table
* This calls save() internally, so can update or create records.
* See save.js for details of how to explicity request an UPDATE or an INSERT.
*/
orm.saveMany(orm.schema.countries,
[
{ id: 358, name: 'Finland' },
{ id: 46, name: 'Sweden' }
],
function (err) {
...
});
/*
* Save to multiple tables. This calls saveMany() internally and wraps all the
* saveMany() calls in one transaction
*/
orm.saveMultipleTables(
{
countries: [ { id: 40, name: 'Romania' } ],
users: [ name: 'Dazza', country: { name: 'Romania' }, ... ]
},
function (err) {
});
/*
* There is no deleteMany; delete will remove any and all matching records
* As with load, a numeric value is interpreted as an ID while an object
* is interpreted as key-value pairs which will be looked up in parent tables
* when needed.
*/
orm.delete(orm.schema.users, 1, callback);
orm.delete(orm.schema.countries, { name: 'Atlantis' }, callback);
orm.logLevel = 3;
/* Now STDOUT will get flooded by debugging messages and SQL code */
orm.debug = true;
/* Now there will be an annoying blocking delay after each logged message */
/* Don't use this in production! */
You can also set logLevel and debug in the orm_options parameter.
FAQs
ORM frontend for MySQL, uses JSON schema to define tables and relationships. This supports automatic table re-generation with indexes, default values, foreign keys, reference options, query logging and more.
The npm package mysql-orm receives a total of 0 weekly downloads. As such, mysql-orm popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that mysql-orm demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
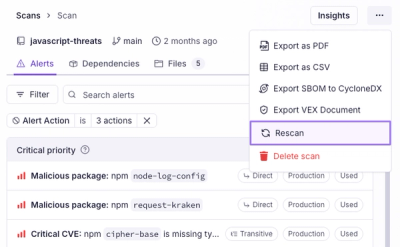
Product
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
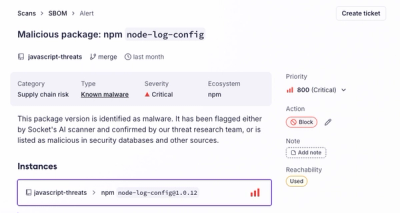
Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.