
Research
/Security News
Critical Vulnerability in NestJS Devtools: Localhost RCE via Sandbox Escape
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).
node-env-run
Advanced tools

Command-line tool to read
.envfiles and execute scripts/commands after loading those environment variables
dotenv under the hood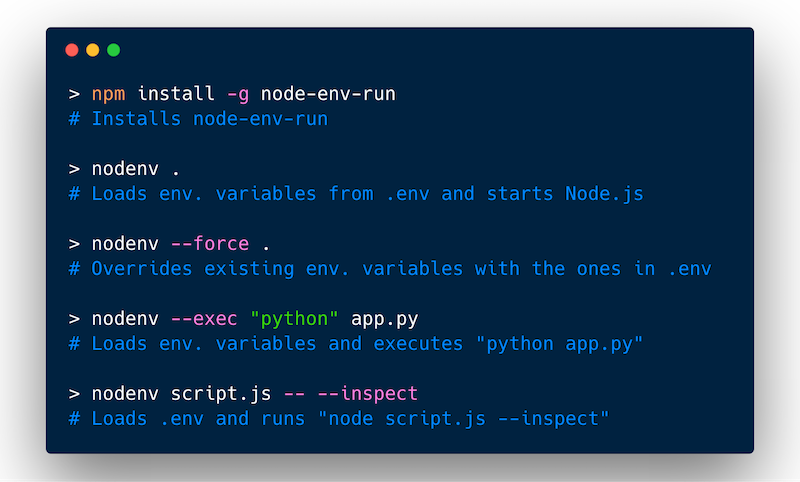
I recommend installing this module as a devDependency for the respective project.
Install via yarn:
yarn add node-env-run --dev
Install via npm:
npm install node-env-run --save-dev
You can alternatively install the module globally if you want to:
npm install node-env-run --global
Add a new scripts entry to your package.json. Example:
{
"scripts": {
"dev": "nodenv .",
"test": "nodenv -E test/.env test/test.js"
}
}
Or use it with npx:
npx node-env-run .
This module uses under the hood the dotenv module to parse the .env file. For more information about how to structure your .env file, please refer to its documentation.
Start up the main file in package.json with the enviornment variables from .env:
nodenv .
Start Node.js REPL with set environment variables from .env.repl:
nodenv -E .env.repl
Run Python file with overridden environment variables:
nodenv app.py --exec python --force
Run server.js file using nodemon:
nodenv server.js --exec nodemon
Pass --inspect flag for debugging after --:
nodenv someScript -- --inspect
You can pass node-env-run a variety of arguments. These are the currently supported arguments:
| Flag | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
--encoding | string | Lets you specify the encoding of the .env file. Defaults to utf8 encoding. |
--env or -E | string | Specifies the path to the .env file that should be read |
--exec or -e | string | This lets you specify a command other than node to execute the script with. More in the next section. |
--force or -f | boolean | Flag to temporarily override existing environment variables with the ones in the .env file |
--help | boolean | Displays the usage/help instructions |
--verbose | boolean | Flag to enable more verbose logging |
--version | boolean | Displays the current version of the package |
node-env-run with other executablesYou can use node-env-run with other executables. This is particularly useful if you try to combine it with things like babel-node or ts-node:
nodenv index.ts --exec "ts-node"
However, you can also use it with completely unrelated executables such as python:
nodenv app.py --exec python
If you want to pass additional flags/arguments to the script you are executing using node-env-run, you can use the empty -- argument and follow it with any arguments you'd want to pass. For example:
nodenv index.js --exec "ts-node" -- --log-level debug
--log-level debug will be passed to index.js.
If you want to do the same with a REPL like node or python you'll have to specify REPL explictly, due to some parsing behavior of yargs. For example:
nodenv REPL --exec node -- -e "console.log('hello world!')"
Using quotes for escaping special characters should generally work out of the box. However, there is one edge case if you are trying to use double quotes (") inside and want to preserve it. In that case you'll have to double escape it due to some inner workings of Node.js. For example:
nodenv REPL --exec echo -- 'A common greeting is "Hello World"'
# outputs: A common greeting is Hello World
nodenv REPL --exec echo -- 'A common greeting is \"Hello World\"'
# outputs: A common greeting is "Hello World"
Similarly if you want to avoid variables to be interpolated you'll have to escape the $ separately. For example:
nodenv REPL --exec echo -- '$PATH'
# outputs your actual values stored in $PATH
nodenv REPL --exec echo -- '\$PATH'
# outputs: $PATH
Dominik Kundel 💻 |
|---|
MIT
FAQs
Wrapper executable to load env variables from .env and run Node
The npm package node-env-run receives a total of 12,029 weekly downloads. As such, node-env-run popularity was classified as popular.
We found that node-env-run demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
/Security News
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).

Product
Customize license detection with Socket’s new license overlays: gain control, reduce noise, and handle edge cases with precision.

Product
Socket now supports Rust and Cargo, offering package search for all users and experimental SBOM generation for enterprise projects.