Open Parse




Open Parse = Parse.com + JSON API + koa
The collection of middleware which provides extra-flexible RESTful API interface for accessing to application data store and schemas, users and security management. Save your time to bootstrap new web and mobile projects.
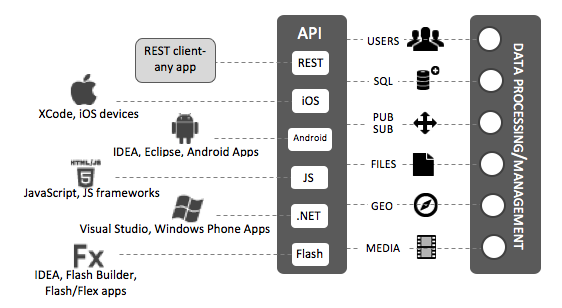
Open Parse is open source BaaS (Backend as a Service). What is BaaS? See the schema below and focus on "Data Proccessing / Management" node:
Out of the box Open Parse supports:
-
bunyan-logger which could be connected to Logentries, Loggly, NewRelic and other cloud log management services just in a 15 seconds.
-
MongoDB for default data providers. But you could implement custom data providers for any other databases (it takes ~20 min).
Built with love to Functional Principles and.. yes, koa.
Content
Basic Usage
The following example has been written with using promised-mongo and koa-router packages.
Prepare new router and utils
const router = new Router();
const dataRequired = function *(next) {
if (typeof this.request.body['data'] === 'object') {
yield next;
} else {
this.throw(400, 'Request data is required');
}
};
Bring up Users API
const users = {
dataProvider: new UsersDataProvider({
collection: pmongo.collection('users')
})
};
router.post('/users', dataRequired, handleUserSignUp(users));
router.get('/login', handleUserLogin(users));
router.post('/logout', handleUserLogout(users));
router.get('/users/me', handleUserFetch(users));
Bring up Classes API
In this example we're using a local data from JSON file.
const classes = {
dataProvider: new ObjectsDataProvider({
collection: pmongo.collection('objects'),
initialCache: require('./cached-objects.json')
}),
};
router.post('/classes/:className', dataRequired, handleObjectCreate(classes));
router.get('/classes/:className', handleObjectsList(classes));
router.get('/classes/:className/:objectId', handleObjectFetch(classes));
router.patch('/classes/:className/:objectId', dataRequired, handleObjectUpdate(classes));
router.delete('/classes/:className/:objectId', handleObjectDelete(classes));
For ObjectsDataProvider an initial cache should be specified as a [className][objectId] hash object:
cached-objects.json
{
"company": {
"our": {
"title": "Startup Makers",
"about": "We are consulting and outsourcing a web-development with cutting-edge JavaScript technologies (ES6, Node.js, React, Redux, koa)"
}
}
}
Bring up Schemas API
const schemas = {
dataProvider: new SchemasDataProvider({
collection: pmongo.collection('schemas')
})
};
router.get('/schemas/:className', handleSchemaFetch(schemas));
Connect the router to your application
app.use('/api', router);
How To Connect a Cloud Log Service?
It's really easy.
Did you initialize a logger?
If you did not, do it right now:
import bunyan from 'bunyan';
import { LogentriesBunyanStream } from 'bunyan-logentries';
const logger = bunyan.createLogger({
name: 'awesome-app',
streams: {
stream: new LogentriesBunyanStream({
token: process.env['LOGENTRIES_TOKEN']
}),
level: 'debug',
type: 'raw'
}
});
Add a one line to your code
const users = {
dataProvider: new UsersDataProvider({
collection: pmongo.collection('users')
}),
logger
};
router.post('/users', dataRequired, handleUserSignUp(users));
router.get('/login', handleUserLogin(users));
router.post('/logout', handleUserLogout(users));
router.get('/users/me', handleUserFetch(users));
Roadmap
Version 0.2
- Support access control layer (ACL)
- Add real world example
- Improve the documentation and architecture schema
Version 0.3
- Support jobs feature
- Support e-mail service
Version 0.4
- Add client SDK for JavaScript and React Native
- Support files feature
Version 0.5






