
Security News
AI Agent Submits PR to Matplotlib, Publishes Angry Blog Post After Rejection
After Matplotlib rejected an AI-written PR, the agent fired back with a blog post, igniting debate over AI contributions and maintainer burden.
psy keeps restarting a process when it crashes. It never stops.
This package is like pm2 or forever, but fewer features so there are less things that can go wrong and fewer options to configure.
Just install psy to get started:
$ npm install -g psy
Now you can start a process called static:
$ psy start -n static -- ecstatic ./public -p 8080
and another process called api:
$ psy start -n api -- node server.js
we can list the running processes:
$ psy ls
static running 5914 less than a minute ago ecstatic ./public -p 8080
api running 5932 less than a minute ago node server.js
restart a process:
$ psy restart static
$ psy ls
static running 6015 less than a minute ago ecstatic ./public -p 8080
api running 5932 2 minutes ago node server.js
stop a process:
$ psy stop api
$ psy ls
static running 6015 less than a minute ago ecstatic ./public -p 8080
api stopped --- --- node server.js
stop and remove a process:
$ psy rm static
$ psy ls
api stopped --- --- node server.js
log lifecycle events and stdout+stderr:
$ psy log msgs
!!! PROCESS SPAWN: PID 12086
!!! PROCESS START
2015-05-18T14:09:26.886Z
/home/substack/projects/psy/msgs.js:3
if (Math.random() < 0.2) (undefined).whatever()
^
TypeError: Cannot read property 'whatever' of undefined
at null._repeat (/home/substack/projects/psy/msgs.js:3:41)
at wrapper [as _onTimeout] (timers.js:267:19)
at Timer.listOnTimeout (timers.js:89:15)
!!! PROCESS EXIT: 1
!!! PROCESS SLEEP
!!! PROCESS SPAWN: PID 12092
2015-05-18T14:09:29.264Z
2015-05-18T14:09:30.303Z
2015-05-18T14:09:31.314Z
!!! PROCESS EXIT: SIGTERM
!!! PROCESS STOP
restart a process on reboot, add the following to your crontab:
@reboot psy daemon
and SEVERAL more!
psy start {OPTIONS} -- [COMMAND...]
Start a process COMMAND.
-n, --name Set a NAME for the process.
--cwd Current working directory for COMMAND
--env.NAME=VALUE Set environment variables explicitly for COMMAND.
--sleep Sleep MS milliseconds between restarts. Default: 1000
--maxRestarts Number of restarts allowed in 60 seconds before stopping.
-1 for Infinity. Default: -1.
-l, --logfile Write stdout, stderr, and process lifecycle events to FILE.
If NAME isn't given, the generated hex name will be printed.
When the process crashes, it will be restarted unless maxRestarts is reached.
psy stop NAME
Stop a process by its NAME.
psy restart NAME
Restart a process by its NAME.
--all Restart all processes
psy rm NAME
psy remove NAME
Stop a process and remove it from the list.
psy list
psy ls
List the running processes as text columns.
--json Print the data as json instead of text columns.
psy log NAME
Show the lifecycle events and stdout+stderr for NAME as it arrives.
-n I, -n I,J Show lines I through J starting from the end of the log.
-N I, -N I,J Show lines I through J starting from the start of the log.
-f, --follow Show live data from running processes.
By default, --follow is enabled when no -n or -N is given.
psy server
Run the monitor service in the foreground.
psy daemon
Run the monitor service in the background.
psy pid
Print the last known PID of the daemon process.
psy reset
Clear any process state and close the server. Processes will not come back
when the server starts up again.
psy close
Close the server. Processes will come back when the server starts up again.
If the service isn't running when a command like `psy start` or `psy ls` is run,
the service will be opened in autoclose mode. In autoclose mode, the service
automatically exits when there are no open connections and no managed processes.
If the monitor service crashes, the next time the service runs it will restart
any processes it was running before.
GLOBAL OPTIONS
--pidfile File to store PID information about the daemon.
--sockfile Where to place the unix socket for RPC connections
--statefile Store process state information here for recovery.
--version Print the version number and exit.
Options take precedence over environment variables.
ENVIRONMENT VARIABLES
PSY_SOCKFILE Unix socket file to use for RPC connections.
PSY_PIDFILE File to store PID information about the daemon.
PSY_STATEFILE File to store information about process state between runs.
PSY_PATH Directory to check for `sock` and `pid` files if PSY_SOCKFILE
or PSY_PIDFILE are not given. Default: $HOME/.config/psy
The JavaScript API will respect the same environment variables as the cli. You can provide overrides in the opts objects, however. See cmd.js for an example.
psy(opts)Constructor.
var psy = require('psy')(opts)
opts:
psypath: PSY_PATHstatefile: PSY_STATEFILEsockfile: PSY_SOCKFILEpidfile: PSY_PIDFILErpcfile: path to rpc serverdebug: boolean to debug.psy.server(cb)Starts a psy server, does not close it.
psy.server(argv, function (err, r, c) {
if (err) error(err)
else c.end()
})
psy.restart(name, cb)psy.restart(name, function (err) {
if (err) throw err
})
psy.stop(name, cb)psy.remove(name, cb)psy.log(name, cb)returns callback with cb(err, stream)
psy.kill(cb)psy.close(cb)psy.list(cb)return callback with cb(err, items)
psy.run(cb)Run a daemon.
cb: runs autod under the hood and returns the same callback.
Used in:
MIT
FAQs
process monitor command
We found that psy demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 4 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
After Matplotlib rejected an AI-written PR, the agent fired back with a blog post, igniting debate over AI contributions and maintainer burden.
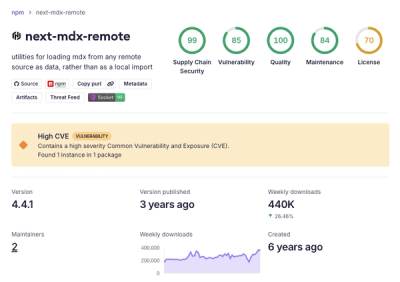
Security News
HashiCorp disclosed a high-severity RCE in next-mdx-remote affecting versions 4.3.0 to 5.x when compiling untrusted MDX on the server.

Security News
Security researchers report widespread abuse of OpenClaw skills to deliver info-stealing malware, exposing a new supply chain risk as agent ecosystems scale.