Product
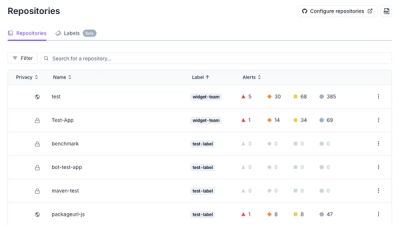
Introducing Repository Labels and Security Policies
Socket is introducing a new way to organize repositories and apply repository-specific security policies.
react-event-tracker
Advanced tools
npm install --save react-event-tracker
App.js - root level component
import { useSiteTracking } from "react-event-tracker";
const trackingConfig = {
siteData: {
site: "my site",
},
pageTracking: {
onPageLoad: ({ siteData, pageData }) => {
// Fire a page view to your analytics solution.
},
},
eventTracking: {
trackEvent: ({ siteData, pageData, eventData }) => {
// Fire a click event to your analytics solution.
},
},
};
function App() {
const { SiteTracking } = useSiteTracking(trackingConfig);
// Wrap your app with SiteTracking
return (
<SiteTracking>
...
</SiteTracking>
);
}
ProductPage.js - page level component
import { usePageTracking } from "react-event-tracker";
const pageData = {
page: "my_product",
};
function ProductPage(props) {
const { PageTracking } = usePageTracking(pageData);
return (
<PageTracking>
<ProductPageContent {...props} />
</PageTracking>
);
}
ProductPageContent.js - any component deep inside the tree
import { useEventTracking } from "react-event-tracker";
function ProductPageContent() {
const { trackEvent } = useEventTracking();
return (
...
<button
onClick={() => {
/*
Here is the core of what this library does.
You call `trackEvent` (provided by `react-event-tracker`) with `eventData`.
In return, `react-event-tracker` will call your own `trackEvent` (that you defined in the `trackingConfig` above) with `siteData`, `pageData`, and `eventData`.
*/
trackEvent({ button: "Apply" });
}}
>
Apply
</button>
...
)
}
If you add onPageLoad to trackingConfig.pageTracking, react-event-tracker will call it whenever your page is first mounted. Your page is the component that calls usePageTracking.
localStorageSometimes, when tracking a page view, you may want to track the traffic source.
For example, say you are tracking page views of the Application page. It could be very useful to know how users have arrived to the Application page. Did they click the "Apply" link in the header on the Home page? Maybe the "Apply" link in the footer? Or, maybe, they landed on the Application page after clicking "Apply" on your Product Page?
One way to track this, is to write to localStorage when users click the "Apply" link. Then, read from localStorage in the onPageLoad function.
const trackingConfig = {
...
eventTracking: {
storeTrafficSource: ({ pageData, eventData }) => {
localStorage.setItem(
"traffic_source",
`${pageData.page}:${eventData.source}`
);
}
}
};
import { useEventTracking } from "react-event-tracker";
function ProductPageContent() {
const { storeTrafficSource } = useEventTracking();
return (
...
{/*
You call `storeTrafficSource` (provided by `react-event-tracker`) with `eventData`.
In return, `react-event-tracker` will call your own `storeTrafficSource` (that you defined in the `trackingConfig` above) with `siteData`, `pageData`, and `eventData`.
*/}
<a
href="/apply"
onClick={() => {
// This will write "my_product:apply" to "traffic_source" in `localStorage`.
storeTrafficSource({ source: "apply" });
}}
>
Apply
</a>
...
)
}
When linking to external sites, you may want to add query string parameters based on siteData, pageData, and/or eventData.
Add a getQueryString function to eventTracking, e.g.:
const trackingConfig = {
eventTracking: {
getQueryString: ({ siteData, pageData, eventData }) => {
const dataLayer = {
...siteData,
...pageData,
...eventData,
};
return Object.keys(dataLayer)
.map((key) => `${key}=${encodeURIComponent(dataLayer[key])}`)
.join("&");
},
},
};
Then, call getQueryString that is given to you by useEventTracking.
import { useEventTracking } from "react-event-tracker";
function ProductPageContent() {
const { getQueryString } = useEventTracking();
return (
...
{/*
You call `getQueryString` (provided by `react-event-tracker`) with `eventData`.
In return, `react-event-tracker` will call your own `getQueryString` (that you defined in the `trackingConfig` above) with `siteData`, `pageData`, and `eventData`.
*/}
<a
href={`https://external-site.com?${getQueryString({
link: "apply"
})}`}
>
Apply on external site
</a>
...
)
}
FAQs
Easily track events in your React application
The npm package react-event-tracker receives a total of 62 weekly downloads. As such, react-event-tracker popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that react-event-tracker demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 5 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket is introducing a new way to organize repositories and apply repository-specific security policies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncovered malicious npm and PyPI packages that steal crypto wallet credentials using Google Analytics and Telegram for exfiltration.

Product
Socket now supports .NET, bringing supply chain security and SBOM accuracy to NuGet and MSBuild-powered C# projects.