
Security News
curl Shuts Down Bug Bounty Program After Flood of AI Slop Reports
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
slonik-utilities
Advanced tools
Utilities for manipulating data in PostgreSQL database using Slonik.
updateimport {
update
} from 'slonik-utilities';
/**
* @param connection Instance of Slonik connection.
* @param {string} tableName Target table name.
* @param {Object.<string, ValueExpression>} namedValueBindings Object describing the desired column values.
* @param {Object.<string, EqualPredicate>} [booleanExpressionValues] Object describing the boolean expression used to construct WHERE condition.
* @returns {UpdateResultType}
*/
update;
Constructs and executes UPDATE query.
Operation:
update(
connection,
'user',
{
givenName: 'foo'
}
);
Is equivalent to:
UPDATE "user"
SET
"given_name" = $1;
Operation:
update(
connection,
'user',
{
givenName: 'foo'
},
{
lastName: 'bar'
}
);
Is equivalent to:
UPDATE "user"
SET
"given_name" = $1
WHERE
"last_name" = $2;
updateDistinctimport {
updateDistinct
} from 'slonik-utilities';
/**
* @param connection Instance of Slonik connection.
* @param {string} tableName Target table name.
* @param {Object.<string, ValueExpression>} namedValueBindings Object describing the desired column values.
* @param {Object.<string, EqualPredicate>} [booleanExpressionValues] Object describing the boolean expression used to construct WHERE condition.
* @returns {UpdateDistinctResultType}
*/
updateDistinct;
Constructs and executes UPDATE query matching only rows with distinct values.
Operation:
update(
connection,
'user',
{
givenName: 'foo'
}
);
Is equivalent to:
UPDATE "user"
SET
"given_name" = $1
WHERE
"given_name" IS DISTINCT FROM $1;
Operation:
update(
connection,
'user',
{
givenName: 'foo'
},
{
lastName: 'bar'
}
);
Is equivalent to:
UPDATE "user"
SET
"given_name" = $1
WHERE
"last_name" = $2 AND
"given_name" IS DISTINCT FROM $1;
upsertimport {
upsert
} from 'slonik-utilities';
/**
* @typedef Configuration~Upsert
* @property identifierName column name. Default: "id".
*/
/**
* @param connection Instance of Slonik connection.
* @param {string} tableName Target table name.
* @param {Object.<string, ValueExpression>} namedValueBindings Object describing the desired column values.
* @param {string[]} [uniqueConstraintColumnNames] Names of columns that describe a unique constraint on the table. Defaults to property names of `namedValueBindings`.
* @param {Configuration~Upsert} [configuration]
*/
upsert;
Inserts a new record to the database. If there is a conflicting unique constraint, updates the existing row.
Table schema:
CREATE TABLE user (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
email_address text NOT NULL
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX user_email_idx ON user(email_address text_ops);
Operation:
upsert(
connection,
'user',
{
emailAddress: 'gajus@gajus.com'
}
);
Behaviour:
If user table already contains a record describing the input email, then the following query will be evaluted:
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1
);
If user table does not contain a record describing the input email, then the following queries will be evaluated:
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1
);
INSERT INTO "user" ("email_address")
VALUES ($1)
ON CONFLICT ("email_address")
DO NOTHING
RETURNING "id";
-- This query will not be evaluted if the preceeding query returns result.
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1
);
Table schema:
CREATE TABLE user (
id SERIAL PRIMARY KEY,
email_address text NOT NULL,
password text NOT NULL,
given_name text NOT NULL,
family_name text NOT NULL
);
CREATE UNIQUE INDEX user_email_idx ON user(email_address text_ops);
Operation:
upsert(
connection,
'user',
{
emailAddress: 'gajus@gajus.com',
familyName: 'Kuizinas',
givenName: 'Gajus'
},
[
'email_address'
]
);
Behaviour:
If user table already contains a record describing the input email, then the following query will be evaluted:
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1 AND
"family_name" = $2 AND
"given_name" = $3
);
If user table does not contain a record describing the input email, then the following queries will be evaluated:
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1 AND
"family_name" = $2 AND
"given_name" = $3
);
INSERT INTO "user" ("email_address", "family_name", "given_name")
VALUES ($1, $2, $3)
ON CONFLICT ("email_address")
DO UPDATE SET
"family_name" = "excluded"."family_name",
"given_name" = "excluded"."given_name"
RETURNING "id"
Named value binding values can be SQL tokens, e.g.
upsert(
connection,
'user',
{
emailAddress: 'gajus@gajus.com',
createdAt: sql.raw('to_timestamp($1)', [1555595070])
}
);
Given the above example, queries equivalent to the following will be evaluated:
SELECT "id"
FROM "user"
WHERE (
"email_address" = $1 AND
"created_at" = to_timestamp($2)
);
-- ...
FAQs
Utilities for manipulating data in PostgreSQL database using Slonik.
The npm package slonik-utilities receives a total of 4,301 weekly downloads. As such, slonik-utilities popularity was classified as popular.
We found that slonik-utilities demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
A surge of AI-generated vulnerability reports has pushed open source maintainers to rethink bug bounties and tighten security disclosure processes.
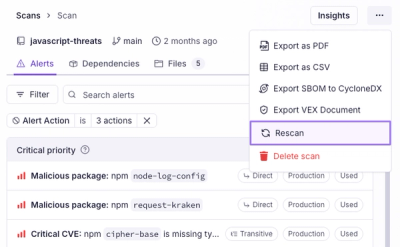
Product
Scan results now load faster and remain consistent over time, with stable URLs and on-demand rescans for fresh security data.
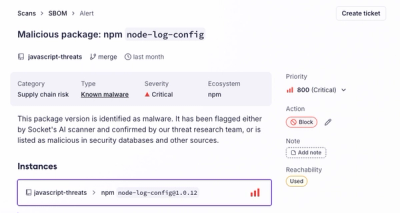
Product
Socket's new Alert Details page is designed to surface more context, with a clearer layout, reachability dependency chains, and structured review.