Spotify Web API JS 



This is a lightweight wrapper for the Spotify Web API (2.6kB gzipped + compressed). It includes helper functions for all Spotify's endpoints, such as fetching metadata (search and look-up of albums, artists, tracks, playlists, new releases, podcasts) and user's information (follow users, artists and playlists, and saved tracks management).
It doesn't have any dependencies and supports callbacks and promises. It is intended to be run on a browser, but if you want to use Node.JS to make the requests, please check spotify-web-api-node.
A list of selected wrappers for different languages and environments is available on the Developer site's Libraries page.
The wrapper includes helper functions to do the following:
Music and Podcast metadata
- Albums, artists, tracks and playlists
- Audio features and audio analysis for tracks
- Albums for a specific artist
- Top tracks for a specific artist
- Artists similar to a specific artist
- Shows and episodes (podcasts)
Profiles
- User's emails, product type, display name, birthdate, image
Search
- Albums, artists, tracks, playlists, shows, and episodes
Playlist Management
- Get a user's playlists
- Create playlists
- Change playlist details
- Add tracks to a playlist
- Remove tracks from a playlist
- Replace tracks in a playlist
- Reorder tracks in a playlist
- Upload custom playlist cover image
User's Library
- Add, remove, and get tracks on a user's library
- Check if a track is in the signed in user's library
- Add, remove, and get shows (podcasts) on a user's library
Personalization
- Get a user’s top artists and tracks based on calculated affinity
- Get current user’s recently played tracks
Browse
- Get new releases
- Get featured playlists
- Get a list of categories
- Get a category
- Get a category's playlists
- Get recommendations based on seeds
- Get available genre seeds
Follow
- Follow and unfollow users
- Follow and unfollow artists
- Check if the logged in user follows a user or artist
- Follow a playlist
- Unfollow a playlist
- Get followed artists
- Check if users are following a Playlist
Player
- Get a user's available devices
- Get information about the user's current playback
- Get the user's currently playing track
- Transfer a user's playback
- Start/Resume a user's playback
- Pause a user's playback
- Skip user's playback to next track
- Skip user's playback to previous track
- Seek to position in currently playing track
- Set repeat mode on user's playback
- Set volume for user's playback
- Toggle shuffle for user's playback
- Queue a track or an episode
Installation
Install via node (since the requests are made using XMLHttpRequest, you will need a tool like Browserify to run this on a browser):
$ npm install -S spotify-web-api-js
Then, in your javascript file
var Spotify = require('spotify-web-api-js');
var s = new Spotify();
or by making a copy of the src/spotify-web-api.js file
Usage
We recommend you have a look at the documentation to get an overview of the supported
.
The wrapper supports callback functions, as well as Promises (you can also use a polyfill), and Promises/A+ libraries such as Q and when.
First, instantiate the wrapper.
var spotifyApi = new SpotifyWebApi();
If you have an access token, you can set it doing:
spotifyApi.setAccessToken('<here_your_access_token>');
When you set an access token, it will be used for signing your requests. An access token is required for all endpoints.
If you want to use a Promises/A+ library, you can set it:
spotifyApi.setPromiseImplementation(Q);
Here you see how to get basic information using a function like getArtistAlbums:
spotifyApi.getArtistAlbums('43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE', function (err, data) {
if (err) console.error(err);
else console.log('Artist albums', data);
});
spotifyApi.getArtistAlbums('43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Artist albums', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
The promises also expose an abort method that aborts the XMLHttpRequest. This is useful to cancel
requests that were made earlier and could be resolved out-of-sync:
var prev = null;
function onUserInput(queryTerm) {
if (prev !== null) {
prev.abort();
}
prev = spotifyApi.searchTracks(queryTerm, { limit: 5 });
prev.then(
function (data) {
prev = null;
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
}
The functions that fetch data from the API support also an optional JSON object with a set of options, such as the ones regarding pagination. These options will be sent as query parameters:
spotifyApi.getArtistAlbums(
'43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE',
{ limit: 10, offset: 20 },
function (err, data) {
if (err) console.error(err);
else console.log('Artist albums', data);
}
);
spotifyApi
.getArtistAlbums('43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE', { limit: 10, offset: 20 })
.then(
function (data) {
console.log('Album information', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
More examples
Note: The following examples use Promises/Q/when as the return object.
Here you can see more examples of the usage of this wrapper:
spotifyApi.getAlbums(['5U4W9E5WsYb2jUQWePT8Xm', '3KyVcddATClQKIdtaap4bV']).then(
function (data) {
console.log('Albums information', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi.getArtist('2hazSY4Ef3aB9ATXW7F5w3').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Artist information', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi
.getArtists(['2hazSY4Ef3aB9ATXW7F5w3', '6J6yx1t3nwIDyPXk5xa7O8'])
.then(
function (data) {
console.log('Artists information', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi.getArtistAlbums('43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Artist albums', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi.searchTracks('Love').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Search by "Love"', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi.searchArtists('Love').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Search artists by "Love"', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
spotifyApi.searchTracks('artist:Love').then(
function (data) {
console.log('Search tracks by "Love" in the artist name', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
Nesting calls
When you need to make multiple calls to get some dataset, you can take advantage of the Promises to get a cleaner code:
spotifyApi
.getAlbum('5U4W9E5WsYb2jUQWePT8Xm')
.then(function (data) {
return data.tracks.map(function (t) {
return t.id;
});
})
.then(function (trackIds) {
return spotifyApi.getTracks(trackIds);
})
.then(function (tracksInfo) {
console.log(tracksInfo);
})
.catch(function (error) {
console.error(error);
});
spotifyApi
.getArtistAlbums('43ZHCT0cAZBISjO8DG9PnE', { limit: 10 })
.then(function (data) {
return data.albums.map(function (a) {
return a.id;
});
})
.then(function (albums) {
return spotifyApi.getAlbums(albums);
})
.then(function (data) {
console.log(data);
});
Getting user's information
In order to get user's information you need to request a user-signed access token, from either the Implicit Grant or Authorization Code flow. Say for instance you want to get user's playlists. Once you get an access token, set it and fetch the data:
...
var spotifyApi = new SpotifyWebApi();
spotifyApi.setAccessToken('<here_your_access_token>');
spotifyApi.getUserPlaylists('jmperezperez')
.then(function(data) {
console.log('User playlists', data);
}, function(err) {
console.error(err);
});
spotifyApi.getPlaylist('4vHIKV7j4QcZwgzGQcZg1x')
.then(function(data) {
console.log('User playlist', data);
}, function(err) {
console.error(err);
});
Some functions don't need to receive the user's id as a parameter, and will use the
user's information from the access token:
var spotifyApi = new SpotifyWebApi();
spotifyApi.setAccessToken('<here_your_access_token>');
spotifyApi
.getUserPlaylists()
.then(
function (data) {
console.log('User playlists', data);
},
function (err) {
console.error(err);
}
);
Integrated Typescript Typings
Get great code completion for this package using the integrated typescript typings. It includes the complete typings of the Spotify Web Api too, so you'll know both how to the navigate the API as well as the response you are getting.
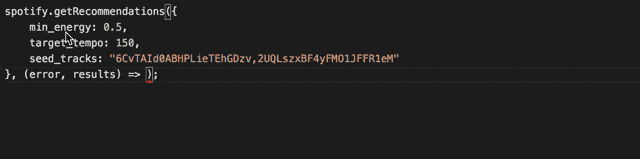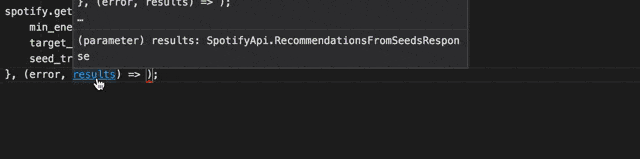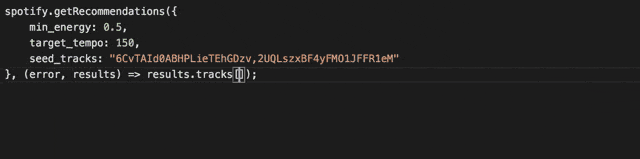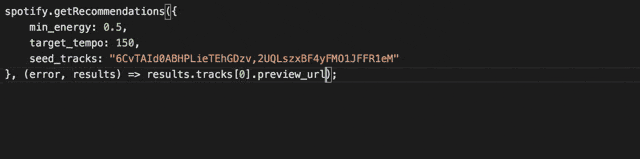
When bundling the library
If you are bundling spotify-web-api-js using e.g. webpack you can include the library and the typings into a typescript file like this:
import SpotifyWebApi from 'spotify-web-api-js';
let spotify = new SpotifyWebApi();
When using the library globally
If you are using the library globally, for example including directly from index.html, include the typings in the top of your typescript file. Typescript will then assume the library is already present globally. Adjust the path to node_modules.
let spotify = new SpotifyWebApi();
Running tests
In order to run the tests, run:
$ npm test
If you want to check out the coverage, run:
$ npm run test:coverage





