
Product
Introducing Socket Fix for Safe, Automated Dependency Upgrades
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.
vue-form-10q
Advanced tools
Form handler component for Vue v2.
NOTE Use v1.0 branch to use this with Vue v1.
View DEMO.
Several installation options are available:
bower install 10q-vue-form.Add the following resources for the component to function correctly.
<!-- Required Javascript -->
<script src="vue.js"></script>
<script src="vue-resource.js"></script>
<script src="[component path]/dist/vue.form.min.js"></script>
Add the component in your vue view.
<!-- Assuming your view app is APP. -->
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template
action="http://some.url.com"
method="POST"
>
<input type="email" v-model="request.email">
<button @click="submit">Submit</button>
<span v-if="isLoading">Loading...</span>
</vform>
</div>
NOTE: inline-template must be present.
List of available props to use in component:
| Prop | Data Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
action | String | Action URL where to send form data. | |
method | String | POST | Request method (i.e. GET or POST). |
headers | Object | Request headers (reference). | |
timeout | Number | Request headers (reference). | |
credentials | Boolean | Flag that indicates if request has credentials (reference). | |
emulate-http | Boolean | Flag that indicates if request should emulate HTTP (reference). | |
emulate-json | Boolean | Flag that indicates if request should emulate JSON (reference). | |
errors | Object | Object | List of default validation rules error messages. |
id | String | Form given ID. | |
key | String | Form given loop key (i.e. in case of being used inside a v-for). | |
response-json | Boolean | false | Forces response to be returned and parsed as JSON. |
response-blob | Boolean | false | Forces response to be returned as Blob. |
Data sent by form should be binded to the request data model. In other words, all the inputs within the form should be binded to request.
As reference, a basic contact form sample:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template action="http://some.url.com">
<label for="name">Name:</label>
<input type="text"
id="name"
v-model="request.name"
/>
<label for="email">Email:</label>
<input type="email"
id="email"
v-model="request.email"
/>
<label for="message">Textarea:</label>
<textarea id="message"
v-model="request.message"
></textarea>
<button @click="submit">Submit</button>
</vform>
</div>
Any response obtained from a request is set to the response data model.
If the following data is found, the form will auto-process the response (json) to facilitate its handling:
{
"error": true,
"message": "Contact information not sent."
}
This response can be displayed in the template like:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<div v-if="hasMessage"
:class="{'with-error': hasError}"
>
{{response.message}}
</div>
</vform>
</div>
Computed properties to use in template:
| Property | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
isLoading | Boolean | Flag that indicates if form is loading, processing or waiting for response. |
hasMessage | Boolean | Flag that indicates if form response returned a message to display. |
hasError | Boolean | Flag that indicates if form response returned as error. |
Another example using Bootstrap:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<div v-show="hasMessage"
class="alert"
:class="{'alert-danger': hasError, 'alert-success': !hasError}"
>
{{response.message}}
</div>
</vform>
</div>
If the following data is found, the form will redirect the current window to the value set in response.redirect:
{
"error": false,
"message": "Information sent.",
"redirect": "http://some.url.com"
}
Form comes with a child component called results. This component will facilitate the handling of data returned by request (thought for searches).
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<label>Search:</label>
<input type="text"
v-model="request.q"
@keyup.enter="submit"
/>
<results inline-template
v-model="response"
fetch-on-ready="true"
clear-on-fetch="false"
>
<div v-show="hasRecords">
<div v-for="record in records">
{{record | json}}
</div>
</div>
</results>
</vform>
</div>
In the example above, results child component is handling search results returned by the response (assuming response contains only results) and it is computing them into a property called records.
NOTE: Results will compute records only if the model is an array.
NOTE: inline-template must be present.
List of available props to use in child component:
| Prop | Data Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
model | Array | Data to compute for results (mostly required). | |
request | Object | If form request is needed to be binded to results. | |
fetch-onready | Boolean | false | Flag that forces form to submit and return response when document is ready. |
clear-on-fetch | Boolean | true | Flag that indicates if records should stack on every submission or not. (used for eager loading) |
Another example:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<results inline-template v-model="response.results">
<div v-for="record in records">
{{record | json}}
</div>
</results>
</vform>
</div>
Form comes with a second child component called input-handler. This component will facilitate the display of errors per input, improving UX.
Example using Bootstrap:
Response:
{
"errors": [
"email": [
"Email is invalid.",
"Fields is required."
],
"name": [
"Too short".
]
]
}
In template:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<input-handler class="form-group"
class-error="has-error"
listen="name"
v-model="response"
>
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="name"
v-model="request.name"
/>
</input-handler>
<input-handler class="form-group"
class-error="has-error"
listen="email"
v-model="response"
>
<label for="email">Email</label>
<input type="email"
class="form-control"
id="email"
v-model="request.email"
/>
</input-handler>
</vform>
</div>
In the example above, the response returned a list of errors per input. input-handler will process the response and if errors are found (response must be passed as v-model), it will add an error class to the input wrapper and will list the erros under the input using a <ul class="errors"> HTML tag.
List of available props to use in child component:
| Prop | Data Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
listen | String | Name of the error key (in response) to listen to. | |
class | String | CSS class to apply to wrapper. (<div>) | |
class-error | String | CSS class to apply to wrapper when errors are available. | |
response | Object | Response to process. (required) | |
validations | String | List of validation rules to apply to input. |
Form comes with a set of validation rules that can be applied to input values prior request. This are set in the validations prop, separated by |.
In the following example, the input will validate that name is not empty (is a required field) and that it has at least 8 characters:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template>
<input-handler class="form-group"
class-error="has-error"
listen="name"
v-model="response"
validations="required|min:8"
>
<label for="name">Name</label>
<input type="text"
class="form-control"
id="name"
v-model="request.name"
/>
</input-handler>
</vform>
</div>
List of available rules to use:
| Rule | Params | Sample | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
required | required | Validates if value is not empty. | |
required_if | 1) comparison field | required_if:email | Validates if value is not empty only if comparison field is not empty. |
email | email | Validates if value has a valid email format. | |
number | number | Validates if value is numeric. | |
min | 1) minimum string length | min:2 | Validates if value's length is not lower than the minimum value set. |
min_number | 1) minimum number | min_number:10 | Validates if value is not lower than the minimum value set. |
max | 1) maximum string length | max:10 | Validates if value's length is not bigger than the maximum value set. |
max_number | 1) maximum number length | max_number:15 | Validates if value is not bigger than the maximum value set. |
between | 1) minimum string length 2) maximum string length | between:5:10 | Validates if value's length is in between the number range set. |
between_number | 1) minimum number 2) maximum number | between_number:1:100 | Validates if value is in between the number range set. |
equals | 1) comparison field | equals:password | Validates if value is the same as comparison field's value. |
url | url | Validates if value has a valid url format. |
Events dispatched by form:
| Event | Data sent | Description |
|---|---|---|
success | Emitted once response is returned and assigned to model response. | |
error | e Error response returned. | Emitted on request error. (Error is thrown to console too). |
complete | Emitted after request completed. (Success or error) | |
invalid | errors List of errors. | Emitted and broadcasted when a validation ocurred. |
Usage example:
<div id="app">
<vform inline-template
@success="eventHandlerMethod"
@error="eventHandlerMethod"
@complete="eventHandlerMethod"
@invalid="eventHandlerMethod"
></vform>
</div>
Copyright (c) 2017 10Quality. Under MIT License.
FAQs
Form component for Vue JS.
The npm package vue-form-10q receives a total of 3 weekly downloads. As such, vue-form-10q popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that vue-form-10q demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Automatically fix and test dependency updates with socket fix—a new CLI tool that turns CVE alerts into safe, automated upgrades.

Security News
CISA denies CVE funding issues amid backlash over a new CVE foundation formed by board members, raising concerns about transparency and program governance.
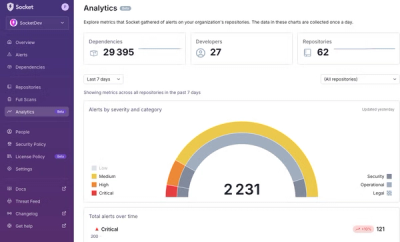
Product
We’re excited to announce a powerful new capability in Socket: historical data and enhanced analytics.