
Product
Announcing Socket Fix 2.0
Socket Fix 2.0 brings targeted CVE remediation, smarter upgrade planning, and broader ecosystem support to help developers get to zero alerts.
CompileTimeObfuscator
Advanced tools
A C# Source Generator for obfuscating string or byte array values using multi-byte xor encryption.
A C# Source Generator for obfuscating string or byte array values using multi-byte xor encryption.
Sample code:
using System;
using System.Buffers;
using System.Text;
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
namespace Sample;
internal static partial class Program
{
private static string PlainText() => "This is a plain string";
[ObfuscatedString("This is an obfuscated string 1")]
private static partial string ObfuscatedText1();
[ObfuscatedString("This is an obfuscated string 2")]
private static partial IMemoryOwner<char> ObfuscatedText2();
private static ReadOnlySpan<byte> PlainBytes() => "This is a plain bytes"u8;
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'T', (byte)'h', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'a', (byte)'n', (byte)' ', (byte)'o', (byte)'b', (byte)'f', (byte)'u', (byte)'s', (byte)'c', (byte)'a', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'d', (byte)' ', (byte)'b', (byte)'y', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'1', })]
private static partial byte[] ObfuscatedBytes1();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'T', (byte)'h', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'i', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'a', (byte)'n', (byte)' ', (byte)'o', (byte)'b', (byte)'f', (byte)'u', (byte)'s', (byte)'c', (byte)'a', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'d', (byte)' ', (byte)'b', (byte)'y', (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)' ', (byte)'2', })]
private static partial IMemoryOwner<byte> ObfuscatedBytes2();
private static void Main()
{
Console.WriteLine(PlainText());
Console.WriteLine(ObfuscatedText1());
using var memoryOwnerChar = ObfuscatedText2();
Console.WriteLine(memoryOwnerChar.Memory.Span.ToString());
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(PlainBytes()));
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(ObfuscatedBytes1()));
using var memoryOwnerByte = ObfuscatedBytes2();
Console.WriteLine(Encoding.UTF8.GetString(memoryOwnerByte.Memory.Span));
}
}
The result of executing the sample code, and the result of strings command indicating that the obfuscation result is not included in a binary:
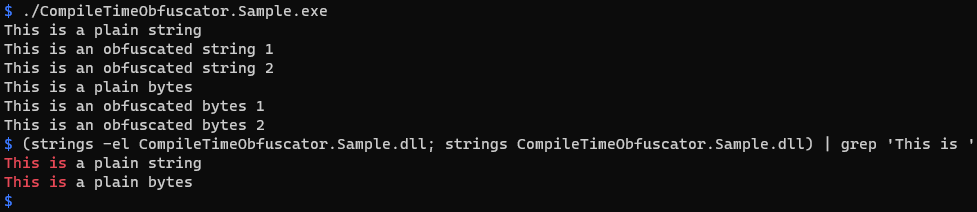
I tested the generator using Visual Studio 2022 Version 17.5.1 and a project using C# 11 and .NET 6.
CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedString and CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedBytes in your source.CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedString can obfuscate a string. The return type of the method can be a string or System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<char>.CompileTimeObfuscator.ObfuscatedString can obfuscate a byte array. The return type of the method can be a byte[] or System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<byte>.IMemoryOwner<T> version if execution efficiency is a priority. string or byte[] versions are wrappers on IMemoryOwner<T> version with additional conversion.IMemoryOwner<T>.Dispose method is called. To configure, add attribute arguments:using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test", KeyLength = 1, ClearBufferWhenDispose = false)]
public static partial string M();
}
The generator generates a following source after initialization:
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
using System;
using System.Buffers;
using System.Diagnostics;
namespace CompileTimeObfuscator;
/// <summary>Obfuscate the specified string to preventing the string from appearing in a metadata. The obfuscated string is deobfuscated at runtime. The method must return <see cref="string"/> or <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> of type <see cref="char"/>.</summary>
[Conditional("COMPILE_TIME_ONLY")]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)]
internal sealed class ObfuscatedStringAttribute: Attribute
{
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ObfuscatedStringAttribute"/> with the specified string.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The string to obfuscate.</param>
internal ObfuscatedStringAttribute(string value)
{
}
/// <summary>Indicates the key length to obfuscate. A default value is 16.</summary>
public int KeyLength = 16;
/// <summary>Indicates whether a deobfuscated buffer will cleared after disposing an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> object. A default value is true.</summary>
public bool ClearBufferWhenDispose = true;
}
/// <summary>Obfuscate the specified bytes to preventing the bytes from appearing in a metadata. The obfuscated bytes is deobfuscated at runtime. The method must return <see cref="byte"/>[] or <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> of type <see cref="byte"/>.</summary>
[Conditional("COMPILE_TIME_ONLY")]
[AttributeUsage(AttributeTargets.Method, AllowMultiple = false, Inherited = false)]
internal sealed class ObfuscatedBytesAttribute: Attribute
{
/// <summary>Initializes a new instance of the <see cref="ObfuscatedBytesAttribute"/> with the specified bytes.</summary>
/// <param name="value">The bytes to obfuscate.</param>
internal ObfuscatedBytesAttribute(byte[] value)
{
}
/// <summary>Indicates the key length to obfuscate. A default value is 16.</summary>
public int KeyLength = 16;
/// <summary>Indicates whether a deobfuscated buffer will cleared after disposing an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> object. A default value is true.</summary>
public bool ClearBufferWhenDispose = true;
}
internal sealed class ClearableBuffer<T> : IMemoryOwner<T>
{
private T[]? _array;
private readonly int _length;
private readonly bool _clearBufferWhenDispose;
internal ClearableBuffer(int length, bool clearBufferWhenDispose)
{
_array = ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Rent(length);
_length = length;
_clearBufferWhenDispose = clearBufferWhenDispose;
}
public void Dispose()
{
if (_array is null) { return; }
// Even if clearArray parameter of ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Return is set to true,
// the array will not be cleared if the array is not returned to the pool.
// Therefore, clear the array manually here.
if (_clearBufferWhenDispose)
{
_array.AsSpan().Fill(default!);
}
ArrayPool<T>.Shared.Return(_array);
_array = null;
}
/// <summary>Returns <see cref="Memory{T}"/> that length is the originally required length. This behavior is different from an <see cref="IMemoryOwner{T}"/> returned from <see cref="MemoryPool{T}.Shared"/>.</summary>
public Memory<T> Memory
{
get
{
if (_array is null) { throw new ObjectDisposedException(GetType().FullName); }
return new Memory<T>(_array, 0, _length);
}
}
}
For a following sample code:
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test")]
public static partial string M1();
}
A generator generates a following code, where key takes a different value for each generation:
// <auto-generated/>
#nullable enable
public partial class C {
public static partial string M1()
{
// The compiler optimize a code if `new byte[]{...}` is converted to ReadOnlySpan<byte>. https://vcsjones.dev/csharp-readonly-span-bytes-static/
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{117,226,34,33,148,30,41,116};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{1,226,71,33,231,30,93,116,226,66,50,253,253,60,3,216};
using var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<char>(obfuscatedValue.Length / 2, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
var span = buffer.Memory.Span;
for (int i = span.Length - 1; i >= 0; i--)
{
byte upper = (byte)(obfuscatedValue[2 * i + 1] ^ key[(2 * i + 1) % key.Length]);
byte lower = (byte)(obfuscatedValue[2 * i + 0] ^ key[(2 * i + 0) % key.Length]);
span[i] = (char)(upper << 8 | lower);
}
return new string(buffer.Memory.Span);
}
}
The same is true when the return type is IMemoryOwner<char> or when obfuscating a byte array instead of a string:
using System.Buffers;
using CompileTimeObfuscator;
public partial class C
{
[ObfuscatedString("test")]
public static partial IMemoryOwner<char> M2();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)'t', })]
public static partial byte[] M3();
[ObfuscatedBytes(new byte[] { (byte)'t', (byte)'e', (byte)'s', (byte)'t', })]
public static partial IMemoryOwner<byte> M4();
}
// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial global::System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<char> M2()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{92,228,183,152,126,175,18,190};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{40,228,210,152,13,175,102,190,199,226,250,53,66,54,118,164};
var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<char>(obfuscatedValue.Length / 2, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer;
}
}
// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial byte[] M3()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{26,241,65,188};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{110,148,50,200,144,242,236,138,214,152,182,90,190,251,180,67};
using var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<byte>(obfuscatedValue.Length, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer.Memory.ToArray();
}
}
// omitted
public partial class C {
public static partial global::System.Buffers.IMemoryOwner<byte> M4()
{
// omitted
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> obfuscatedValue = new byte[]{70,203,42,46};
System.ReadOnlySpan<byte> key = new byte[]{50,174,89,90,38,90,34,100,22,82,253,238,231,239,130,127};
var buffer = new CompileTimeObfuscator.ClearableBuffer<byte>(obfuscatedValue.Length, clearBufferWhenDispose: true);
// omitted
return buffer;
}
}
Currently, a generator generates a source file for each method.
FAQs
A C# Source Generator for obfuscating string or byte array values using multi-byte xor encryption.
We found that compiletimeobfuscator demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Socket Fix 2.0 brings targeted CVE remediation, smarter upgrade planning, and broader ecosystem support to help developers get to zero alerts.

Security News
Socket CEO Feross Aboukhadijeh joins Risky Business Weekly to unpack recent npm phishing attacks, their limited impact, and the risks if attackers get smarter.

Product
Socket’s new Tier 1 Reachability filters out up to 80% of irrelevant CVEs, so security teams can focus on the vulnerabilities that matter.