
Research
/Security News
10 npm Typosquatted Packages Deploy Multi-Stage Credential Harvester
Socket researchers found 10 typosquatted npm packages that auto-run on install, show fake CAPTCHAs, fingerprint by IP, and deploy a credential stealer.

AilingBot - One-stop solution to empower your IM bot with AI.
AilingBot is an open-source engineering development framework and an all-in-one solution for integrating AI models into IM chatbots. With AilingBot, you can:
Below is a guide on how to quickly start an AI chatbot based on the command-line interface using AilingBot. The effect is shown in the following figure:

💡 First, you need to have an OpenAI API key. If you don't have one, refer to relevant materials on the Internet to obtain it.
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -it --rm \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key} \
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot chat
pip install ailingbot
ailingbot init --silence --overwrite
This will create a file called settings.toml in the current directory, which is the configuration file for AilingBot.
Next, modify the necessary configurations. To start the bot, only one configuration is needed. Find the following
section in settings.toml:
[policy.llm]
_type = "openai"
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
openai_api_key = ""
temperature = 0
Change the value of openai_api_key to your actual OpenAI API key.
Start the chatbot with the following command:
ailingbot chat
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -it --rm \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key} \
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot api
pip install ailingbot
Same as starting the command line bot.
Start the bot using the following command:
ailingbot api
Now, enter http://localhost:8080/docs in your browser to see the API documentation. (If it is not a local start,
please enter http://{your public IP}:8080/docs)
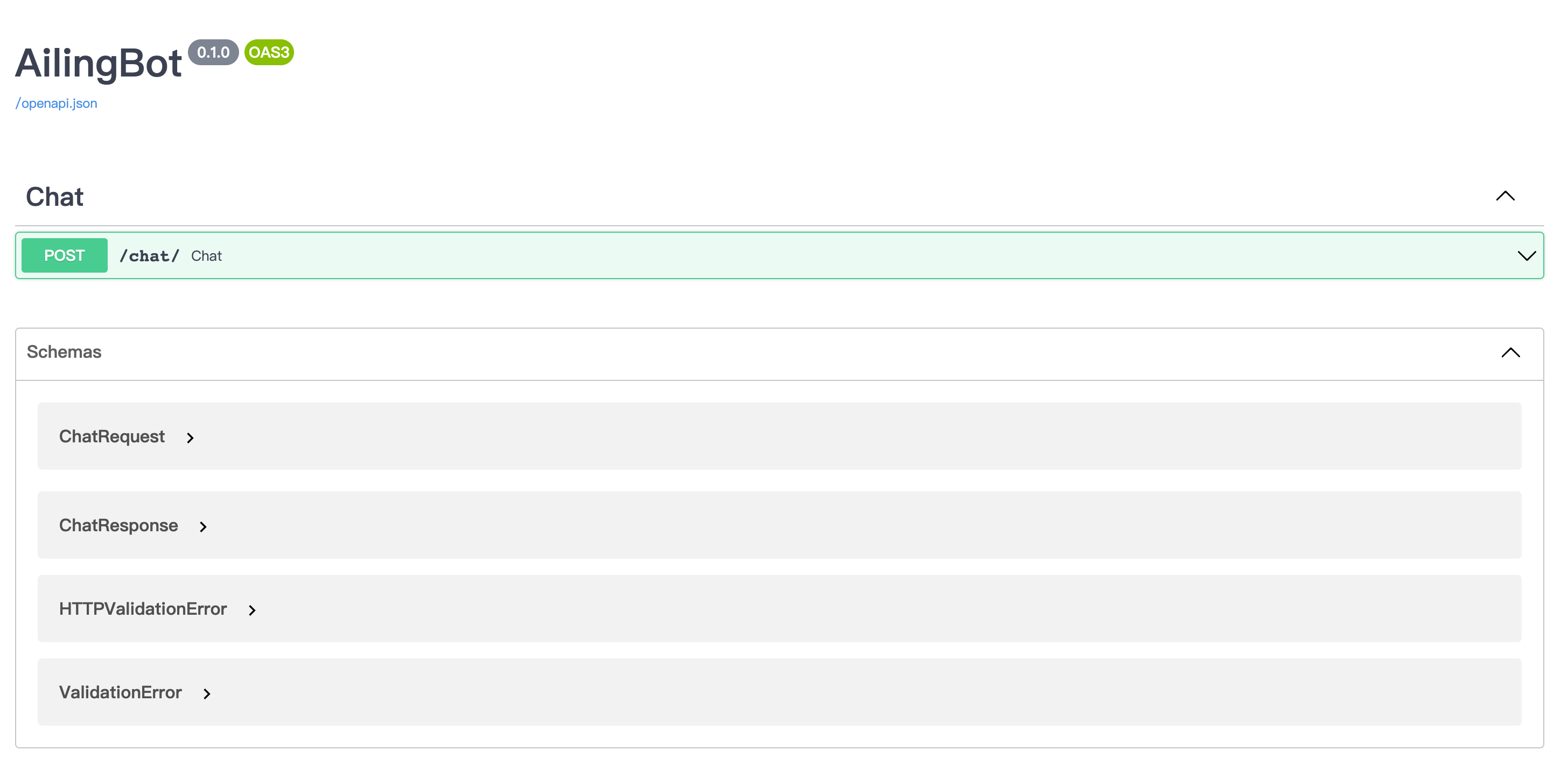
Here is an example request:
curl -X 'POST' \
'http://localhost:8080/chat/' \
-H 'accept: application/json' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
-d '{
"text": "你好"
}'
And the response:
{
"type": "text",
"conversation_id": "default_conversation",
"uuid": "afb35218-2978-404a-ab39-72a9db6f303b",
"ack_uuid": "3f09933c-e577-49a5-8f56-fa328daa136f",
"receiver_id": "anonymous",
"scope": "user",
"meta": {},
"echo": {},
"text": "你好!很高兴和你聊天。有什么我可以帮助你的吗?",
"reason": null,
"suggestion": null
}
Here's a guide on how to quickly integrate the chatbot with WeChat Work.
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -d \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__NAME=conversation \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__HISTORY_SIZE=5 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key
} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__NAME=wechatwork \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__CORPID={your WeChat Work robot's corpid} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__CORPSECRET={
your WeChat Work robot's corpsecret} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__AGENTID={your WeChat Work robot's agentid} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__TOKEN={
your WeChat Work robot's webhook token} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__AES_KEY={your WeChat Work robot's webhook aes_key} \
-p 8080: 8080
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot serve
pip install ailingbot
ailingbot init --silence --overwrite
Open settings.toml, and fill in the following section with your WeChat Work robot's real information:
[channel]
name = "wechatwork"
corpid = "" # Fill in with real information
corpsecret = "" # Fill in with real information
agentid = 0 # Fill in with real information
token = "" # Fill in with real information
aes_key = "" # Fill in with real information
In the llm section, fill in your OpenAI API Key:
[policy.llm]
_type = "openai"
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo"
openai_api_key = "" # Fill in with your real OpenAI API Key here
temperature = 0
ailingbot serve
Finally, we need to go to the WeChat Work admin console to configure the webhook address so that WeChat Work knows to
forward the received user messages to our webhook.
The webhook URL is: http(s)://your_public_IP:8080/webhook/wechatwork/event/
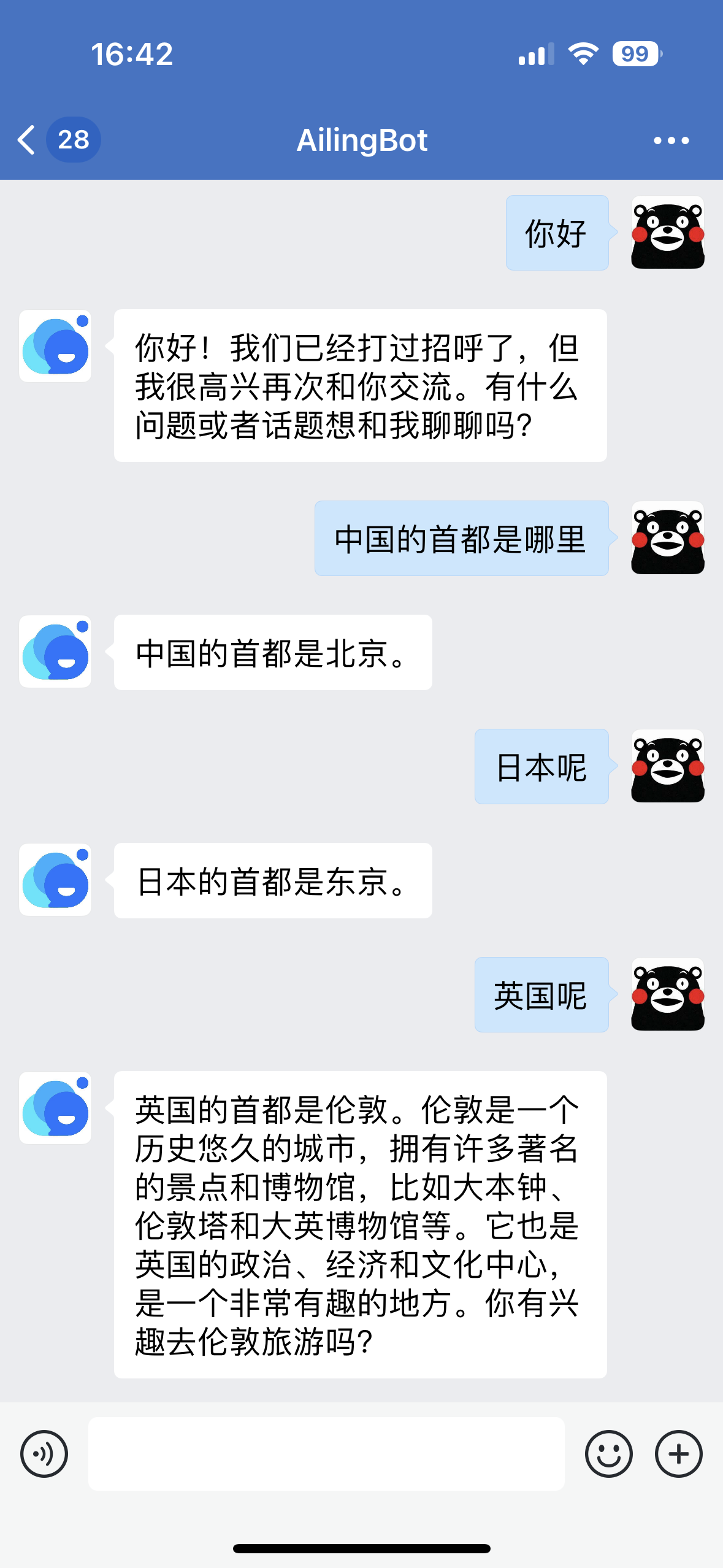
After completing the above configuration, you can find the chatbot in WeChat Work and start chatting:
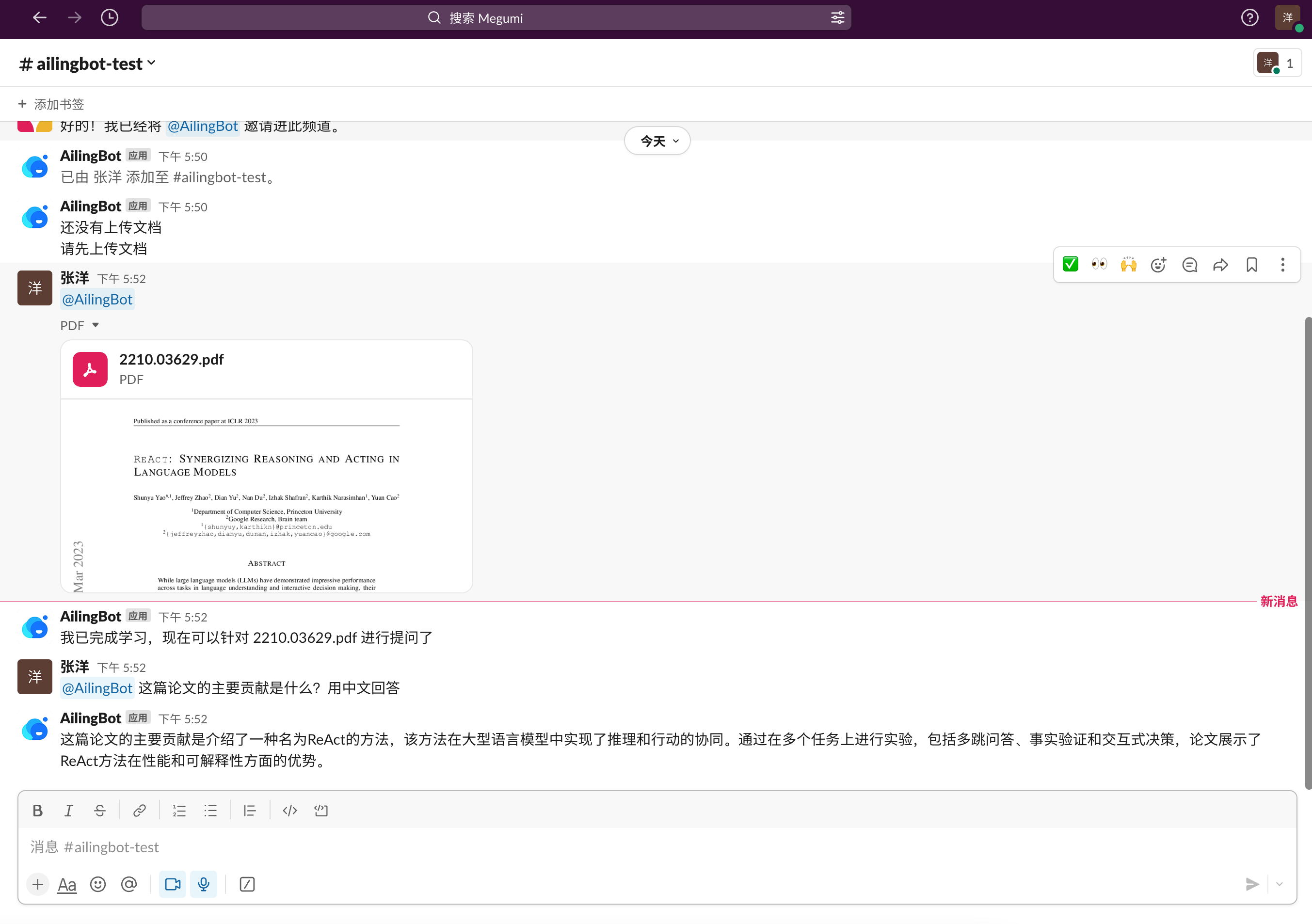
Here's a guide on how to quickly integrate the chatbot with Feishu and enable a new conversation policy: uploading documents and performing knowledge-based question answering on them.
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -d \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__NAME=document_qa \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_SIZE=1000 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_OVERLAP=0 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key} \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__MODEL_NAME=gpt-3.5-turbo-16k \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__NAME=feishu \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__APP_ID={your Feishu robot's app id} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__APP_SECRET={your Feishu robot's app secret} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__VERIFICATION_TOKEN={your Feishu robot's webhook verification token} \
-p 8080:8080
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot serve
pip install ailingbot
ailingbot init --silence --overwrite
Open settings.toml, and change the channel section to the following, filling in your Feishu robot's real
information:
[channel]
name = "feishu"
app_id = "" # Fill in with real information
app_secret = "" # Fill in with real information
verification_token = "" # Fill in with real information
Replace the policy section with the following document QA policy:
[policy]
name = "document_qa"
chunk_size = 1000
chunk_overlap = 5
Finally, it is recommended to use the 16k model when using the document QA policy. Therefore,
change policy.llm.model_name to the following configuration:
[policy.llm]
_type = "openai"
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo-16k" # Change to gpt-3.5-turbo-16k
openai_api_key = "" # Fill in with real information
temperature = 0
ailingbot serve
Finally, we need to go to the Feishu admin console to configure the webhook address.
The webhook URL for Feishu is: http(s)://your_public_IP:8080/webhook/feishu/event/
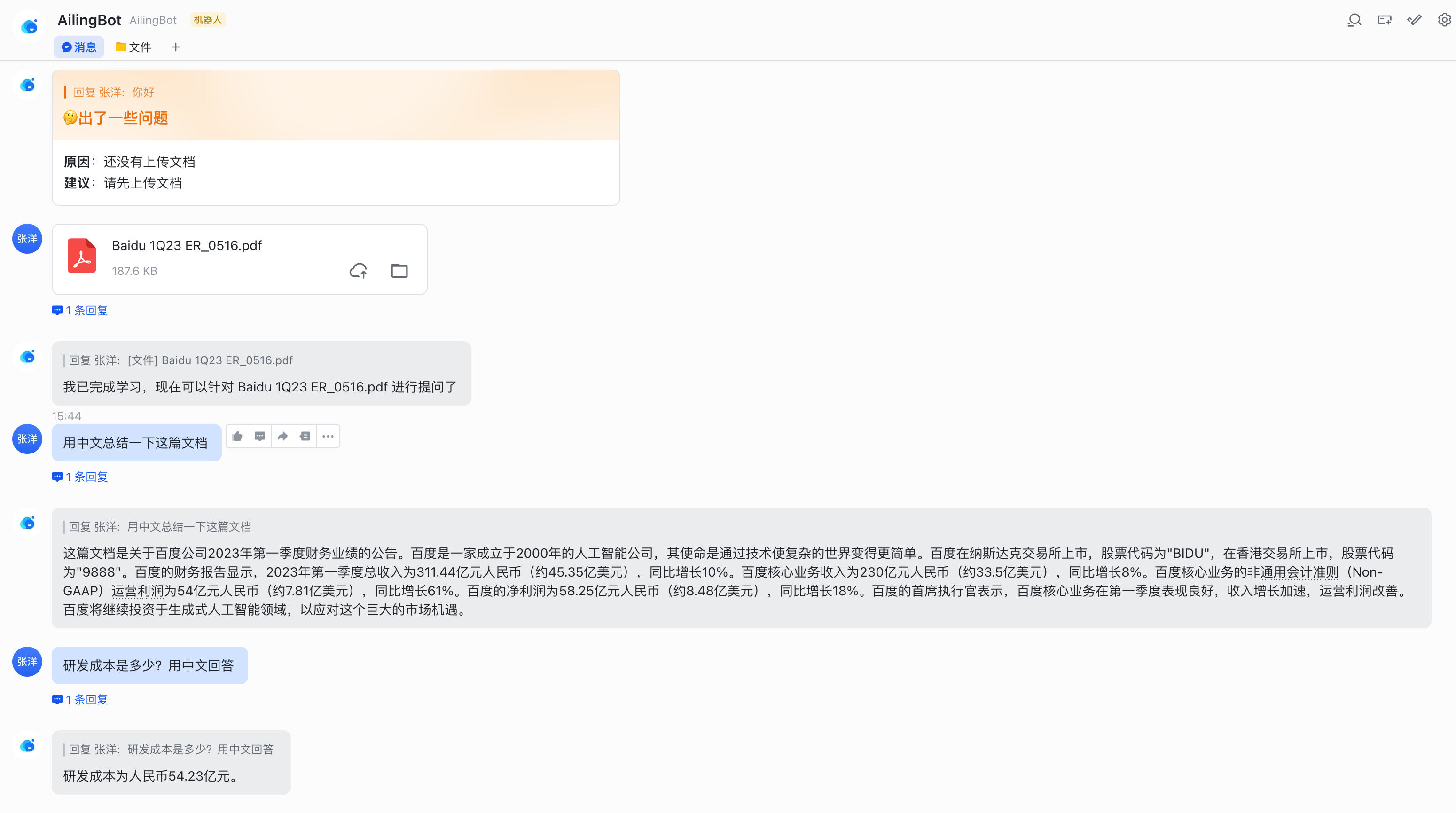
After completing the above configuration, you can find the chatbot in Feishu and start chatting:
Here's a guide on how to quickly integrate the chatbot with DingTalk.
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -d \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__NAME=conversation \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__HISTORY_SIZE=5 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__NAME=dingtalk \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__APP_KEY={your DingTalk robot's app key} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__APP_SECRET={your DingTalk robot's app secret} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__ROBOT_CODE={your DingTalk robot's robot code} \
-p 8080:8080
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot serve
pip install ailingbot
ailingbot init --silence --overwrite
Open settings.toml, and change the channel section to the following, filling in your DingTalk robot's real
information:
[channel]
name = "dingtalk"
app_key = "" # Fill in with real information
app_secret = "" # Fill in with real information
robot_code = "" # Fill in with real information
ailingbot serve
Finally, we need to go to the DingTalk admin console to configure the webhook address.
The webhook URL for DingTalk is: http(s)://your_public_IP:8080/webhook/dingtalk/event/
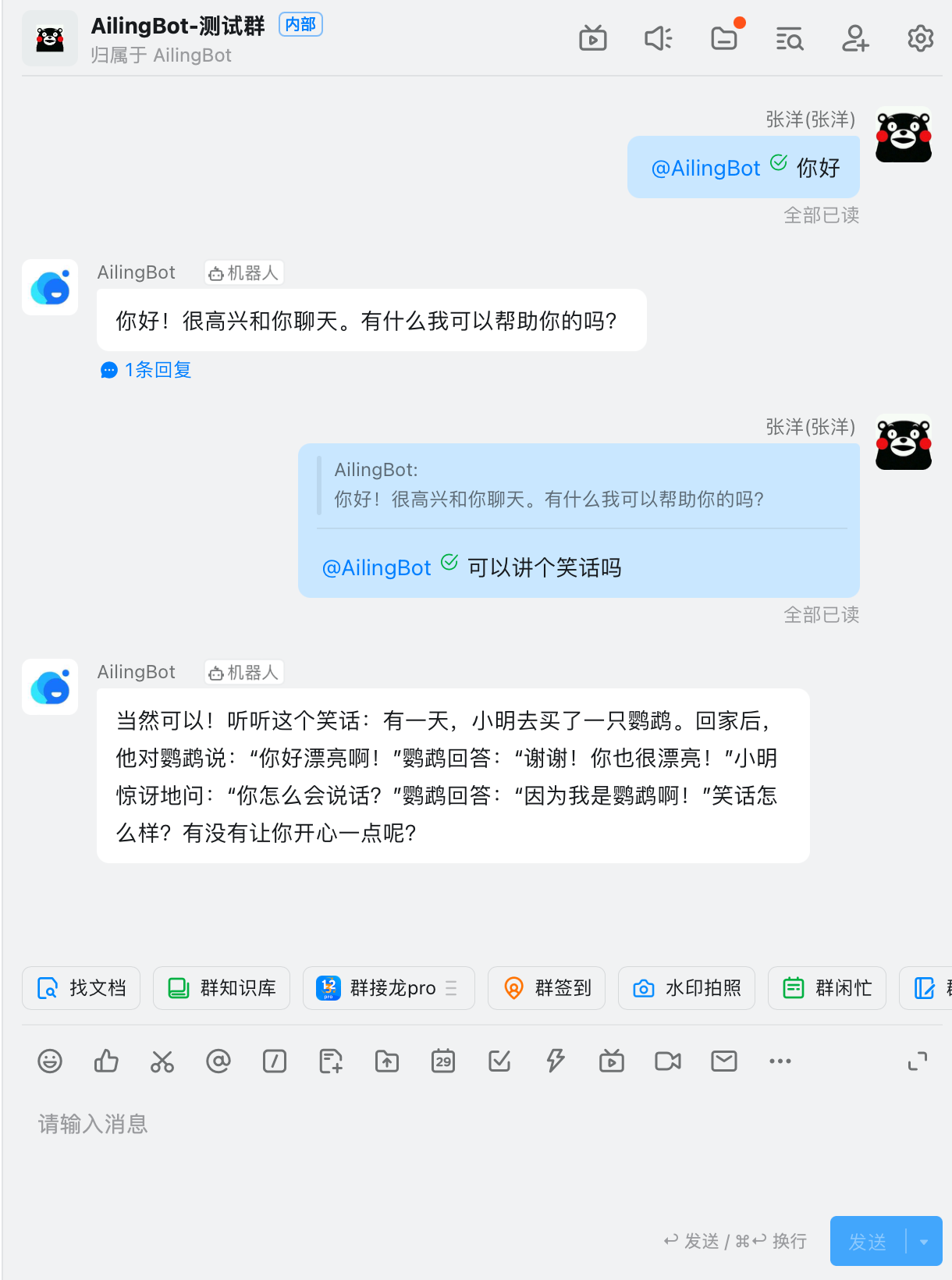
After completing the above configuration, you can find the chatbot in DingTalk and start chatting:
Here's a guide on how to quickly integrate the chatbot with Slack and enable a new conversation policy: uploading documents and performing knowledge-based question answering on them.
git clone https://github.com/ericzhang-cn/ailingbot.git ailingbot
cd ailingbot
docker build -t ailingbot .
docker run -d \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__NAME=document_qa \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_SIZE=1000 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_OVERLAP=0 \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__OPENAI_API_KEY={your OpenAI API key} \
-e AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__MODEL_NAME=gpt-3.5-turbo-16k \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__NAME=slack \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__VERIFICATION_TOKEN={your Slack App webhook verification token} \
-e AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__OAUTH_TOKEN={your Slack App oauth token} \
-p 8080:8080
ailingbot poetry run ailingbot serve
pip install ailingbot
ailingbot init --silence --overwrite
Open settings.toml, and change the channel section to the following, filling in your Slack robot's real information:
[channel]
name = "slack"
verification_token = "" # Fill in with real information
oauth_token = "" # Fill in with real information
Replace the policy section with the following document QA policy:
[policy]
name = "document_qa"
chunk_size = 1000
chunk_overlap = 5
Finally, it is recommended to use the 16k model when using the document QA policy. Therefore,
change policy.llm.model_name to the following configuration:
[policy.llm]
_type = "openai"
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo-16k" # Change to gpt-3.5-turbo-16k
openai_api_key = "" # Fill in with real information
temperature = 0
ailingbot serve
Finally, we need to go to the Slack admin console to configure the webhook address.
The webhook URL for Slack is: http(s)://your_public_IP:8080/webhook/slack/event/
After completing the above configuration, you can find the chatbot in Slack and start chatting:
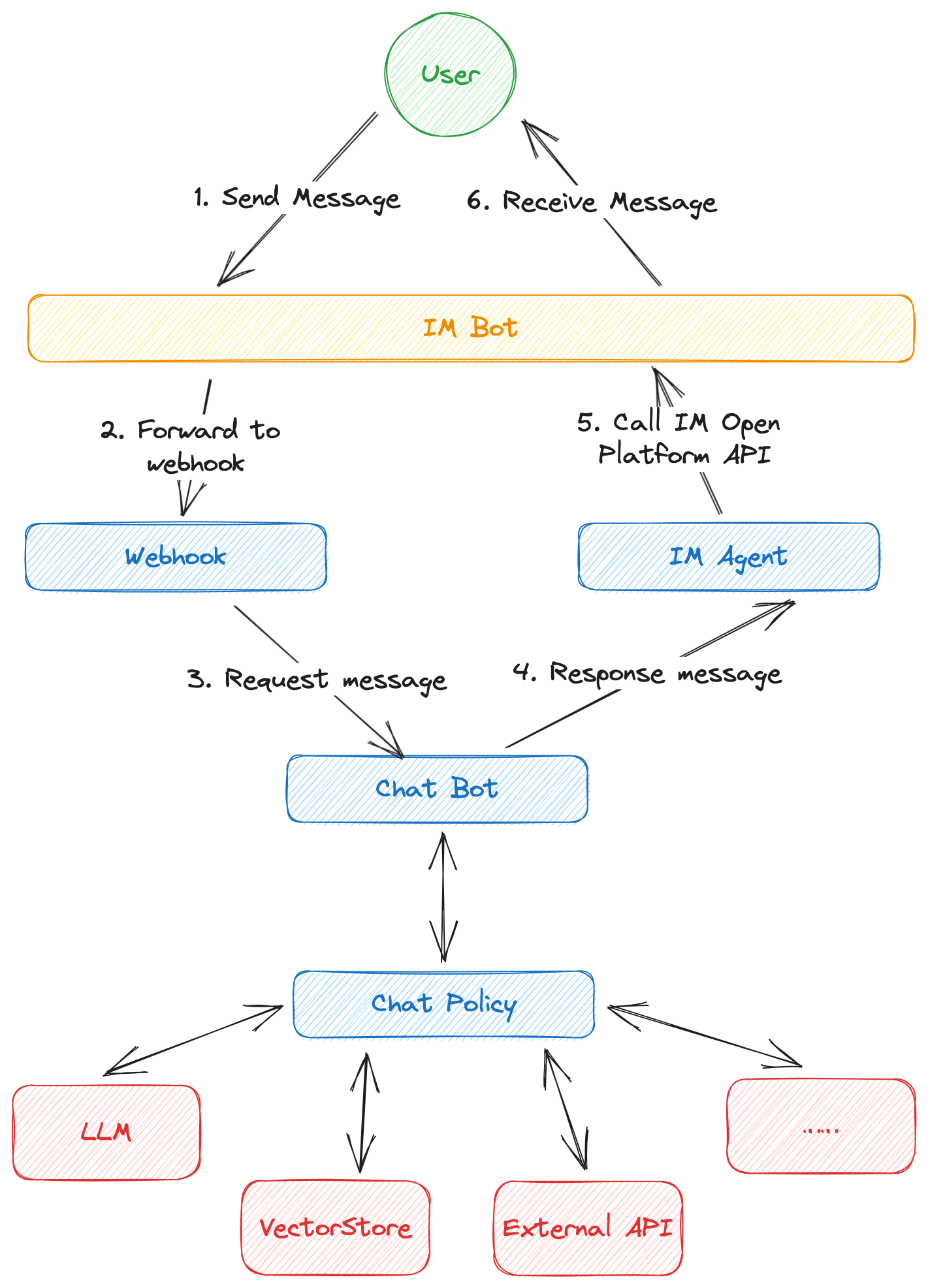
The main processing flow of AilingBot is as follows:
AilingBot can be configured in two ways:
settings.toml in the current directory as the configuration file
in TOML format. Please refer to the following section for specific configuration items.💡 Both configuration files and environment variables can be used together. If a configuration item exists in both, the environment variable takes precedence.
All configurations have the following mappings between TOML keys and environment variables:
AILINGBOT_.__ are used as separators between levels.For example:
some_conf is AILINGBOT_SOME_CONF.some_conf.conf_1 is AILINGBOT_SOME_CONF__CONF_1.some_conf.conf_1.subconf is AILINGBOT_SOME_CONF__CONF_1__SUBCONF.| Configuration Item | Description | TOML | Environment Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Language | Language code (Reference: http://www.lingoes.net/en/translator/langcode.htm) | lang | AILINGBOT_LANG |
| Timezone | Timezone code (Reference: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_tz_database_time_zones) | tz | AILINGBOT_TZ |
| Policy Name | Predefined policy name or complete policy class path | policy.name | AILINGBOT_POLICY__NAME |
| Channel Name | Predefined channel name | channel.name | AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__NAME |
| Webhook Path | Complete class path of non-predefined channel webhook | channel.webhook_name | AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__WEBHOOK_NAME |
| Agent Path | Complete class path of non-predefined channel agent | channel.agent_name | AILINGBOT_CHANNEL__AGENT_NAME |
| Uvicorn Config | All uvicorn configurations (Reference: uvicorn settings). These configurations will be passed to uvicorn | uvicorn.* | AILINGBOT_UVICORN__* |
Configuration example:
lang = "zh_CN"
tz = "Asia/Shanghai"
[policy]
name = "conversation"
# More policy configurations
[channel]
name = "wechatwork"
# More channel configurations
[uvicorn]
host = "0.0.0.0"
port = 8080
Conversation uses LangChain's Conversation as the policy, which enables direct interaction with LLM and has a conversation history context, enabling multi-turn conversations.
| Configuration Item | Description | TOML | Environment Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| History Size | Indicates how many rounds of historical conversations to keep | policy.history_size | AILINGBOT_POLICY__HISTORY_SIZE |
Configuration example:
# Use the conversation policy and keep 5 rounds of historical conversations
[policy]
name = "conversation"
history_size = 5
Document_qa uses LangChain's Stuff as the policy. Users can upload a document and then ask questions based on the document content.
| Configuration Item | Description | TOML | Environment Variable |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chunk Size | Corresponds to LangChain Splitter's chunk_size | policy.chunk_size | AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_SIZE |
| Chunk Overlap | Corresponds to LangChain Splitter's chunk_overlap | policy.chunk_overlap | AILINGBOT_POLICY__CHUNK_OVERLAP |
Configuration example:
# Use the document_qa policy, with chunk_size and chunk_overlap set to 1000 and 0, respectively
[policy]
name = "document_qa"
chunk_size = 1000
chunk_overlap = 0
The model configuration is consistent with LangChain. The following is an example.
[policy.llm]
_type = "openai" # Corresponding environment variable: AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM___TYPE
model_name = "gpt-3.5-turbo" # Corresponding environment variable: AILINGBOT_POLICY__LLM__MODEL_NAME
openai_api_key = "sk-pd8I'm sorry, it seems like your message got cut off. Can you please provide me with more information or clarify your request?
The init command generates a configuration file settings.toml in the current directory. By default, the user will be
prompted interactively. You can use the --silence option to generate the configuration file directly using default
settings.
Usage: ailingbot init [OPTIONS]
Initialize the AilingBot environment.
Options:
--silence Without asking the user.
--overwrite Overwrite existing file if a file with the same name already
exists.
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| --silence | Generate the default configuration directly without asking the user. | Flag | |
| --overwrite | Allow overwriting the settings.toml file in the current directory. | Flag |
The config command reads the current environment configuration (including the configuration file and environment
variables) and merges them.
Usage: ailingbot config [OPTIONS]
Show current configuration information.
Options:
-k, --config-key TEXT Configuration key.
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| -k, --config-key | Configuration key | String | If not passed, the complete configuration information will be displayed. |
The chat command starts an interactive command-line bot for testing the current chat policy.
Usage: ailingbot chat [OPTIONS]
Start an interactive bot conversation environment.
Options:
--debug Enable debug mode.
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| --debug | Enable debug mode | Flag | The debug mode will output more information, such as the prompt. |
The serve command starts a Webhook HTTP server for interacting with specific IM.
Usage: ailingbot serve [OPTIONS]
Run webhook server to receive events.
Options:
--log-level [TRACE|DEBUG|INFO|SUCCESS|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]
The minimum severity level from which logged
messages should be sent to(read from
environment variable AILINGBOT_LOG_LEVEL if
is not passed into). [default: TRACE]
--log-file TEXT STDOUT, STDERR, or file path(read from
environment variable AILINGBOT_LOG_FILE if
is not passed into). [default: STDERR]
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| --log-level | The minimum severity level from which logged messages should be sent to. | String | By default, all log levels will be displayed (TRACE). |
| --log-file | The location where logs are output. | String | By default, logs will be output to standard error (STDERR). |
The api command starts the API HTTP server.
Usage: ailingbot api [OPTIONS]
Run endpoint server.
Options:
--log-level [TRACE|DEBUG|INFO|SUCCESS|WARNING|ERROR|CRITICAL]
The minimum severity level from which logged
messages should be sent to(read from
environment variable AILINGBOT_LOG_LEVEL if
is not passed into). [default: TRACE]
--log-file TEXT STDOUT, STDERR, or file path(read from
environment variable AILINGBOT_LOG_FILE if
is not passed into). [default: STDERR]
--help Show this message and exit.
| Option | Description | Type | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|
| --log-level | Display log level, which will display logs at this level and above | String | By default, all levels are displayed (TRACE) |
| --log-file | Log output location | String | By default, logs are printed to standard error (STDERR) |
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
document_qa
policy cannot be used for WeChat Work.FAQs
An all-in-one solution to empower your IM bot with AI.
We found that ailingbot demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
/Security News
Socket researchers found 10 typosquatted npm packages that auto-run on install, show fake CAPTCHAs, fingerprint by IP, and deploy a credential stealer.

Product
Socket Firewall Enterprise is now available with flexible deployment, configurable policies, and expanded language support.

Security News
Open source dashboard CNAPulse tracks CVE Numbering Authorities’ publishing activity, highlighting trends and transparency across the CVE ecosystem.