
Security News
AGENTS.md Gains Traction as an Open Format for AI Coding Agents
AGENTS.md is a fast-growing open format giving AI coding agents a shared, predictable way to understand project setup, style, and workflows.
High Availability (HA) DAG Utility
<<<<<<< before updating
This library provides an operator called HighAvailabilityOperator, which inherits from PythonSensor and runs a user-provided python_callable.
The return value can trigger the following actions:
| Return | Result | Current DAGrun End State |
|---|---|---|
(PASS, RETRIGGER) | Retrigger the same DAG to run again | pass |
(PASS, STOP) | Finish the DAG, until its next scheduled run | pass |
(FAIL, RETRIGGER) | Retrigger the same DAG to run again | fail |
(FAIL, STOP) | Finish the DAG, until its next scheduled run | fail |
(*, CONTINUE) | Continue to run the Sensor | N/A |
=======
after updating [!NOTE] Note: if the sensor times out, the behavior matches
(Result.PASS, Action.RETRIGGER).
Arguments to HighAvailabilityOperator can be used to configure finishing behavior outside of the callable:
runtime: A timedelta or int (seconds). The operator will turn off cleanly after dag.start_date + runtime ((PASS, STOP))endtime: A time or str (isoformat time). The operator will turn off cleanly after today + endtime ((PASS, STOP))maxretrigger: An integer. The operator will turn off after maxretrigger retriggers ((<previous status, STOP))[!NOTE] These can be configured as arguments to
HighAvailabilityOperator, and will be automatically included as DAG Params. This also allows them to be overridden by the DAG Config during a manual run. There is also aforce-runoption when running the DAG manually, which will cause theHighAvailabilityOperatorto ignore the above 3 limiters.
Consider the following DAG:
with DAG(
dag_id="test-high-availability",
description="Test HA Operator",
schedule=timedelta(days=1),
start_date=datetime(2024, 1, 1),
catchup=False,
):
ha = HighAvailabilityOperator(
task_id="ha",
timeout=30,
poke_interval=5,
python_callable=lambda **kwargs: choice(
(
(Result.PASS, Action.CONTINUE),
(Result.PASS, Action.RETRIGGER),
(Result.PASS, Action.STOP),
(Result.FAIL, Action.CONTINUE),
(Result.FAIL, Action.RETRIGGER),
(Result.FAIL, Action.STOP),
)
),
)
pre = PythonOperator(task_id="pre", python_callable=lambda **kwargs: "test")
pre >> ha
retrigger_fail = PythonOperator(task_id="retrigger_fail", python_callable=lambda **kwargs: "test")
ha.retrigger_fail >> retrigger_fail
stop_fail = PythonOperator(task_id="stop_fail", python_callable=lambda **kwargs: fail_, trigger_rule="all_failed")
ha.stop_fail >> stop_fail
retrigger_pass = PythonOperator(task_id="retrigger_pass", python_callable=lambda **kwargs: "test")
ha.retrigger_pass >> retrigger_pass
stop_pass = PythonOperator(task_id="stop_pass", python_callable=lambda **kwargs: "test")
ha.stop_pass >> stop_pass
This produces a DAG with the following topology:
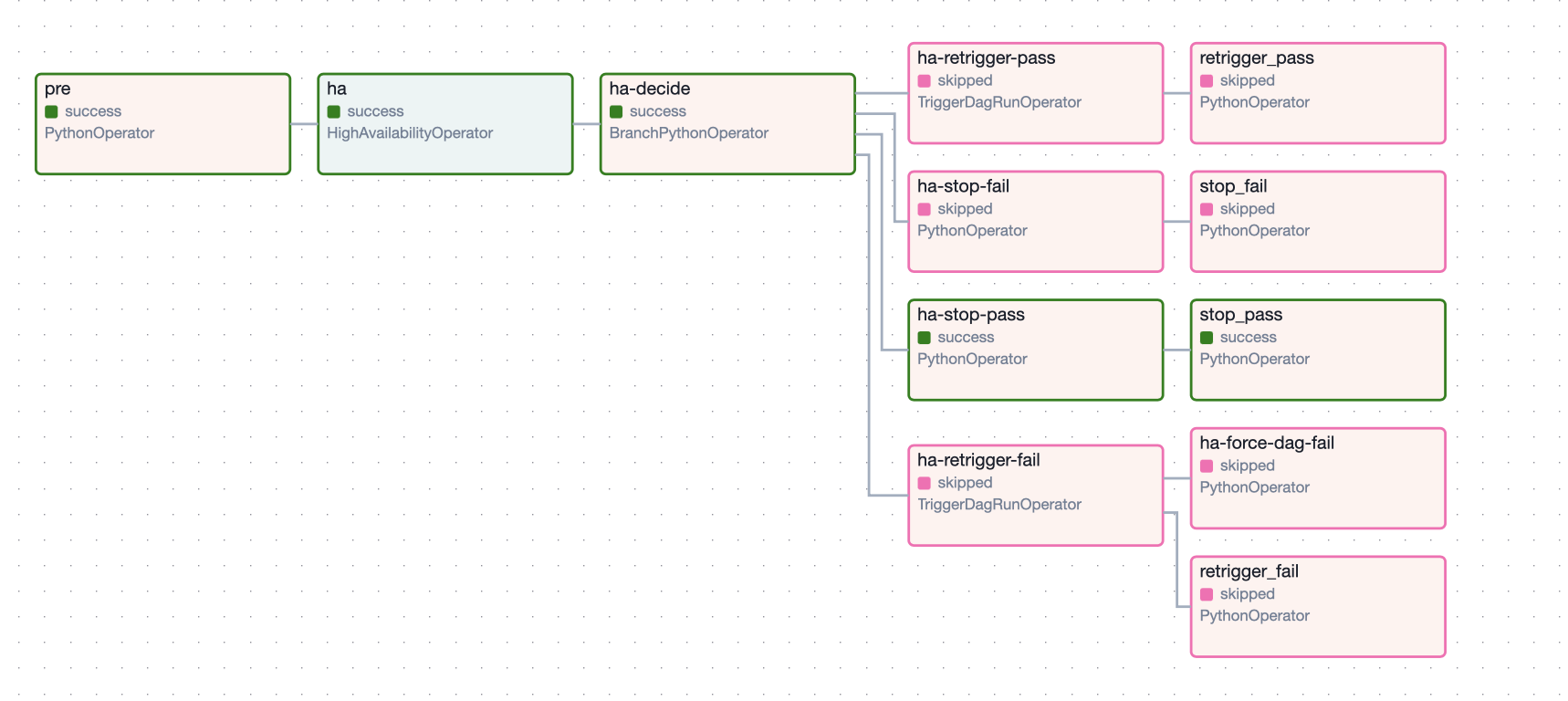
This DAG exhibits cool behavior.
If the check returns CONTINUE, the DAG will continue to run the sensor.
If the check returns RETRIGGER or the interval elapses, the DAG will re-trigger itself and finish.
If the check returns STOP, the DAG will finish and not retrigger itself.
If the check returns PASS, the current DAG run will end in a successful state.
If the check returns FAIL, the current DAG run will end in a failed state.
This allows the one to build "always-on" DAGs without having individual long blocking tasks.
This library is used to build airflow-supervisor, which uses supervisor as a process-monitor while checking and restarting jobs via airflow-ha.
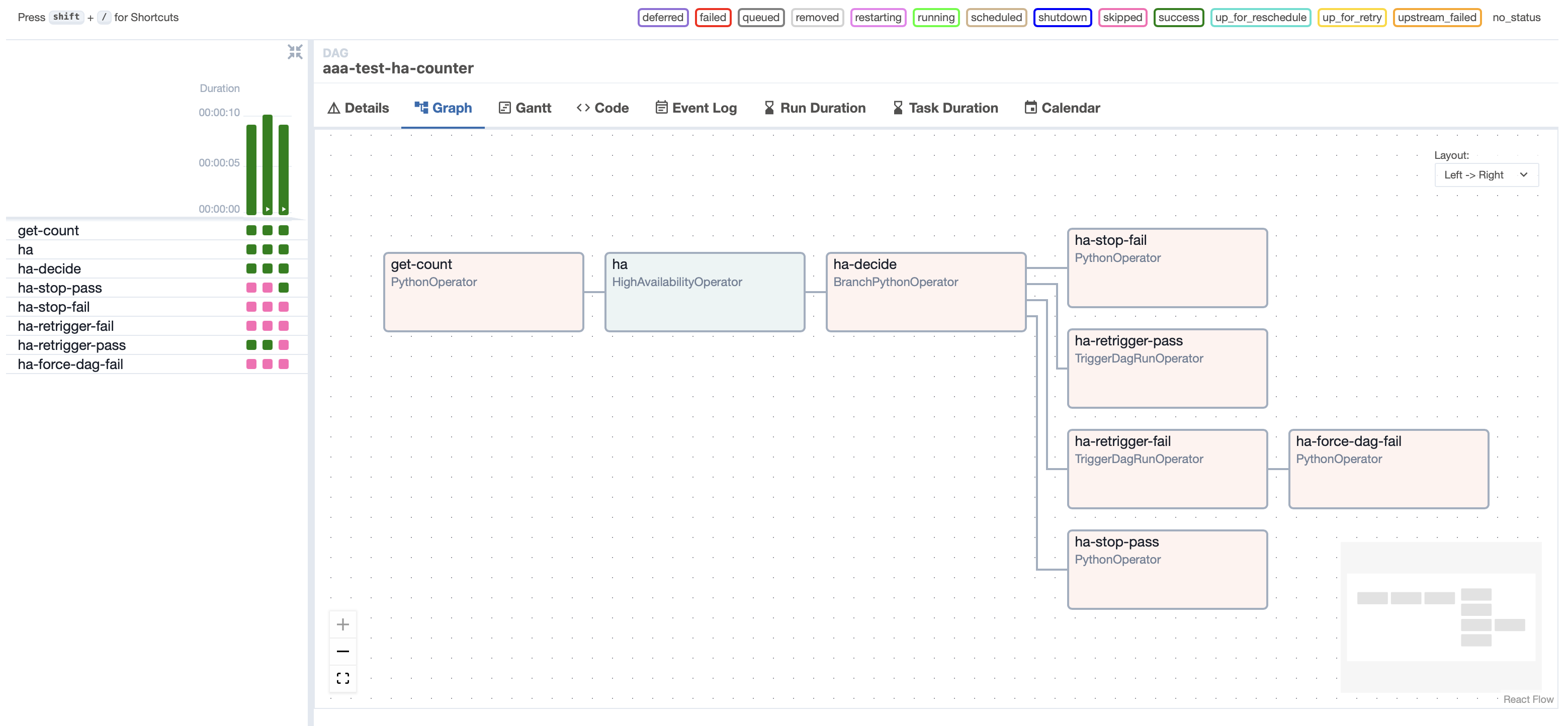
You can also use this library to build recursive DAGs - or "Cyclic DAGs", despite the oxymoronic name.
The following code makes a DAG that triggers itself with some decrementing counter, starting with value 3:
with DAG(
dag_id="test-ha-counter",
description="Test HA Countdown",
schedule=timedelta(days=1),
start_date=datetime(2024, 1, 1),
catchup=False,
):
def _get_count(**kwargs):
# The default is 3
return kwargs['dag_run'].conf.get('counter', 3) - 1
get_count = PythonOperator(task_id="get-count", python_callable=_get_count)
def _keep_counting(**kwargs):
count = kwargs["task_instance"].xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="get-count")
return (Result.PASS, Action.RETRIGGER) if count > 0 else (Result.PASS, Action.STOP) if count == 0 else (Result.FAIL, Action.STOP)
keep_counting = HighAvailabilityOperator(
task_id="ha",
timeout=30,
poke_interval=5,
python_callable=_keep_counting,
pass_trigger_kwargs={"conf": '''{"counter": {{ ti.xcom_pull(key="return_value", task_ids="get-count") }}}'''},
)
get_count >> keep_counting
This software is licensed under the Apache 2.0 license. See the LICENSE file for details.
FAQs
High Availability (HA) DAG Utility
We found that airflow-ha demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
AGENTS.md is a fast-growing open format giving AI coding agents a shared, predictable way to understand project setup, style, and workflows.

Security News
/Research
Malicious npm package impersonates Nodemailer and drains wallets by hijacking crypto transactions across multiple blockchains.

Security News
This episode explores the hard problem of reachability analysis, from static analysis limits to handling dynamic languages and massive dependency trees.