
Research
wget to Wipeout: Malicious Go Modules Fetch Destructive Payload
Socket's research uncovers three dangerous Go modules that contain obfuscated disk-wiping malware, threatening complete data loss.
Providing the top-performing algorithms from the Brain Tumor Segmentation (BraTS) challenges, through an easy-to-use Python API powered by Docker.
With a Python 3.8+ environment, you can install brats directly from PyPI:
pip install brats
[!IMPORTANT]
To runbrats, you require a Docker installation.
Many algorithms also require GPU support (NVIDIA Docker).
In case you do not have access to a CUDA-capable GPU, the overview tables in the Available Algorithms and Usage section indicate which algorithms are CPU compatible.
Adult Glioma Segmentation on pre-treatment brain MRI exams.
from brats import AdultGliomaPreTreatmentSegmenter
from brats.constants import AdultGliomaPreTreatmentAlgorithms
segmenter = AdultGliomaPreTreatmentSegmenter(algorithm=AdultGliomaPreTreatmentAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm of 2023 will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Note: If you're interested in Adult Glioma Segmentation, the BrainLes GlioMODA package may also be of interest.
Class: brats.AdultGliomaPreTreatmentSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2023: Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 1st | André Ferreira, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Andriy Myronenko, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Fadillah Adamsyah Maani, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_3 |
Adult Glioma Segmentation on post-Treatment brain MRI exams.
from brats import AdultGliomaPostTreatmentSegmenter
from brats.constants import AdultGliomaPostTreatmentAlgorithms
segmenter = AdultGliomaPostTreatmentSegmenter(algorithm=AdultGliomaPostTreatmentAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm of 2024 will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.AdultGliomaPostTreatmentSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2024: Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | André Ferreira, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | Heejong Kim, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Adrian Celaya | N/A | ✅ | BraTS24_3 |
Adult Glioma Segmentation on brain MRI exams in Sub-Sahara-Africa patient population.
from brats import AfricaSegmenter
from brats.constants import AfricaAlgorithms
segmenter = AfricaSegmenter(algorithm=AfricaAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.AfricaSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2023 Link
Challenge Paper 2024: N/A
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Zhifan Jiang et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | Long Bai, et al. | N/A | ✅ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Sarim Hashmi, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS24_3 |
| 2023 | 1st | Andriy Myronenko, et al. | TODO | ❌ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Alyssa R Amod, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Ziyan Huang, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS23_3 |
Segmentation of Meningioma on brain MRI exams.
Unlike other segmentation challenges, the expected inputs for the Meningioma Segmentation Algorithms differ between years.
Therefore, the usage differs slightly, depending on which algorithm is used. To understand why, please refer to the 2024 challenge manuscript.
from brats import MeningiomaSegmenter
from brats.constants import MeningiomaAlgorithms
### Example for 2023 algorithms
segmenter = MeningiomaSegmenter(algorithm=MeningiomaAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation_23.nii.gz",
)
### Example for 2024 algorithms
segmenter = MeningiomaSegmenter(algorithm=MeningiomaAlgorithms.BraTS24_1, cuda_devices="0")
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation_24.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.MeningiomaSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2024 Link
Challenge Paper 2023 Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Valeria Abramova | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | Mehdi Astaraki | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Andre Ferreira, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS24_3 |
| 2023 | 1st | Andriy Myronenko, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Ziyan Huang, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Daniel Capell'an-Mart'in et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_3 |
Segmentation on brain metastases on MRI exams for pre- and post-treatment cases.
from brats import MetastasesSegmenter
from brats.constants import MetastasesAlgorithms
segmenter = MetastasesSegmenter(algorithm=MetastasesAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Note: If you're interested in Brain Metastases Segmentation, the BrainLes AURORA package may also be of interest.
Class: brats.MetastasesSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2023 Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2023 | 1st | Andriy Myronenko, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Siwei Yang, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Ziyan Huang, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS23_3 |
Segmentation of pediatric brain tumors on MRI exams.
from brats import PediatricSegmenter
from brats.constants import PediatricAlgorithms
segmenter = PediatricSegmenter(algorithm=PediatricAlgorithms.BraTS23_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Note: If you're interested in Pediatric Segmentation, the BrainLes PeTu package may also be of interest.
Class: brats.PediatricSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2024 Link
Challenge Paper 2023 Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Tim Mulvany, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | Mehdi Astaraki | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Sarim Hashmi, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS24_3 |
| 2023 | 1st | Zhifan Jiang et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Andriy Myronenko, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Yubo Zhou | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_3 |
Segmentation algorithm, adapting and generalizing to different brain tumors with segmentation labels of different tumor sub-regions.
from brats import GoATSegmenter
from brats.constants import GoATAlgorithms
segmenter = GoATSegmenter(algorithm=GoATAlgorithms.BraTS24_1, cuda_devices="0")
# these parameters are optional, by default the winning algorithm will be used on cuda:0
segmenter.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="segmentation.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.PediatricSegmenter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2024: N/A
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Frank Miao, Shengjie Niu | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
Algorithm to realistically synthesize and fill 3D healthy brain tissue in a region affected by glioma in brain MRI exams.
from brats import Inpainter
from brats.constants import InpaintingAlgorithms
inpainter = Inpainter(algorithm=InpaintingAlgorithms.BraTS24_1, cuda_devices="0")
inpainter.infer_single(
t1n="path/to/voided_t1n.nii.gz",
mask="path/to/mask.nii.gz",
output_file="inpainting.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.Inpainter (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2023 and 2024 Link
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Ke Chen, Juexin Zhang, Ying Weng | N/A | ✅ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | André Ferreira, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Alicia Durrer, et al. | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_3 |
| 2023 | 1st | Juexin Zhang, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS23_1 |
| 2023 | 2nd | Alicia Durrer, et al. | Link | ❌ | BraTS23_2 |
| 2023 | 3rd | Jiayu Huo, et al. | Link | ✅ | BraTS23_3 |
Algorithm to realistically synthesize missing MRI modalities from available sequences to enhance brain tumor segmentation.
from brats import MissingMRI
from brats.constants import MissingMRIAlgorithms
missing_mri = MissingMRI(algorithm=MissingMRIAlgorithms.BraTS24_1, cuda_devices="0")
# Example to synthesize t2f modality (whichever modality is missing will be inferred)
missing_mri.infer_single(
t1c="path/to/t1c.nii.gz",
t1n="path/to/t1n.nii.gz",
# t2f="path/to/t2f.nii.gz",
t2w="path/to/t2w.nii.gz",
output_file="inferred_t2f.nii.gz",
)
Class: brats.MissingMRI (Docs)
Challenge Paper 2024: N/A
| Year | Rank | Author | Paper | CPU Support | Key Enum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 1st | Jihoon Cho, Seunghyuck Park, Jinah Park | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_1 |
| 2024 | 2nd | Haowen Pang | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_2 |
| 2024 | 3rd | Minjoo Lim, Bogyeong Kang | N/A | ❌ | BraTS24_3 |
[!TIP] For a full notebook example with more details, please check here:
If you use BraTS in your research, please cite it to support the development!
TODO: citation will be added asap
We welcome all kinds of contributions from the community!
Please open a new issue here.
Nice to have you on board! Please have a look at our CONTRIBUTING.md file.
FAQs
BraTS algorithms
We found that brats demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Socket's research uncovers three dangerous Go modules that contain obfuscated disk-wiping malware, threatening complete data loss.
Research
Socket uncovers malicious packages on PyPI using Gmail's SMTP protocol for command and control (C2) to exfiltrate data and execute commands.
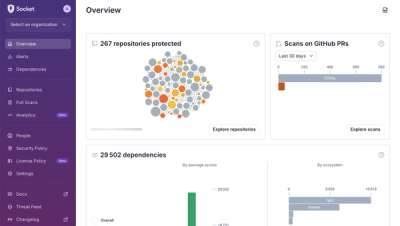
Product
We redesigned Socket's first logged-in page to display rich and insightful visualizations about your repositories protected against supply chain threats.