
Security News
GitHub Actions Pricing Whiplash: Self-Hosted Actions Billing Change Postponed
GitHub postponed a new billing model for self-hosted Actions after developer pushback, but moved forward with hosted runner price cuts on January 1.
camtools
Advanced tools

Docs | Repo | Installation
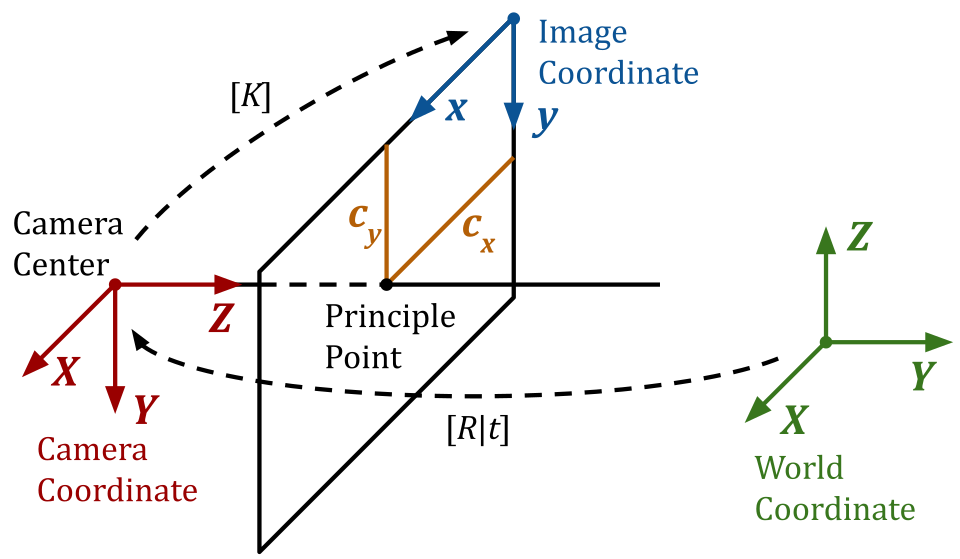
CamTools is a collection of tools for handling cameras in computer vision. It can be used for plotting, converting, projecting, ray casting, and doing more with camera parameters. It follows the standard camera coordinate system with clear and easy-to-use APIs.
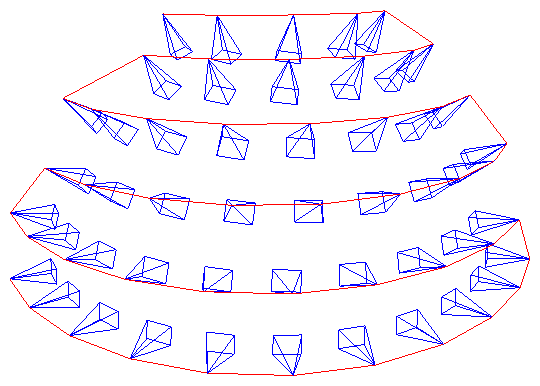
Plot cameras. Useful for debugging 3D reconstruction and NeRFs!
import camtools as ct
import open3d as o3d
cameras = ct.camera.create_camera_frustums(Ks, Ts)
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([cameras])
Convert camera parameters.
pose = ct.convert.T_to_pose(T) # Convert T to pose
T = ct.convert.pose_to_T(pose) # Convert pose to T
R, t = ct.convert.T_to_R_t(T) # Convert T to R and t
C = ct.convert.pose_to_C(pose) # Convert pose to camera center
K, T = ct.convert.P_to_K_T(P) # Decompose projection matrix P to K and T
# And more...
Projection and ray casting.
# Project 3D points to pixels.
pixels = ct.project.points_to_pixel(points, K, T)
# Back-project depth image to 3D points.
points = ct.project.im_depth_to_points(im_depth, K, T)
# Ray cast a triangle mesh to depth image given the camera parameters.
im_depth = ct.raycast.mesh_to_im_depth(mesh, K, T, height, width)
# And more...
Image and depth I/O with no surprises.
Strict type checks and range checks are enforced. The image and depth I/O APIs are specifically designed to solve the following pain points:
float32 or uint8?[0, 1] or [0, 255]?.png, is it correctly scaled?ct.io.imread()
ct.io.imwrite()
ct.io.imread_detph()
ct.io.imwrite_depth()
Command-line tools ct (runs in terminal).
# Crop image boarders.
ct crop-boarders *.png --pad_pixel 10 --skip_cropped --same_crop
# Draw synchronized bounding boxes interactively.
ct draw-bboxes path/to/a.png path/to/b.png
# For more command-line tools.
ct --help

And more.
To install CamTools, simply do:
pip install camtools
Alternatively, you can install CamTools from source with one of the following methods:
git clone https://github.com/yxlao/camtools.git
cd camtools
# Installation mode, if you want to use camtools only.
pip install .
# Editable mode, if you want to modify camtools on the fly.
pip install -e .
# Editable mode and dev dependencies.
pip install -e .[dev]
# Help VSCode resolve imports when installed with editable mode.
# https://stackoverflow.com/a/76897706/1255535
pip install -e .[dev] --config-settings editable_mode=strict
# Enable torch-related features (e.g. computing image metrics)
pip install camtools[torch]
# Enable torch-related features in editable mode
pip install -e .[torch]
A homogeneous point [X, Y, Z, 1] in the world coordinate can be projected to a
homogeneous point [x, y, 1] in the image (pixel) coordinate using the
following equation:
$$ \lambda \left[\begin{array}{l} x \ y \ 1 \end{array}\right]=\left[\begin{array}{ccc} f_{x} & 0 & c_{x} \ 0 & f_{y} & c_{y} \ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{llll} R_{00} & R_{01} & R_{02} & t_{0} \ R_{10} & R_{11} & R_{12} & t_{1} \ R_{20} & R_{21} & R_{22} & t_{2} \end{array}\right]\left[\begin{array}{c} X \ Y \ Z \ 1 \end{array}\right]. $$
We follow the standard OpenCV-style camera coordinate system as illustrated at the beginning of the README.
ct.convert.T_opencv_to_opengl()ct.convert.T_opengl_to_opencv()ct.convert.pose_opencv_to_opengl()ct.convert.pose_opengl_to_opencv()K: (3, 3) camera intrinsic.
K = [[fx, s, cx],
[ 0, fy, cy],
[ 0, 0, 1]]
T or W2C: (4, 4) camera extrinsic.
T = [[R | t = [[R00, R01, R02, t0],
0 | 1]] [R10, R11, R12, t1],
[R20, R21, R22, t2],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1]]
T is also known as the world-to-camera W2C matrix, which transforms a
point in the world coordinate to the camera coordinate.T's shape is (4, 4), not (3, 4).T is the inverse of pose, i.e., np.linalg.inv(T) == pose.C in world coordinate is projected to [0, 0, 0, 1] in
camera coordinate.R: (3, 3) rotation matrix.
R = T[:3, :3]
R is a rotation matrix. It is an orthogonal matrix with determinant 1, as
rotations preserve volume and orientation.
R.T == np.linalg.inv(R)np.linalg.norm(R @ x) == np.linalg.norm(x), where x is a (3,)
vector.t: (3,) translation vector.
t = T[:3, 3]
t's shape is (3,), not (3, 1).pose or C2W: (4, 4) camera pose. It is the inverse of T.
pose is also known as the camera-to-world C2W matrix, which transforms a
point in the camera coordinate to the world coordinate.pose is the inverse of T, i.e., pose == np.linalg.inv(T).C: camera center.
C = pose[:3, 3]
C's shape is (3,), not (3, 1).C is the camera center in world coordinate. It is also the translation
vector of pose.P: (3, 4) the camera projection matrix.
P is the world-to-pixel projection matrix, which projects a point in the
homogeneous world coordinate to the homogeneous pixel coordinate.P is the product of the intrinsic and extrinsic parameters.
# P = K @ [R | t]
P = K @ np.hstack([R, t[:, None]])
P's shape is (3, 4), not (4, 4).P into intrinsic and extrinsic matrices by QR
decomposition.P with pose. Don't confuse P with T.To build and view the documentation locally:
# Install documentation dependencies
pip install -e .[docs]
# Build the documentation
make -C docs clean && make -C docs html
# (Optional) Build the documentation with warnings as errors
make -C docs clean && make -C docs html SPHINXOPTS="-W --keep-going"
# Start a local server to view the documentation
python -m http.server 8000 --directory docs/_build/html
Then open your browser and navigate to http://localhost:8000 to view the documentation.
The documentation is also automatically built by GitHub Actions on pull requests and pushes to main. After merging to main, you can view:
main.build, ci, docs, feat, fix, perf, refactor, test.If you use CamTools in your project, consider adding one of the following badges to your project.
FAQs
CamTools: Camera Tools for Computer Vision.
We found that camtools demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
GitHub postponed a new billing model for self-hosted Actions after developer pushback, but moved forward with hosted runner price cuts on January 1.

Research
Destructive malware is rising across open source registries, using delays and kill switches to wipe code, break builds, and disrupt CI/CD.

Security News
Socket CTO Ahmad Nassri shares practical AI coding techniques, tools, and team workflows, plus what still feels noisy and why shipping remains human-led.