Product
Redesigned Repositories Page: A Faster Way to Prioritize Security Risk
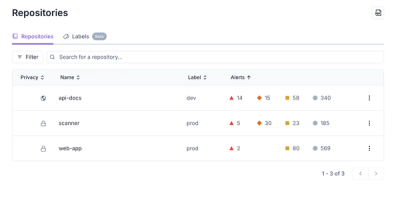
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.
DigCNV: Discriminating True CNVs from artifacts from genotyping without further visualisation



False CNVs bring noise to analysis and could distort a diagnosis. CNV calling produce false negative and positive identifications. To remove false negative it's recommended to use multiple CNV caller at a time. So we present here, a statistical approach to clean CNV results coming from two calling algorithms, PennCNV or QuantiSNP
This machine learning can be used in two different ways:
# To run only once to install package
pip install digcnv
python3 -m digcnv [-v] <Path to config file>
Example of config file needed for the one line execution. Example can be download with function getConfigFileExample(output_path)
[Inputs]
pc_output_path = Path to the PennCNV output file
pc_qc_path = Path to the PennCNV microarray quality file
qs_output_path = Path to the QuantiSNP output file
[Output]
Save_to_file = True
Output_path = /home/thomas/Documents/scripts/DigCNV/temp_data/DigCNV_pred.tsv
[DigCNV]
model_path": Path of the downloaded model. Available at :
from digcnv import CNVision, dataPreparation
# Import and merge CNV coming from two CNV calling algorthims (only PennCNV and QuantiSNP in this version)
cnvs = CNVision.mergeMultipleCNVCallingOutputs("<list of PennCNV and QuantiSNP output pathways>", ["PennCNV", "QuantiSNP"])
# Add microarray quality data to the list of CNVs
cnvs = dataPreparation.addMicroArrayQualityData(cnvs, "<path to the PennCNV microarray quality file>")
# Compute derived features and add it to the CNV list
cnvs = dataPreparation.addDerivedFeatures(cnvs)
# Add Chromosomic information such as centromere and Segmental Duplications overlap
cnvs = dataPreparation.addChromosomicAnnotation(cnvs, parameters["centromeres"], parameters["seg_dups"])
cnvs = dataPreparation.transformTwoAlgsFeatures(cnvs)
More information in "article--WIP"
from digcnv import digCnvModel, dataVerif
# Create an empty DigCNV model
model = digCnvModel.DigCnvModel()
# Open pre-trained model and update object
model_path = join(split(__file__)[0], 'data', 'DigCNV_model_multiple_technos.pkl')
model.openPreTrainedDigCnvModel(model_path)
# Check if mandatory columns for the DigCNV model exist and have right formats
dataVerif.checkIfMandatoryColumnsExist(cnvs, post_data_preparation=True)
dataVerif.checkColumnsformats(cnvs, post_data_preparation=True)
# Optional plot a correlation heatmap between different predictors used in model
dataVerif.plotCorrelationHeatMap(cnvs, list_dim=model._dimensions, output_path="<Pathway where output plot (.pdf or .png)>")
# Check NaN data within mandatory columns and split data into two dataframes: first for CNVs with all information available
# and a second one with all CNVs with at least one missing data (can't be used for prediction)
cnvs, cnvs_with_na = dataVerif.computeNaPercentage(cnvs, dimensions=model._dimensions, remove_na_data=True)
# Discriminate true from false CNVs from CNVs with all data, then produce a list of classes
predicted_cnvs = model.predictCnvClasses(cnvs)
cnvs["DigCNVpred"] = predicted_cnvs
from digcnv import digCnvModel, DigCnvPreProcessing
# Uses CNVs created in Prepare data section :
# Add your own annotation to your CNVs (0 for false CNVs and 1 for true)
cnvs["visualized_class"] = ["<classes of each CNV visualized>"]
# Dimensions used to classify CNVs (Recommended dimensions you can use your own)
predictors = ["",""]
# Remove CNVs with at least one missing values in used predictors or in visualized column
cnvs, removed = dataVerif.computeNaPercentage(data, dimensions=predictors + ["visualized_class"], remove_na_data=True)
# Split dataset into two groups a training dataset and a testing dataset (70% - 30%)
X_train, y_train, X_test, y_test = DigCnvPreProcessing.createTrainingTestingDatasets(cnvs, dimensions=predictors, X_dimension="visualized_class")
# If ratio between the two classes is too unbalanced uniformize classes by split majoritary class and adding new pseudo CNVs to minority class
X_train, y_train = DigCnvPreProcessing.uniformizeClassesSizes(X_train, y_train, 17, 0.4, 0.5)
# Create a DigCNV model
model = digCnvModel.DigCnvModel()
model.createDigCnvClassifier()
chr20:44356194-44378577 numsnp=7 length=22,384 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs232258 endsnp=rs380421 conf=16.163
chr9:17583310-17622213 numsnp=21 length=38,904 state5,cn=3 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs1028594 endsnp=rs3808750 conf=101.052
chr10:47543322-47703613 numsnp=47 length=160,292 state5,cn=3 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs11259779 endsnp=rs4128664 conf=156.227
chr6:4263349-4472587 numsnp=69 length=209,239 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10002 startsnp=rs6937085 endsnp=rs7746329 conf=120.225
chr6:80608294-80611616 numsnp=6 length=3,323 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10002 startsnp=rs17833835 endsnp=rs1887571 conf=20.441
...
SampleID LRR_mean LRR_median LRR_SD BAF_mean BAF_median BAF_SD BAF_DRIFT WF GCWF
10001 -0.004
# Train the DigCNV model with the given training dataset
model.trainDigCnvModel(training_data=X_train, training_cat=y_train)
# Save the trained model into the specified path
model.saveDigCnvModelToPkl("<output_path>")
chr20:44356194-44378577 numsnp=7 length=22,384 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs232258 endsnp=rs380421 conf=16.163
chr9:17583310-17622213 numsnp=21 length=38,904 state5,cn=3 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs1028594 endsnp=rs3808750 conf=101.052
chr10:47543322-47703613 numsnp=47 length=160,292 state5,cn=3 /path/to/finalreport/10001 startsnp=rs11259779 endsnp=rs4128664 conf=156.227
chr6:4263349-4472587 numsnp=69 length=209,239 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10002 startsnp=rs6937085 endsnp=rs7746329 conf=120.225
chr6:80608294-80611616 numsnp=6 length=3,323 state2,cn=1 /path/to/finalreport/10002 startsnp=rs17833835 endsnp=rs1887571 conf=20.441
...
SampleID LRR_mean LRR_median LRR_SD BAF_mean BAF_median BAF_SD BAF_DRIFT WF GCWF
10001 -0.0045 0.0000 0.1474 0.5028 0.5000 0.0268 0.000036 -0.0141 -0.0002
10002 0.0056 0.0000 0.1588 0.5027 0.5000 0.0259 0.000000 0.0194 0.0018
10003 -0.0090 0.0000 0.1564 0.5031 0.5000 0.0308 0.000000 0.0132 0.0053
10004 0.0014 0.0000 0.1494 0.5032 0.5000 0.0280 0.000000 0.0184 0.0018
10005 0.0031 0.0000 0.1412 0.5025 0.5000 0.0272 0.000000 0.0170 0.0001
...
Sample Name Chromosome Start Position (bp) End Position (bp) Start Probe ID End Probe ID Length (bp) No. Probes Copy Number Max. Log BF Log BF: State 0 Log BF: State 1 Log BF: State 2 Log BF: State 3 Log BF: State 4 Log BF: State 5 Log BF: State 6
10001 1 31943355 31943355 rs7545865 rs7545865 1 1 1 1.2152 -24.0258 -2.5507 0 1.2152 -16.1517 -19.4123 -25.013
10001 1 111930916 111934304 rs12077338 rs4839132 3389 4 1 4.57286 -42.9409 4.57286 0 2.93527 -29.2398 -35.802 -44.9483
10001 2 44082362 44096010 rs6718187 rs6752551 13649 4 3 0.954579 -62.543 -41.1676 0 -14.003 0.954579 0.576184 -60.5049
10001 2 92308395 92308395 rs4509760 rs4509760 1 1 1 0.0218224 -26.3579 -4.38718 0 0.0218224 -19.0042 -21.9322 -27.2609
10001 3 59820539 59821071 rs1905866 rs17362486 533 2 4 0.33986 -9.54639 -22.8223 0 -3.94108 -6.15468 0.33986 -8.45724
...
FAQs
DigCNV: Discriminating True CNVs from artifacts from genotyping without further visualisation
We found that digcnv demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.

Security News
Slopsquatting is a new supply chain threat where AI-assisted code generators recommend hallucinated packages that attackers register and weaponize.

Security News
Multiple deserialization flaws in PyTorch Lightning could allow remote code execution when loading untrusted model files, affecting versions up to 2.4.0.