django-extended-makemessages


Extended version of Django's makemessages command that exposes selected GNU gettext tools options and adds new custom options, which further simplify message detection and translation files management.
🎉 Features
All the options of makemessages command are available, plus:
- Sorting messages by
msgid
- Disabling fuzzy translations
- Detecting message marked with
gettext functions imported as aliases
- Keeping the header from constantly changing
- Extracting all string
- Removing flags from the output files
- Checking for untranslated messages and outdated
.po files
- Copying comments from code to
.po files for context
- Compiling
.po files to .mo without running compilemessages command separately
🔌 Instalation
[!NOTE]
This package is useful only during development or CI/CD workflows. There is no need to install it in production environments.
-
Install using pip:
$ pip3 install django-extended-makemessages
-
Add 'django_extended_makemessages' to your INSTALLED_APPS setting.
INSTALLED_APPS = [
...
'django_extended_makemessages',
]
🚀 Overview
Sorting messages by msgid
Django's makemessages command sorts messages based on location in the source code. This leads to situations where code refactoring can change in the order of messages in the .po file. As a result, the version control system shows a lot of changes that do not reflect the actual changes in the code and are confusing.
Below you can see, that despite only adding the "Delivery" message, the diff shows more changes.
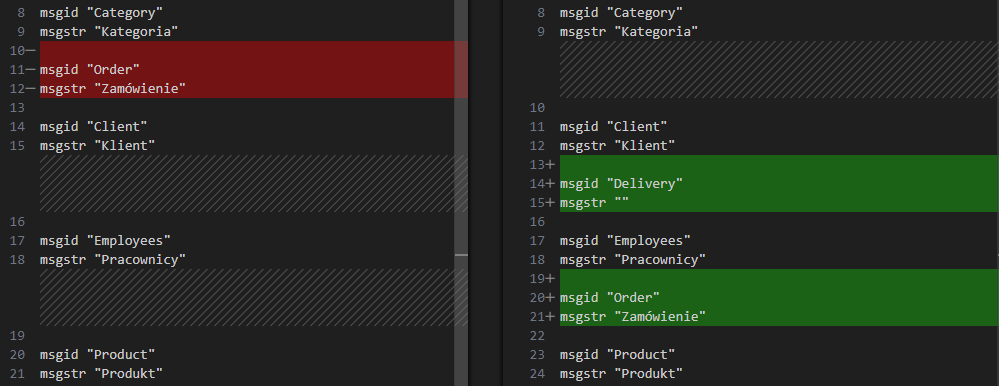
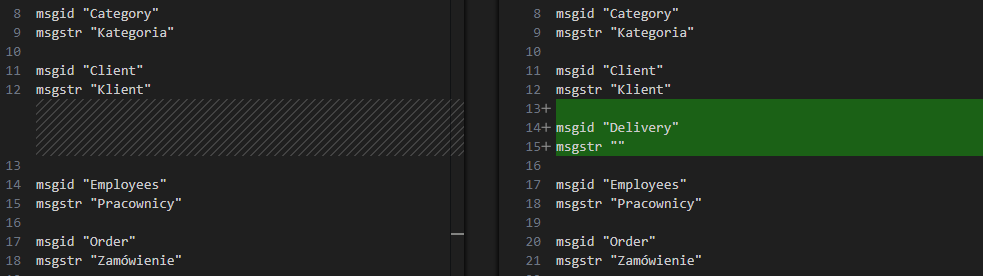
Using the --sort-output option sorts messages by msgid. As a result, the diff will show only added or removed messages, since the order in which they appear in the source code does not affect the generated .po files.
Disabling fuzzy translations
By default, similar messages are marked as fuzzy and their translation is inferred from previously translated strings within the same .po file. This often leads to incorrect translations and requires additional manual review.
In the following example, "Dessert 🍨" is marked as fuzzy and its translation is inferred from the "Desert 🐪" message.

You can use the --no-fuzzy-matching option to disable fuzzy matching. This way all messages will have to be translated manually.

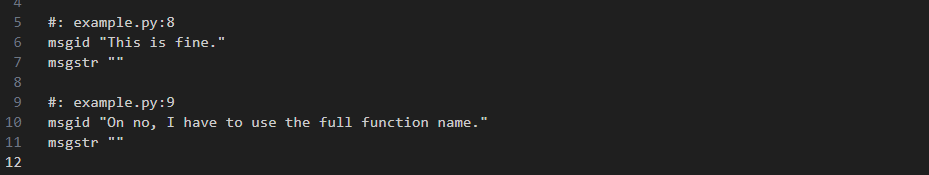
Detecting messages marked with gettext functions imported as aliases
It is a common practice to import functions from django.utils.translation module as _ alias. This works because under the hood, xgettext command accepts it as one of the keywords for marking strings for translation.
That is not a problem, if you import only one function. However, if you need to import more than one function, you have to use its full name. This is because xgettext does not recognize aliases for functions other than _.
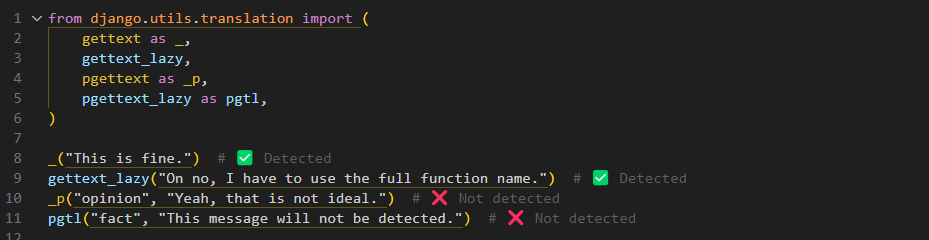
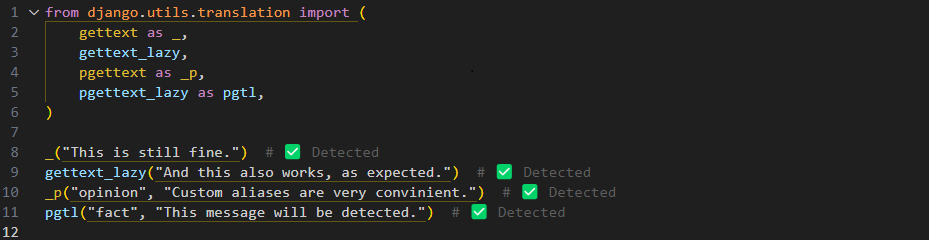
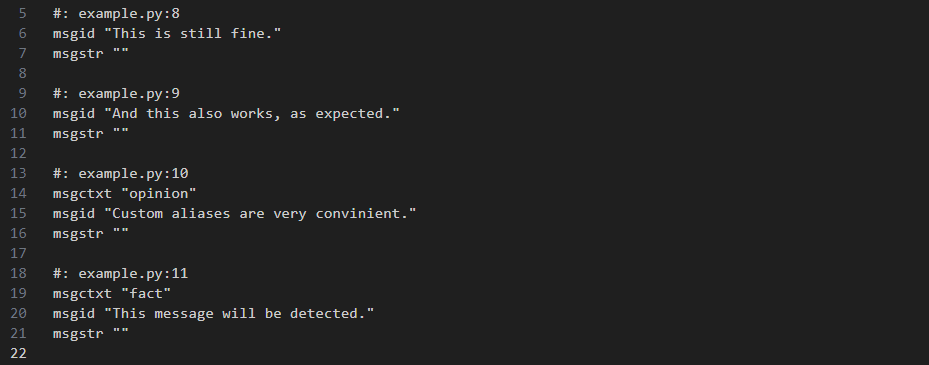
You can manually add aliases using the --keyword option with this syntax. However, a more convenient way is to use the --detect-aliases option, which will automatically recognize and add aliases for functions from the django.utils.translation module.
By doing so all messages marked with aliases will be detected and added to the .po file.
Using the --keep-header argument preserves the header of the .po file exactly as it was before the command was run. This is useful when you want to keep the header unchanged, for example, if you do not want to include the "Report-Msgid-Bugs-To" or "POT-Creation-Date" fields in the .po file.
By default, makemessages command extracts only strings marked for translation. However, you can use the --extract-all option to extract all strings from the source code.
The usefullness of this is questionable, but xgettext command provides such option, so it is exposed here as well.
Removing flags from the output files
Messages with placeholders are marked with flags, e.g. python-format or python-brace-format. These flags might be useful for translators, but are not required and can make the .po file harder to read.
You can use the --no-flags option to remove all or the --no-flag option to remove specific flags from the output files.
Checking for untranslated messages and outdated .po files
It is not hard to forget about updating translations after changing the source code. To prevent this, you can add a step to your CI/CD pipeline or a helper script, that will check it for you.
Option --show-untranslated will count all messages without translation and in more verbose mode, also display their locations in .po files.
When more restrictive approach is needed, e.g. in CI/CD pipelines, you could consider using the following options that exit with a non-zero status code in specific situations.
Option --no-untranslated checks for untranslated messages in the .po files. If any untranslated messages are found, the command will fail.
Using --check option allows you to verify that all translations are properly extracted and included in the .po files. It works similarly to the makemigrations --check, but for translations. If any .po file would be added or changed, the command will fail.
Combining these options can help you keep your translations up to date.
When translating messages, the context in which they are used is very important, as it and can greatly affect wording, grammar or even the translation itself.
Functions like pgettext accept an context parameter, which can be used to differentiate between messages with the same msgid. However, in many cases, a longer, more detailed comment could provide a clearer description of how the message is used.
Django's makemessages command by default only copies comments that start with "Translators":
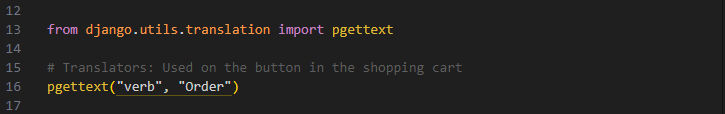
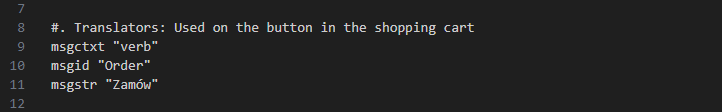
You can use --add-comments TAG to override this, or use --add-comments to copy all comments.
Compiling .po files to .mo without running compilemessages command separately
Normally after the .po files change, you have to run the compilemessages command to compile them to .mo files.
This step is required, because without it, Django will not be able to use the translations.
Most of the time, you will want to run makemessages and compilemessages one after another, or
you could do it in one step by using the --compile option.
🧰 Usage
usage: manage.py extendedmakemessages [-h] [--locale LOCALE] [--exclude EXCLUDE] [--domain DOMAIN] [--all] [--extension EXTENSIONS]
[--symlinks] [--ignore PATTERN] [--no-default-ignore] [--no-wrap] [--no-location]
[--add-location [{full,file,never}]] [--no-obsolete] [--keep-pot] [--no-fuzzy-matching]
[--add-comments [TAG]] [--extract-all] [--keyword [KEYWORD]] [--force-po] [--indent] [--width WIDTH]
[--sort-output | --sort-by-file] [--detect-aliases] [--keep-header] [--no-flags]
[--no-flag {fuzzy,python-format,python-brace-format,no-python-format,no-python-brace-format}]
[--no-previous] [--no-untranslated] [--check] [--dry-run] [--compile] [--version] [-v {0,1,2,3}]
[--settings SETTINGS] [--pythonpath PYTHONPATH] [--traceback] [--no-color] [--force-color]
Runs over the entire source tree of the current directory and pulls out all strings marked for translation. It creates (or updates)
a message file in the conf/locale (in the django tree) or locale (for projects and applications) directory.
You must run this command with one of either the --locale, --exclude, or --all options.
In addition to the options available in Django's makemessages command, this command exposes selected
msgmerge/msguniq/msgattrib/xgettext options that make sense for usage in a Django project.
On top of that, this command also includes some custom options, which further simplify managing translations,
but are not part of GNU gettext tools.
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
--locale LOCALE, -l LOCALE
Creates or updates the message files for the given locale(s) (e.g. pt_BR). Can be used multiple
times.
--exclude EXCLUDE, -x EXCLUDE
Locales to exclude. Default is none. Can be used multiple times.
--domain DOMAIN, -d DOMAIN
The domain of the message files (default: "django").
--all, -a Updates the message files for all existing locales.
--extension EXTENSIONS, -e EXTENSIONS
The file extension(s) to examine (default: "html,txt,py", or "js" if the domain is "djangojs").
Separate multiple extensions with commas, or use -e multiple times.
--symlinks, -s Follows symlinks to directories when examining source code and templates for translation strings.
--ignore PATTERN, -i PATTERN
Ignore files or directories matching this glob-style pattern. Use multiple times to ignore more.
--no-default-ignore Don't ignore the common glob-style patterns 'CVS', '.*', '*~' and '*.pyc'.
--no-wrap Don't break long message lines into several lines.
--no-location Don't write '#: filename:line' lines.
--add-location [{full,file,never}]
Controls '#: filename:line' lines. If the option is 'full' (the default if not given), the lines
include both file name and line number. If it's 'file', the line number is omitted. If it's
'never', the lines are suppressed (same as --no-location). --add-location requires gettext 0.19 or
newer.
--no-obsolete Remove obsolete message strings.
--keep-pot Keep .pot file after making messages. Useful when debugging.
--no-fuzzy-matching Do not use fuzzy matching when an exact match is not found. This may speed up the operation
considerably.
--add-comments [TAG] Place comment blocks starting with tag and preceding keyword lines in the output file.
Without a tag, the option means to put all comment blocks preceding keyword lines
in the output file.
--extract-all Extract all strings.
--keyword [KEYWORD] Specify keywordspec as an additional keyword to be looked for. Without a keywordspec, the option
means to not use default keywords.
--force-po Always write an output file even if no message is defined.
--indent Write the .po file using indented style.
--width WIDTH Set the output page width. Long strings in the output files will be split across multiple lines in
order to ensure that each line's width (= number of screen columns) is less or equal to the given
number.
--sort-output Generate sorted output.
--sort-by-file Sort output by file location.
--detect-aliases Detect gettext functions aliases in the project and add them as keywords to xgettext command.
--show-untranslated Show number of untranslated messages and, in more verbose mode, their location in .po files.
--keep-header Keep the header of the .po file exactly the same as it was before the command was run. Do nothing
if the .po file does not exist.
--no-flags Don't write '#, flags' lines.
--no-flag {fuzzy,python-format,python-brace-format,no-python-format,no-python-brace-format}
Remove specific flag from the '#, flags' lines.
--no-previous Don't write '#| previous' lines.
--no-untranslated Exit with a non-zero status if any untranslated messages are found in any .po file.
--check Exit with a non-zero status if any .po file would be added or changed. Implies --dry-run.
--dry-run Restore the .po file to its original state after running the command.
--compile Compile .po files to .mo files after running the command.
--version Show program's version number and exit.
-v {0,1,2,3}, --verbosity {0,1,2,3}
Verbosity level; 0=minimal output, 1=normal output, 2=verbose output, 3=very verbose output
--settings SETTINGS The Python path to a settings module, e.g. "myproject.settings.main". If this isn't provided, the
DJANGO_SETTINGS_MODULE environment variable will be used.
--pythonpath PYTHONPATH
A directory to add to the Python path, e.g. "/home/djangoprojects/myproject".
--traceback Raise on CommandError exceptions.
--no-color Don't colorize the command output.
--force-color Force colorization of the command output.