
Security News
ECMAScript 2025 Finalized with Iterator Helpers, Set Methods, RegExp.escape, and More
ECMAScript 2025 introduces Iterator Helpers, Set methods, JSON modules, and more in its latest spec update approved by Ecma in June 2025.
🔥 Fast-Flet is a package built as a complement to Flet, designed for newbies which facilitates the handling of flet events, designed to work with numerous pages and be customizable.
Fast-Flet is a package built as a complement to Flet, designed for newbies which facilitates the handling of flet events, designed to work with numerous pages of your created application. It also provides a better MVC construction of your code, which can be scalable and easy to read. But it not only limits the MVC model but you can adapt it according to your preferences.
on_route_change : Dynamic routing (automatic and manual)on_view_popon_keyboard_eventon_resizeon_errorFlet_Fastapi. viewFast-Flet? viewclass of Fast-Flet
ViewPage class. viewMyController class. viewon_resize. viewon_keyboard_event. viewIt is installed automatically:
pip install fast-flet
pip install fast-flet --upgrade
Fast-Flet CliContains new quickstart commands that you can use in the terminal. They will allow you to start developing immediately and without any effort.
fast-flet init mvc
fast-flet init mvc --async
views folder and the app.py file will be created.fast-flet init app
views folder and the app.py file will be created. (async)fast-flet init app --async
fast-flet version
Fast-Flet presents a main structure based on MVC and the other is according to how the user wants to adapt it.
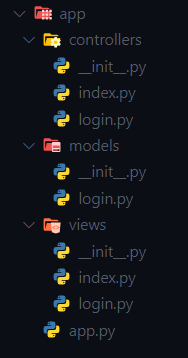
In this case it only requires the app.py file and the views folder, the rest is already customizable in terms of more folders or files.
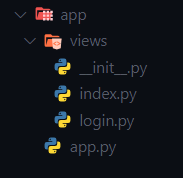
We create the main file app.py in the root path of the project, which is where Flet will be initialized.
import flet as ft
from fast_flet import RoutePage, ConfView
def main(page: ft.Page):
# CONFIGURACION GENERAL
theme = ft.Theme()
platforms = ["android", "ios", "macos", "linux", "windows"]
for platform in platforms: # Removing animation on route change.
setattr(theme.page_transitions, platform, ft.PageTransitionTheme.NONE)
page.theme = theme
# View flet configuration in all views
view = ConfView(
appbar=lambda: ft.AppBar(
title=ft.Text("fast-flet"),
center_title=False,
bgcolor=ft.colors.SURFACE_VARIANT,
actions=[
ft.IconButton(ft.icons.WB_SUNNY_OUTLINED),
ft.IconButton(ft.icons.FILTER_3),
ft.PopupMenuButton(
items=[
ft.PopupMenuItem(text="Item 1"),
ft.PopupMenuItem(
text="Checked item", checked=False
),
]
),
],
)
)
# ROUTING AND HANDLING VIEWS IN AUTOMATICO
fast_flet = RoutePage(
page=page,
route="/index",
route_login='/login',
route_404="/404-fast-flet",
view=view,
)
# WE RUN THE ROUTING OF THE VIEWS
fast_flet.run()
ft.app(main,
port=8000,
view=ft.AppView.WEB_BROWSER,
web_renderer=ft.WebRenderer.AUTO,
route_url_strategy='hash'
)
RoutePage:By default this Fast-Flet class performs automatic routing. It has the following attributes.
page: 'page' parameter of the main function of the app or website (mandatory).
route: Path where the app or website will be initialized (mandatory).
route_login: Login route, where it will be redirected.
route_404: Custom page path not found.
view: General configuration of all the 'View' of the page '(page.views)'
manual_routing: Use manual routing of 'views'
ConfView:Contains all View Flet properties to assign to all pages.
Note: if the parameter receives a flet class, lambda is used. (Not in async)
Example:
controls: list = None
appbar: AppBar = None # use lambda
floating_action_button: FloatingActionButton = None # use lambda
navigation_bar: NavigationBar = None # use lambda
vertical_alignment: MainAxisAlignment = None # use lambda
horizontal_alignment: CrossAxisAlignment = None # use lambda
spacing: int = None
padding: int = None # use lambda
bgcolor: str = None # use lambda
# ScrollableControl specific
scroll: ScrollMode = None # use lambda
auto_scroll: bool = None
fullscreen_dialog: bool = None
on_scroll_interval: OptionalNumber = None # use lambda
on_scroll = None
To perform manual routing, it is required to use the add_routes() method from RoutePage and import add_view() from Fast-Flet.
🔎 Note: To use it you must first activate it in the RoutePage class with its attribute manual_routing= True (by default it is False).
import flet as ft
from fast_flet import RoutePage,add_view
# Import the View classes from the views folder to use in add_routes
from views.index import View
from views.task import View as Taskview
from views.contador import View as ContadorView
from views.login import View as LoginView
from views.resize import View as ResizeView
from views.page_404 import View as Page_404View
def main(page: ft.Page):
# CONFIGURACION GENERAL
theme = ft.Theme()
platforms = ["android", "ios", "macos", "linux", "windows"]
for platform in platforms: # Removing animation on route change.
setattr(theme.page_transitions, platform, ft.PageTransitionTheme.NONE)
page.theme = theme
fast_flet = RoutePage(
page=page,
route="/index",
route_login='/login',
route_404="/404-fast-flet",
manual_routing= True
)
# ROUTING AND MANAGEMENT VIEWS IN MANUAL'
fast_flet.add_routes(
[
add_view(url='/index',view=View()),
add_view(url='/task',view=Taskview(),clear=False),
add_view(url='/counter/:id/:name',view=ContadorView(), clear=False),
add_view(url='/login',view=LoginView()),
add_view(url='/resize',view=ResizeView(), clear=False),
add_view(url='/404-fast-flet',view=Page_404View(), clear=False),
]
)
# WE RUN THE ROUTING OF THE VIEWS
fast_flet.run()
ft.app(main,
port=8000,
view=ft.AppView.WEB_BROWSER,
web_renderer=ft.WebRenderer.AUTO,
route_url_strategy='hash'
)
add_view() functionThe parameters that this function has are:
url We set the url.view We use the class imported from the views folder.clear All views stored in page.views are removed (default is true).run() methodrun() Initialize Fast-Flet
To use Flet in async mode, it is initialized with the run_async() method of the RoutePage class
views folder a file is created for example index.py🔎Note: When using automatic routing the class must be called View and inherit ViewPage from Fast-Flet.
import flet as ft
from fast_flet import ViewPage
class View(ViewPage):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.call.route = '/index'
# remove icon return to previous view of 'appbar', if it is activated
self.call.page_clear = True # clean the list of views added to the page (default is false)
# View general configuration
def build(self):
# we assign a url
self.route = '/index'
page = self.call.page
page.title = 'Index'
# modify View properties : https://flet.dev/docs/controls/view
self.appbar.title = ft.Text('Home')
self.controls = [
ft.Column(
[
ft.Container(
content=ft.Column(
[
ft.FilledButton(
'go Counter',
on_click=lambda e: e.page.go(
'/counter/100/fast-flet')
),
ft.FilledButton(
'go Task',
on_click=lambda e:e.page.go('/task')
),
ft.FilledButton(
'go Resize',
on_click=lambda e:e.page.go('/resize')
),
],
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER,
horizontal_alignment=ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
),
width=450,
height=450,
bgcolor='blue800',
alignment=ft.alignment.center,
border_radius=20
),
]
)
]
self.horizontal_alignment = ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
self.vertical_alignment = ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER
self.bgcolor = ft.colors.BLACK
View class inherits:self.callself.call.page: Page Receives the page from the main function.
self.call.route: str = '/' Establish a route (Automatic Routing).
self.call.page_clear:bool = False Set removal of list page.views stored by flet (Automatic Routing).
self.call.url_params: list = None Receives the parameters sent through the url.
self.call.is_login: bool = False Establish if the page requires login.
self.call.on_keyboard_event: Mykeyboard Receive information about the event: 'on_keyboard_event'.
self.call.on_resize: MyPageResize Receive information about the event: on_resize.
flet.View, It is used in the build() method.In the build() method that inherits from the ViewPage class, you can add new controllers and assign value of the page properties.
self.controls: list = Noneself.appbar: AppBar = Noneself.floating_action_button: FloatingActionButton = Noneself.navigation_bar: NavigationBar = Noneself.vertical_alignment: MainAxisAlignment = Noneself.horizontal_alignment: CrossAxisAlignment = Noneself.spacing: int = Noneself.padding: int = Noneself.bgcolor: str = NoneScrollableControl specific
self.scroll: ScrollMode = Noneself.auto_scroll: bool = Noneself.fullscreen_dialog: bool = Noneself.on_scroll_interval: int = Noneself.on_scroll = Nonelogin_required() method that inherits from the ViewPage class, the configuration will only be done once.self.call.is_login = True Requires login to access the page (previously configured)class View(ViewPage):
def __init__(self) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.call.route = '/login' # we assign a url
self.call.is_login = True # requires login to access the page (previously configured)
# required login configuration
def login_required(self) -> bool:
super().login_required()
class_login = Login() # import the login controller class
add_login_required = lambda:class_login.login() #We use the method of the class where the login configuration has been made
return add_login_required() # Returns login validation.
# View general configuration
def build(self):
self.call.page.title = 'Login'
.......
........
self.call.on_keyboard_eventOnce the ViewPage attributes are inherited we can use them.
🔎self.call.on_keyboard_event It has the following methods:
add_control('<controller method>') Adds a controller configuration (controller method), which is executed with the on_keyboard_event event.
def key() Returns the value entered by keyboard.
def shift() Returns the value entered by keyboard.
def ctrl() Returns the value entered by keyboard.
def alt() Returns the value entered by keyboard.
def meta() Returns the value entered by keyboard.
def test() Returns a message of all the values entered by keyboard. (key, Shift, Control, Alt, Meta)
self.call.on_resize🔎 self.call.on_resize It has the following methods:
controls Stores the checklist to be responseve.
add_control('<control>', '<height>', '<max_height>') Add a control that will be a response when executing the 'on_resize' event.
add_controls = '<lambda>' Stores an anonymous function.
response('<'controls>') Configure the response of all controls.
add_def_control = <lambda> Add a function that will be executed with the on_resize event, the function must be from the controllers folder.
🗂️ In the views folder of the task.py file
def build(self):
# ------
# We configure all the values of the page.
page = self.call.page # we get all the values of the page.
page.title = 'test'
# --------
on_resize = self.call.on_resize # on_resize values are obtained
on_keyboard = self.call.on_keyboard_event # the values of on_keyboard_event are obtained
task = ContentTask(on_resize, on_keyboard) # flet custom control
# modify View properties : https://flet.dev/docs/controls/view
self.appbar.title = ft.Text('Task')
self.controls = [
task
]
Flet custom control
class ContentTask(ft.UserControl):
def __init__(self, on_resize: MyPageResize, on_keyboard: Mykeyboard):
super().__init__()
# We create an object of the controller class of this class, to be able to use its methods.
self.new_control = ContentTaskC(self, on_resize, on_keyboard)
self.on_keyboard = on_keyboard # the values of on_keyboard_event are obtained
# add a function to on_keyboard, which will be executed according to what is established in the function, it will be executed with keyboard input.
self.on_keyboard.add_control(self.new_control.add_on_keyboard)
self.on_resize = on_resize # on_resize values are obtained
self.new_control.user_control = Task # # We send the class that we are going to use in the controller of this class
self.input = ft.TextField(
col=8,
label='Enter the task',
multiline=True,
autocorrect=True,
helper_text="'Alt'+'L' -> to add task",
on_focus=self.new_control.update_input,
)
self.colum_task = ft.Column(scroll=ft.ScrollMode.ADAPTIVE)
self.response_page = ft.Container(
col={'sm': 5},
bgcolor=ft.colors.BLACK26,
height=self.on_resize.height - 80,
padding=10,
border_radius=10
)
self.response_task = ft.Container(
col={'sm': 11},
bgcolor=ft.colors.BLACK12,
height=self.on_resize.height-244,
padding=10,
border_radius=10,
)
# We add the controllers that are height responsive, if it is not displayed the page has to be reloaded (possible flet error)
self.on_resize.add_control(self.response_page, 80, 420)
self.on_resize.add_control(self.response_task, 244, 383)
self.on_resize.add_controls = lambda: self.new_control.response(
self.on_resize.controls) # we add all the controls
def build(self):
self.response_task.content = self.colum_task
self.response_page.content = ft.ResponsiveRow(
controls=[
ft.Text('Task', size=25,
text_align=ft.TextAlign.CENTER),
ft.ResponsiveRow(
controls=[
self.input,
ft.FilledButton(
'ADD',
col=4,
on_click=self.new_control.add_task
)
],
vertical_alignment=ft.CrossAxisAlignment.CENTER
),
self.response_task
],
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER
)
return ft.ResponsiveRow(
controls=[
self.response_page
],
alignment=ft.MainAxisAlignment.CENTER,
)
controllers folder of the task.py fileThe Fast-Flet MyController class contains the following inheriting attributes.
self.call.model = None It is assigned the class of the file.py in the models folder.self.call.on_resize = on_resize It is assigned the self.call.on_resize of the View class from the file.py in the views folder.self.call.on_keyboard_event = on_keyboard It is assigned the self.call.on_keyboard_event of the View class in the .py file in the views folder.self.x = _self The custom control object is stored.self._user_control = None The class that will be used in the custom control is stored.# view's ContentTask class handler
class ContentTaskC(MyController):
def __init__(self, _self: object, on_resize: MyPageResize = None, on_keyboard=None) -> None:
super().__init__(_self, on_resize, on_keyboard)
def _add_task(self):
if self.x.input.value != '':
input_task = self.x.input.value
task = self.user_control(self.delete, input_task, self.call.on_keyboard_event)
self.x.colum_task.controls.append(task)
self.x.input.value = ''
self.x.input.label = 'Enter a task'
else:
self.x.input.label = 'Enter a task please'
self.x.input.border_color=ft.colors.RED
self.x.update()
sleep(2)
self.x.input.border_color=None
self.x.update()
def add_task(self,e):
self._add_task()
def delete(self, task):
self.x.colum_task.controls.remove(task)
self.x.update()
def update_input(self,e):
self.x.input.border_color=None
self.x.update()
# used with keyboard input
def add_on_keyboard(self):
keyboard = self.call.on_keyboard_event
if keyboard.key() == 'L' and keyboard.alt():
self._add_task()
In the previous example you can see the responsible use of the page height.
self.response_page = ft.Container(
col={'sm': 5},
bgcolor=ft.colors.BLACK26,
height=self.on_resize.height - 80,
padding=10,
border_radius=10
)
self.response_task = ft.Container(
col={'sm': 11},
bgcolor=ft.colors.BLACK12,
height=self.on_resize.height-244,
padding=10,
border_radius=10,
)
# We add the controllers that are height responsive, if it is not displayed the page has to be reloaded (possible flet error)
self.on_resize.add_control(self.response_page, 80, 420)
self.on_resize.add_control(self.response_task, 244, 383)
self.on_resize.add_controls = lambda: self.new_control.response(
self.on_resize.controls) # we add all the controls
threading (defect Flet)Async (with flet_fastapi) watch onlineFAQs
🔥 Fast-Flet is a package built as a complement to Flet, designed for newbies which facilitates the handling of flet events, designed to work with numerous pages and be customizable.
We found that fast-flet demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
ECMAScript 2025 introduces Iterator Helpers, Set methods, JSON modules, and more in its latest spec update approved by Ecma in June 2025.

Security News
A new Node.js homepage button linking to paid support for EOL versions has sparked a heated discussion among contributors and the wider community.

Research
North Korean threat actors linked to the Contagious Interview campaign return with 35 new malicious npm packages using a stealthy multi-stage malware loader.