Product
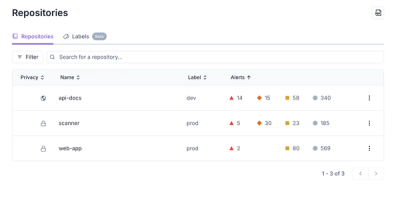
Redesigned Repositories Page: A Faster Way to Prioritize Security Risk
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.
Geonomics
.. image:: ./img/gnx_mini_350dpi.png :width: 250 :align: left
A Python package for simulation of genomic evolution on complex and dynamic landscapes
Geonomics allows users to build and run arbitrarily complex, forward-time, agent-based, and spatially explicit simulations for landscape genomics. It is designed to allow even novice Python users to create sophisticated simulations with minimal code, while also allowing advanced users a high level of extensibility and customizability.
We will continue to expand and add functionality in future versions. Please contact us with questions, suggestions, or requests!
The following is a short list of highlights. For the full monty, please see
the homepage <https://github.com/drewhart/geonomics>,
the docs <https://geonomics.readthedocs.org>,
and the original methods paper <PAPER_URL_HERE>_.
- a model object, which serves as the primary user interface and which
contains all other model components
- a landscape object consisting of an arbitrary number of environmental
raster layers
- a community object consisting of an arbitrary number of species objects,
each consisting of an arbitrary number of individuals
- an optional genomic-architecture object, upon which individuals' genomes
are based
- spatialized logistic growth regulating local population densities
- the capability to model realistic movement and offspring dispersal
across conductance surfaces
- neutral and non-neutral evolution capabilities, with spatially contingent
selection
- demographic- and environmental-change capabilities
- the capability to run an arbitrary number of iterations of a model
- the capability to sample data and a variety of statistics at any desired
timesteps during a model run
- numerous visualization methods to aid in model design, exploration,
analysis, and presentation
Geonomics can be installed with pip:
.. code-block:: python
pip install geonomics
For impatient beginners, the following code will run Geonomics' default model::
import geonomics as gnx mod = gnx.run_default_model(delete_params_file=False)
This will build and run geonomics' default model, return its Model object
as mod, and leave its parameters file in your current working directory under
the name 'GNX_default_model_params.py'.
For patient folks, the following diagrams should provide more insight, and the
documentation <https://geonomics.readthedocs.org>_
provides full details.
Procedural Diagram
.. image:: ./img/procedural_diagram.jpg
Users can run Geonomics models in as few as three steps.
1. **Create and edit a parameters file**: After importing geonomics as `gnx`,
users can run the function `gnx.make_parameters_file()` function, feeding in
a series of arguments to indicate the desired number and type of landscape layers,
number and parameterization of species, data and statistics to be recorded, and parameters
file name. Users can then edit the default parameter values in the resulting file to parameterize
their model. Within the parameters file, they have the option of referencing external files
to be used by their model, including static raster files or directories of raster time series, as well
as a CSV file defining a custom genomic architecture.
2. **Use the parameters file to create a model**: After setting up their parameters file, users can
call the `gnx.make_model()` function, providing their parameters file's name as an argument. This
will create a new `gnx.Model` object, containing a `gnx.Landscape` with the defined number of layers,
and a `gnx.Community` with the defined number of species composed of starting individuals. The landscape,
species, and individuals will all be described by a number of characteristics, in accordance with the values
defined in the parameters file.
3. **Run the model**: Users can then call the model's `mod.run` or `mod.walk` methods, to either run their model
to completion or run it manually for some number of time steps. Each time step will include, as applicable,
movement, mating, mortality, environmental and demographic change, and data-writing operations. For more detail
on these operations, see the conceptual diagram that follows.
Conceptual Diagram
.. image:: ./img/conceptual_diagram.jpg
Operations during the main phase of a Geonomics model run. In the center is a species on a multi-layer landscape that includes a selection layer (above) and a movement and carrying capacity layer (below). Surrounding the landscape is a flow-diagram of the major operations during a time step. Operations in dashed boxes are optional.
movement: During the movement stages (top-left), individuals move along movement vectors drawn from various distribution options.
mating: During the mating stage (top-right), an individual (purple outline) randomly chooses a mate (green outline) from all potential mates within its mating radius (dashed circle). The resulting offspring (dashed outline) disperses from its parents' midpoint along a randomly drawn dispersal vector.
mortality: During the mortality stage (bottom-right), deaths are modeled as a Bernoulli process, with the probability of mortality being a product of density-dependence and selection on all traits.
changes: During the changes stage (bottom-left), demographic change events (not pictured) and environmental change events (represented as a series of change rasters corresponding to scheduled time steps, t1, t2, …, tn), take place.
Attribution
This package was written by Drew Ellison Terasaki Hart, as part of his PhD work. It is available to freely distribute and modify, with proper attribution, under the MIT License. Should you have any questons or concerns, please feel free to get in touch! (drew hart berkeley edu)
Should you use Geonomics for research, education, or any other purpose, please cite as:
Terasaki Hart, D.E., Bishop, A.P., Wang, I.J. 2021. Geonomics:
forward-time, spatially explicit, and arbitrarily complex
landscape genomic simulations. Manuscript submitted for publication.
.. code-block:: python
. . :::::: ::: :: :::::::::::. .
.:::::: :::: ::: :: :: :: ::::::::::: ::. .
. . .::::::::: :: :: :::::::::::::::::::::::::. .
.:::::::::: :::::::::: :::::: :::::::: ::.
. . : :::: :: :::: : :: :::::::: : :: : . .
. 55555 :3333: 00000 44 44 00000 44 44 111111 66666 55555 .
. 55 33 00 00 444 44 00 00 44 44 11 66 55 . .
. . 55 33 00 00 44 4 44 00 00 444 444 11 66 555555 . . 55 555 3333 00 00 44 444 00 00 44 4 44 11 66 55 . . 55 5 33 00 00 44 44 00 00 44 44 11 66 555 . . . 55555 :3333: 00000 44 44 00000 44 44 111111 66666 55555 . . . . : :::::::: :::::::::: :: :: : : . . .: ::::: :::::: ::: ::::::: . . . . ::: ::::: :: ::::: . . . . :: :::: . . :: . .
Geonomics claims no affiliation with the philosophy and economic ideology
Georgism <https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Georgism>_, sometimes referred to as
'geonomics'.
Rather, it is a portmanteau of geo\graphy and ge\ nomics. We thought it sounded neat, and found it delightfully confusing.
FAQs
A package for landscape genomic simulation
We found that geonomics demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.

Security News
Multiple deserialization flaws in PyTorch Lightning could allow remote code execution when loading untrusted model files, affecting versions up to 2.4.0.

Security News
NVD now marks all pre-2018 CVEs as "Deferred," signaling it will no longer enrich older vulnerabilities, further eroding trust in its data.