
Security News
/Research
npm Phishing Email Targets Developers with Typosquatted Domain
A phishing attack targeted developers using a typosquatted npm domain (npnjs.com) to steal credentials via fake login pages - watch out for similar scams.
google-nest-camera-proxy
Advanced tools
Proxy your Nest Camera through rtsp-simple-server so you can view it on any RTSP reader
Proxy your Nest Camera through mediamtx so you can view it on any RTSP reader.
Unfortunately, Google does not let you just connect to an RTSP stream, or even an RTSPS string, and read your cameras. It is much more complicated than that. There are a few hoops that you have to jump through:
Once this process is running what it does is reaches out to Google and gets an authentication token for the RTSPS stream, however that token only lasts for 5 minutes. It also includes an extension token, and this code will extend the token every 4 minutes so that you can record a continuous stream.
This is a fairly onerous process, so make sure to read the details before you begin. (There is some more nice documentation of going through the process with screenshots at https://geoffhudik.com/tech/2023/03/04/trying-google-nest-api-with-postman-and-python/)
The biggest roadblock is that access to this API requires registering with Google for Device Access https://developers.google.com/nest/device-access/registration. This has a one time $5 fee.
The documentation https://developers.google.com/nest/device-access/get-started walks you through the rest of the process.
I'm not going to cover all the details on how to get this done, because it is documented better elsewhere. Some addition documentation from Google about using their APIs is here:
mediamtx, which you can download at https://github.com/bluenviron/mediamtx. This is the rtsp proxy that I use to translate from Google RTSPS to RTSP. Make a note of where you install it for the configuration file$ pip install google_nest_camera_proxy
~/.config/nest/config. See the Configuration section below for the details.These instructions were taken from the python-google-nest package (https://pypi.org/project/python-google-nest/) which provides the underlying libraries that I use to connect to the cameras. At a high level it involves:
Be careful as you follow along the guide in https://developers.google.com/nest/device-access/get-started, since you're dealing with so many similar accounts and keys it can be easy to mix something up, and you won't get particularly useful errors.
You should end up with the following pieces of information:
project_id
: ID of the project you created in https://console.nest.google.com/device-access 
client_id
: value from setting up OAuth in https://console.cloud.google.com/ project 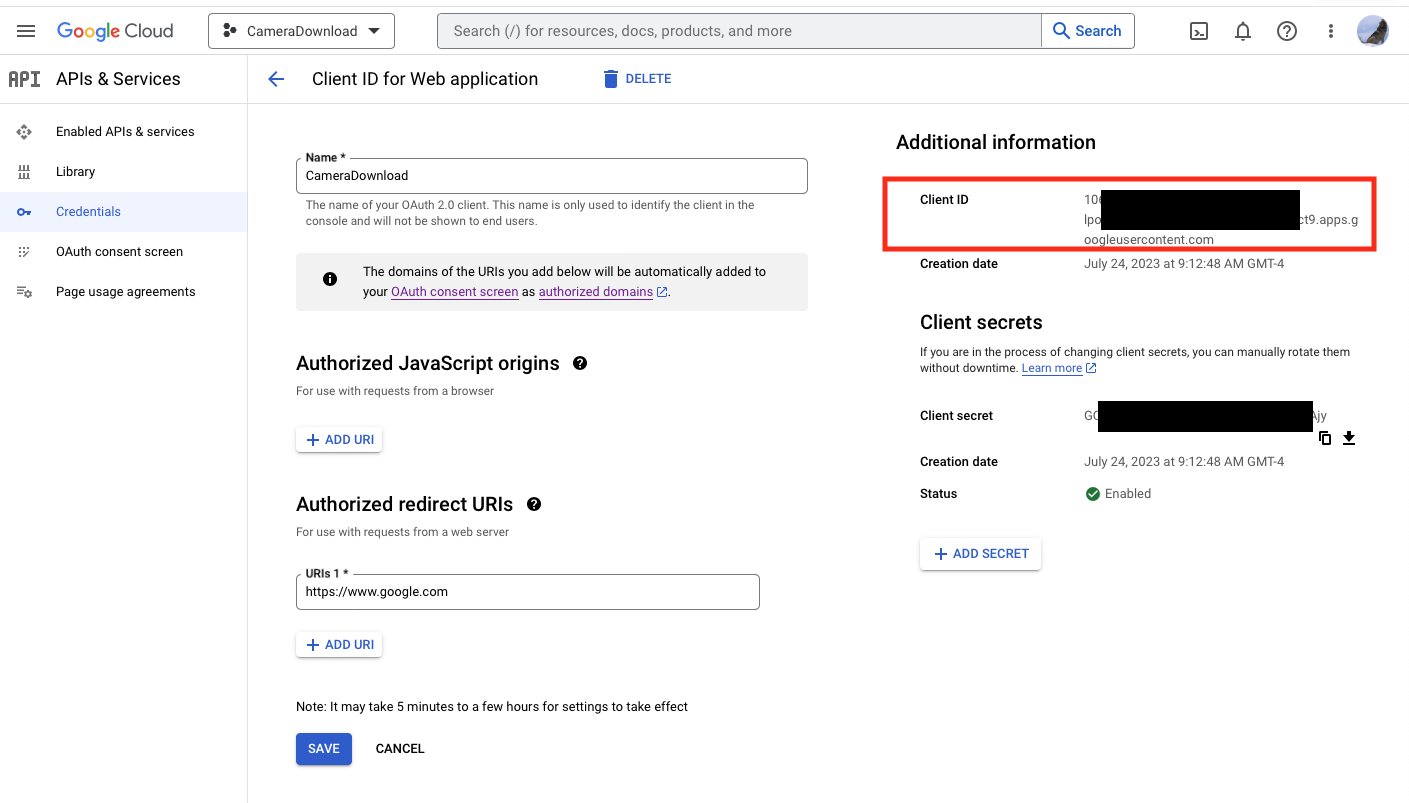
client_secret
: value from setting up OAuth in https://console.cloud.google.com/ project 
You will need those values in the next section.
You need to create a confiuration file with the authentication details, and information about setting up the mediamtx server. Below is a sample file:
[AUTH]
client_id = MYCLIENTID
client_secret = MYSECRET
project_id = MYPROJECTID
access_token_cache_file = /Users/ME/.config/nest/token_cache
[RTSP_SERVER]
executable = /usr/local/bin/mediamtx
config_filename = /Users/ME/.config/nest/rtsp.yml
client_id : This is the client_id from your project (from the credentials page on the Google console)
client_secret : The client secret (from the credentials page on the Google console)
project_id : The project ID (from the project page on the Google console)
access_token_cache_file : Where the token cache is stored
executable
: The location you installed the mediamtx executable.
config_filename
: The location of the mediamtx configuration file. This program adds all the cameras to the configuration file
As part of the pyhon-google-nest package installation that is a dependency of this project, it creates a nest application. The first time you run nest show it will tell you to go to a URL (https://nestservices.google.com/partnerconnections with some parameters), and then you will step through selecting and authorizing the cameras that you want to stream. When you finish this process your browser will have a URL that looks like https://www.google.com/?state=SOME_STATE_VALUE&code=SOME_AUTHENTICATION_CODE&scope=https://www.googleapis.com/auth/sdm.service that you need to copy and paste into the callback, which is then stored in the ~/.config/nest/token_cache file.
Usage: google-nest-camera-proxy [OPTIONS]
Configures the proxy rtsp server, and keeps it updated
CONFIGURATION
-------------
The configuration file looks like this:
[AUTH]
client_id = client_id from Google
client_secret = client secret from Google
project_id = project id from Google
access_token_cache_file = /Users/ME/.config/nest/token_cache
[RTSP_SERVER]
executable = /usr/local/bin/rtsp-simple-server
config_filename = /Users/ME/.config/nest/rtsp
See the README.md file to see how to get those values.
Options:
-c, --configuration-file PATH Where the configuration for this program is
located
-v, --verbose Turn on more informational output
-d, --debug Turn on debugging output
-n, --no-server Update the file, but don't run the mediamtx
server as a subprocess
--help Show this message and exit.
mediamtx Configurationmediamtx comes with a default configuration file that you can leave alone except for changing a few parameters. The only ones you have to change are readUser and readPass. You should put in a username and password, and those will need to be provided to the program that reads the camera.
In addition, mediamtx provides a lot of options that you won't need, so you can turn them off. This is optional, but here are my settings for these fields:
protocols: [tcp]
rtmp: no
hls: no
webrtc: no
When you run google-nest-camera-proxy it regularly modifies the mediamtx configuration file, adding the camera configuration to the bottom of it. Do not edit below this line"
# NEST EDITS BELOW -- DO NOT EDIT THIS LINE OR BELOW
I have found SecuritySpy (https://bensoftware.com/securityspy/) the best product to view and record cameras. To configure SecuritySpy to view the cameras:
+ and select Add Network DeviceAddress box, put the IP address of the box that is running the mtxmedia server. In my case, I use 127.0.0.1, since both the server and SecuritySpy are running on the same hostrtspAddress parameter in the mediamtx.yml file, put 8554 in the RTSP port box.Manual Profile from the Profile dropdown.mediamtx.yml file at the bottom, there are lines that look like this. The tag is the name of the camera, and the source is the rtsps stream that changes regularly. Use the name in the file as the name of the camera, and put it in the Request box. Backyard:
source: rtsps://stream-ue1-bravo.dropcam.com:443/sdm_live_stream/CiUA2vuxr2D61w4Y5ZU2awZvBxZoVD5zE-WgFM5ofLJiMML9NnXLEnEAEGF6Sh1PFqMRG4ynOX1qGu4MgBGjmBwDHgWpkCsHKWybOA?auth=g.0.eyJraWQiOiIyMzhiNTUxZmMyM2EyM2Y4M2E2ZTE3MmJjZTg0YmU3ZjgxMzAzMmM4IiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MBhaOhZ0Y5utipHFESKsG4499KfxIs_xuQ8HF1f6vzicaQ9zBGu3yFAWq6bx5hkd5rcrJRmRDjTgfKO96fy9UIYZZAmJptW9r8KGw
readUser: admin
readPass: mysecurepassword
FrontDoor:
source: rtsps://stream-us1-foxtrot.dropcam.com:443/sdm_live_stream/CiUA2vuxr32E11B1alS1QRyq7w4mwEX8NRJEhMnJ_m2mTO9EiXXCEnEAEGF6SmAHpELf7bUIco7Dx3enLdzFi5I?auth=g.0.eyJraWQiOiIyMzhiNTUxZmMyM2EyM2Y4M2E2ZTE3MmJjZTg0YmU3ZjgxMzAzMmM4IiwiYWxnIjoiUlMyNTYifQ.eyJpc3MiOiJuZXN0LXNlY3VyaXR5LWF1dGhwcm94eSIsInN1YiI6Im5lc3RfaWQ6bmVzdC1waG9lbml4LXByb2Q6MTQxNDQwMSIsInBvbCI6IjNwLW9hdXRoLXNjb3BlLUFQSV9TRE1fU0VSVklDNzfcmq51D5VEk8P8ksPEeUNld-xl7BgO0844T-FjXMk7MKqMDYoum6qwYYwtwVGSP5V0KkMgg50E8PP_rUfm6bKp4KG2i50PGxcNOWFi2Uz0EVH1Q8rmCfX6TWHJb-n3I9I2XH6zv3Z-zjLba7fxvSdgmMjPgRfEF61xNOwnOkja3lqva7I6cWkw
readUser: admin
readPass: mysecurepassword
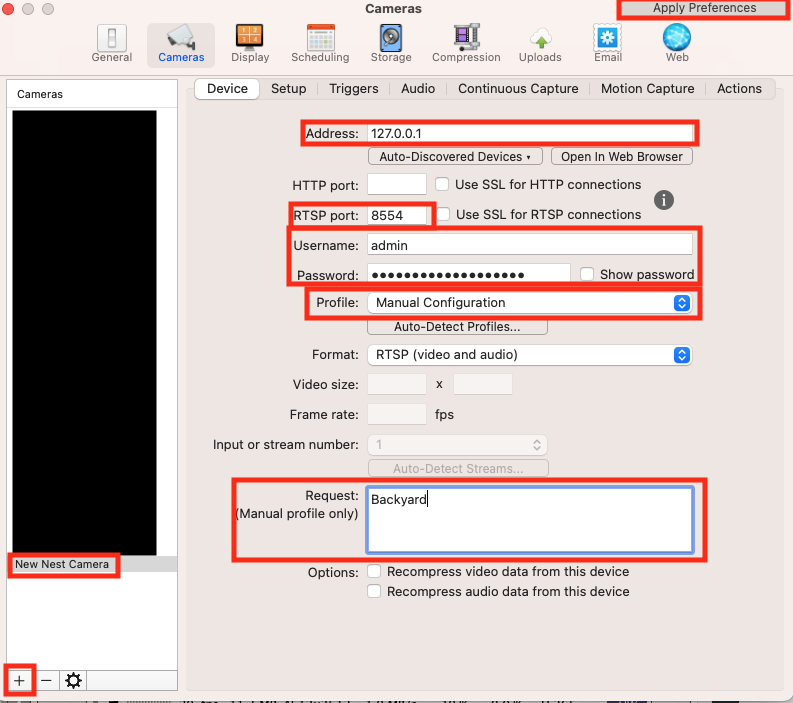
Apply Preferences and in just a few minutes it should start receiving the video.Interested in contributing? Check out the contributing guidelines. Please note that this project is released with a Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
google_nest_camera_proxy was created by Xev Gittler. It is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
google_nest_camera_proxy was created with cookiecutter and the py-pkgs-cookiecutter template.
FAQs
Proxy your Nest Camera through rtsp-simple-server so you can view it on any RTSP reader
We found that google-nest-camera-proxy demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
/Research
A phishing attack targeted developers using a typosquatted npm domain (npnjs.com) to steal credentials via fake login pages - watch out for similar scams.

Security News
Knip hits 500 releases with v5.62.0, refining TypeScript config detection and updating plugins as monthly npm downloads approach 12M.

Security News
The EU Cyber Resilience Act is prompting compliance requests that open source maintainers may not be obligated or equipped to handle.