
Security News
TC39 Advances 11 Proposals for Math Precision, Binary APIs, and More
TC39 advances 11 JavaScript proposals, with two moving to Stage 4, bringing better math, binary APIs, and more features one step closer to the ECMAScript spec.

Image was generated by ImageGen at 12th Feb 2025
PyMARLzoo+ is an extension of EPyMARL, and includes
Algorithms (9) maintained from EPyMARL:
If you find PyMARLzoo+ useful or use PyMARLzoo+ in your research, please cite it in your publications.
@article{papadopoulos2025extended,
title={An Extended Benchmarking of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Complex Fully Cooperative Tasks},
author={Papadopoulos, George and Kontogiannis, Andreas and Papadopoulou, Foteini and Poulianou, Chaido and Koumentis, Ioannis and Vouros, George},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.04773},
year={2025}
}
Before installing PyMARLzoo+, we recommend creating a conda environment:
conda create -y -n pymarlzooplus python=3.8.18
conda activate pymarlzooplus
To install and use PyMARLzoo+ as a package, run the following commands:
pip install pymarlzooplus
To build it from source, run the following commands:
git clone https://github.com/AILabDsUnipi/pymarlzooplus.git
cd pymarlzooplus
pip install -e .
Known issues:
Before running an atari environment (from PettingZoo) for the first time, you have to run:
AutoROM -y
Installation error for box2d-py, run:
sudo apt-get install swig
In case you get ImportError: Library "GLU" not found., run:
sudo apt-get install python3-opengl
In case you get IndexError: list index out of range for pyglet in a non-headless machine using render=True,
set __GLX_VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME=nvidia and __NV_PRIME_RENDER_OFFLOAD=1 as environment variables.
For example, if you want to run your own file example.py , run:
__GLX_VENDOR_LIBRARY_NAME=nvidia __NV_PRIME_RENDER_OFFLOAD=1 python example.py
In case you get ERROR: Failed building wheel for multi-agent-ale-py, probably the problem is with the compiler (if cmake is already installed), so run:
sudo apt-get install g++-9 gcc-9
export CC=gcc-9 CXX=g++-9
In case you get SystemError: ffi_prep_closure(): bad user_data (it seems that the version of the libffi library seen at runtime is different from the 'ffi.h' file seen at compile-time), probably for "waterworld_v4" of PettingZoo, run:
pip install --upgrade --force-reinstall pymunk cffi
In case you get ImportError: ../bin/../lib/libstdc++.so.6: 'version GLIBCXX_3.4.32' not found, run:
conda install -c conda-forge libstdcxx-ng
You can also use the provided Docker files in docker/ to build and run a Docker container with the pymarlzooplus installed as a headless machine.
To build the image, run the container and get into the container, run the following commands after you clone the repository:
docker compose -f docker/docker-compose.yml up --build
docker exec -it $(docker ps | awk 'NR > 1 {print $1}') /bin/bash
In the following instructions, <algo> (or "algo") can be replaced with one of the following algoriths:
You can specify the algorithm arguments:
"algo_args".
"algo" and "scenario"): from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "gymma",
"env_args": {
"key": "scenario",
"time_limit": 50,
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the LBF arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/gymma.yaml.
<algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=gymma with env_args.time_limit=25 env_args.key=<scenario>
Available scenarios (replace "scenario" or <scenario>) we run experiments (our experiments were conducted with v2):
All the above scenarios are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
As a package (replace "algo" and "scenario"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "gymma",
"env_args": {
"key": "scenario",
"time_limit": 500,
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the RWARE arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/gymma.yaml.
From source (replace <algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=gymma with env_args.time_limit=500 env_args.key=<scenario>
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/gymma.yaml.
Available scenarios we run experiments (our experiments were conducted with v1):
All the above scenarios are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
As a package (replace "algo" and "scenario"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "gymma",
"env_args": {
"key": "scenario",
"time_limit": 25,
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the MPE arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/gymma.yaml.
From source (replace <algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=gymma with env_args.time_limit=25 env_args.key=<scenario>
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/gymma.yaml.
Available scenarios we run experiments:
More available scenarios:
All the above scenarios are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
As a package (replace "algo", "task", and 0000):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "pettingzoo",
"env_args": {
"key": "task",
"time_limit": 0000,
"render_mode": "rgb_array", # Options: "human", "rgb_array
"image_encoder": "ResNet18", # Options: "ResNet18", "SlimSAM", "CLIP"
"image_encoder_use_cuda": True, # Whether to load image-encoder in GPU or not.
"image_encoder_batch_size": 10, # How many images to encode in a single pass.
"partial_observation": False, # Only for "Emtombed: Cooperative" and "Space Invaders"
"trainable_cnn": False, # Specifies whether to return image-observation or the encoded vector-observation
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the PettingZoo arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/pettingzoo.yaml. Also, there you can find useful comments for each task's arguments.
From source (replace <algo>, <time-limit>, and <task>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=pettingzoo with env_args.time_limit=<time-limit> env_args.key=<task>
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/pettingzoo.yaml.
Available tasks we run experiments:
The above tasks are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API. Below, we list more tasks which are compatible only with the environment API:
As a package (replace "algo", "scenario", and "rewardType"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "overcooked",
"env_args": {
"time_limit": 500,
"key": "scenario",
"reward_type": "rewardType",
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the Overcooked arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/overcooked.yaml.
From source (replace <algo>, <scenario>, and <reward_type>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=overcooked with env_args.time_limit=500 env_args.key=<scenario> env_args.reward_type=<reward_type>
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/overcooked.yaml.
Available scenarios we run experiments:
More available scenarios:
Reward types available:
All the above scenarios are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
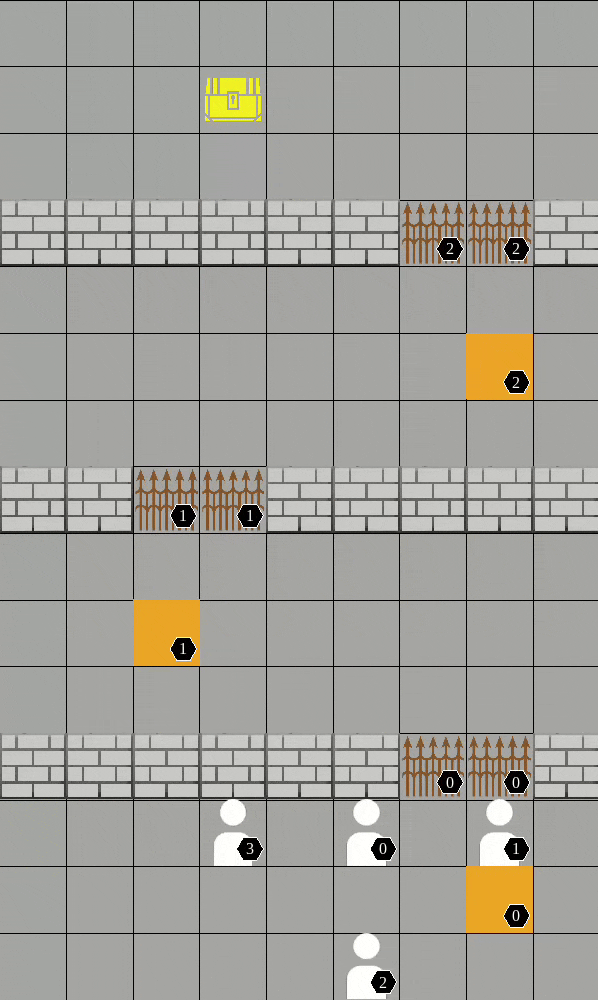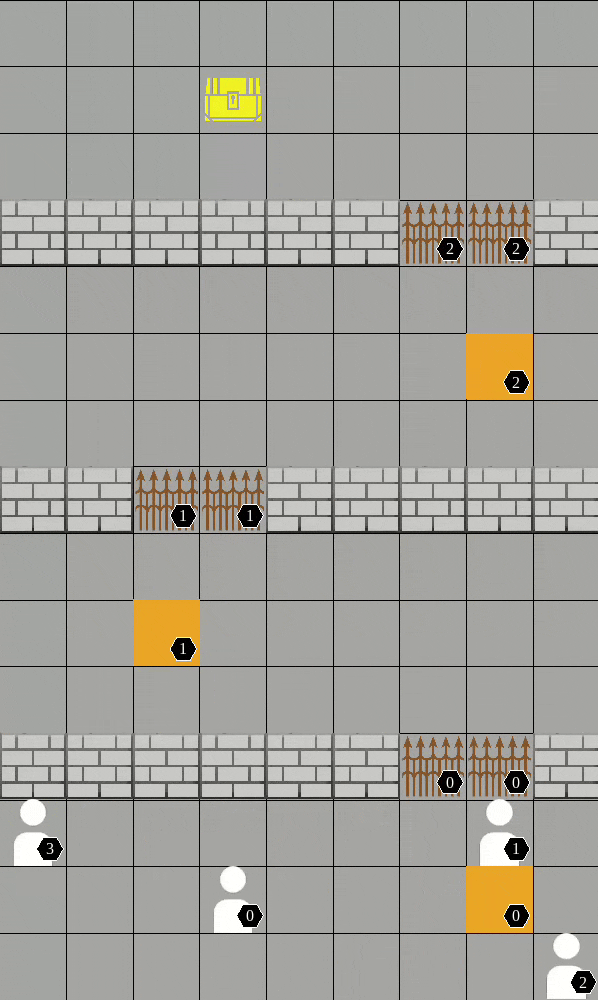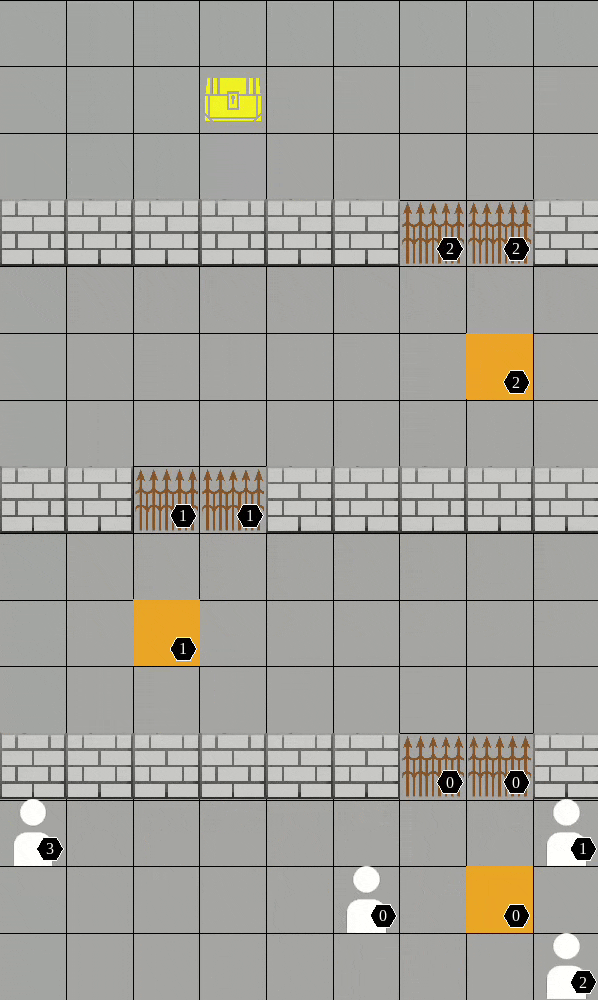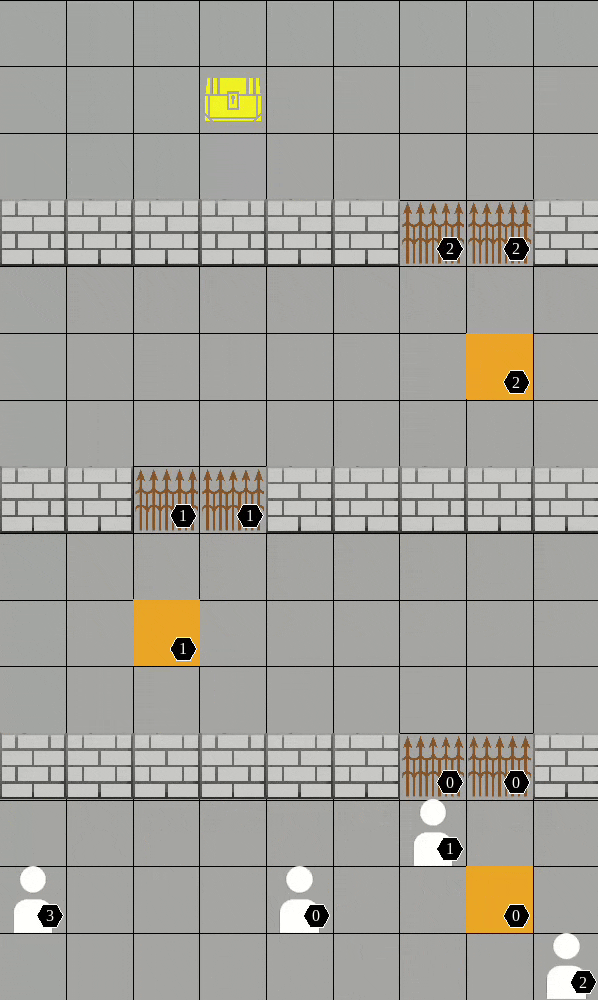
As a package (replace "algo" and "scenario"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "pressureplate",
"env_args": {
"key": "scenario",
"time_limit": 500,
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the Pressure Plate arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/pressureplate.yaml.
From source (replace <algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=pressureplate with env_args.key=<scenario> env_args.time_limit=500
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/pressureplate.yaml.
Available scenarios we run experiments:
More available scenarios:
All the above scenarios are compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
As a package (replace "algo" and "scenario"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "capturetarget",
"env_args": {
"time_limit": 60,
"key" : "scenario",
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the Capture Target arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/capturetarget.yaml.
From source (replace <algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=capturetarget with env_args.key=<scenario> env_args.time_limit=60
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/capturetarget.yaml. Also, there you can find useful comments for the rest of arguments.
Available scenario:
The above scenario is compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
As a package (replace "algo" and "scenario"):
from pymarlzooplus import pymarlzooplus
params_dict = {
"config": "algo",
"algo_args": {},
"env-config": "boxpushing",
"env_args": {
"key": "scenario",
"time_limit": 60,
"seed": 2024
}
}
pymarlzooplus(params_dict)
Find all the Box Pushing arguments in the configuration file pymarlzooplus/config/envs/boxpushing.yaml.
From source (replace <algo> and <scenario>):
python pymarlzooplus/main.py --config=<algo> --env-config=boxpushing with env_args.key=<scenario> env_args.time_limit=60
Before running an experiment, edit the configuration file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs/boxpushing.yaml.
Available scenario:
The above scenario is compatible both with our training framework and the environment API.
Except from using our training framework, you can use PyMARLzoo+ in your custom training pipeline as follows:
# Import package
from pymarlzooplus.envs import REGISTRY as env_REGISTRY
# Example of arguments for PettingZoo
args = {
"env": "pettingzoo",
"env_args": {
"key": "pistonball_v6",
"time_limit": 900,
"render_mode": "rgb_array",
"image_encoder": "ResNet18",
"image_encoder_use_cuda": True,
"image_encoder_batch_size": 10,
"centralized_image_encoding": False,
"partial_observation": False,
"trainable_cnn": False,
"kwargs": "('n_pistons',10),",
"seed": 2024
}
}
# Initialize environment
env = env_REGISTRY[args["env"]](**args["env_args"])
n_agns = env.get_n_agents()
n_acts = env.get_total_actions()
# Reset the environment
obs, state = env.reset()
done = False
# Run an episode
while not done:
# Render the environment (optional)
env.render()
# Insert the policy's actions here
actions = env.sample_actions()
# Apply an environment step
reward, done, extra_info = env.step(actions)
obs = env.get_obs()
state = env.get_state()
info = env.get_info()
# Terminate the environment
env.close()
The code above can be used as is (changing the arguments accordingly) with the fully cooperative tasks (see section Run training to find out which tasks are fully cooperative).
n_agns (int)
Number of agents in the environment.
n_acts (int)
Number of available actions per agent (all agents share the same action space).
reward (float)
Sum of all agents’ rewards for the current step.
done (bool)
False if any agent is still active; True only when all agents are done.
extra_info (dict)
Typically is an empty dictionary.
info (dict)
Contains a single key, "TimeLimit.truncated", which is False if any agent’s time limit has not been exceeded.
obs (tuple of numpy arrays)
One array per agent.
(cnn_features_dim,) (default 128).(3, h, w).state (numpy array)
The global state:
(cnn_features_dim * n_agns,).(n_agents, 3, h, w).In the file pymarlzooplus/scripts/api_script.py, you can find a complete example for all the supported environments.
For a description of each environment's arguments, please see the corresponding config file in pymarlzooplus/config/envs.
We include a script named search.py which reads a search configuration file (e.g. the included search.config.example.yaml) and runs a hyperparameter search in one or more tasks. The script can be run using
python search.py run --config=search.config.example.yaml --seeds 5 locally
In a cluster environment where one run should go to a single process, it can also be called in a batch script like:
python search.py run --config=search.config.example.yaml --seeds 5 single 1
where the 1 is an index to the particular hyperparameter configuration and can take values from 1 to the number of different combinations.
You can save the learnt models to disk by setting save_model = True, which is set to False by default. The frequency of saving models can be adjusted using save_model_interval configuration. Models will be saved in the result directory, under the folder called models. The directory corresponding each run will contain models saved throughout the experiment, each within a folder corresponding to the number of timesteps passed since starting the learning process.
Learnt models can be loaded using the checkpoint_path parameter, after which the learning will proceed from the corresponding timestep.
If you use PyMARLzoo+ in your research, please cite the An Extended Benchmarking of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Complex Fully Cooperative Tasks .
George Papadopoulos, Andreas Kontogiannis, Foteini Papadopoulou, Chaido Poulianou, Ioannis Koumentis, George Vouros. An Extended Benchmarking of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Complex Fully Cooperative Tasks, AAMAS 2025.
@article{papadopoulos2025extended,
title={An Extended Benchmarking of Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Complex Fully Cooperative Tasks},
author={Papadopoulos, George and Kontogiannis, Andreas and Papadopoulou, Foteini and Poulianou, Chaido and Koumentis, Ioannis and Vouros, George},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:2502.04773},
year={2025}
}
If you use EPyMARL in your research, please cite the following:
Georgios Papoudakis, Filippos Christianos, Lukas Schäfer, & Stefano V. Albrecht. Benchmarking Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Cooperative Tasks, Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks (NeurIPS), 2021
@inproceedings{papoudakis2021benchmarking,
title={Benchmarking Multi-Agent Deep Reinforcement Learning Algorithms in Cooperative Tasks},
author={Georgios Papoudakis and Filippos Christianos and Lukas Schäfer and Stefano V. Albrecht},
booktitle = {Proceedings of the Neural Information Processing Systems Track on Datasets and Benchmarks (NeurIPS)},
year={2021},
url = {http://arxiv.org/abs/2006.07869},
openreview = {https://openreview.net/forum?id=cIrPX-Sn5n},
code = {https://github.com/uoe-agents/epymarl},
}
If you use the original PyMARL in your research, please cite the SMAC paper.
M. Samvelyan, T. Rashid, C. Schroeder de Witt, G. Farquhar, N. Nardelli, T.G.J. Rudner, C.-M. Hung, P.H.S. Torr, J. Foerster, S. Whiteson. The StarCraft Multi-Agent Challenge, CoRR abs/1902.04043, 2019.
In BibTeX format:
@article{samvelyan19smac,
title = {{The} {StarCraft} {Multi}-{Agent} {Challenge}},
author = {Mikayel Samvelyan and Tabish Rashid and Christian Schroeder de Witt and Gregory Farquhar and Nantas Nardelli and Tim G. J. Rudner and Chia-Man Hung and Philiph H. S. Torr and Jakob Foerster and Shimon Whiteson},
journal = {CoRR},
volume = {abs/1902.04043},
year = {2019},
}
If you encounter a bug, have a feature request, or any other questions about the project, we encourage you to open an issue. Please follow these steps:
Thank you for contributing to the project and helping us improve!
All the source code that has been taken from the EPyMARL and PyMARL repository was licensed (and remains so) under the Apache License v2.0 (included in LICENSE file).
Any new code is also licensed under the Apache License v2.0
FAQs
An extended benchmarking of multi-agent reinforcement learning algorithms
We found that pymarlzooplus demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
TC39 advances 11 JavaScript proposals, with two moving to Stage 4, bringing better math, binary APIs, and more features one step closer to the ECMAScript spec.

Research
/Security News
A flawed sandbox in @nestjs/devtools-integration lets attackers run code on your machine via CSRF, leading to full Remote Code Execution (RCE).

Product
Customize license detection with Socket’s new license overlays: gain control, reduce noise, and handle edge cases with precision.