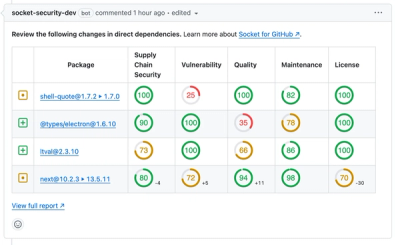
Product
A New Design for GitHub PR Comments
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.
.. image:: https://travis-ci.org/mapbox/snuggs.svg?branch=master :target: https://travis-ci.org/mapbox/snuggs
.. image:: https://coveralls.io/repos/mapbox/snuggs/badge.svg :target: https://coveralls.io/r/mapbox/snuggs
Snuggs are s-expressions for Numpy
.. code-block:: python
>>> snuggs.eval("(+ (asarray 1 1) (asarray 2 2))")
array([3, 3])
Snuggs wraps Numpy in expressions with the following syntax:
.. code-block::
expression = "(" (operator | function) *arg ")"
arg = expression | name | number | string
.. code-block:: python
import snuggs
snuggs.eval('(+ 1 2)')
# 3
Arrays can be created using asarray.
.. code-block:: python
snuggs.eval("(* 3.5 (asarray 1 1))")
# array([ 3.5, 3.5])
Expressions can also refer by name to arrays in a local context.
.. code-block:: python
snuggs.eval("(+ (asarray 1 1) b)", b=np.array([2, 2]))
# array([3, 3])
This local context may be provided using keyword arguments (e.g.,
b=np.array([2, 2])), or by passing a dictionary that stores
the keys and associated array values. Passing a dictionary, specifically
an OrderedDict, is important when using a function or operator that
references the order in which values have been provided. For example,
the read function will lookup the i-th value passed:
.. code-block:: python
ctx = OrderedDict((
('a', np.array([5, 5])),
('b', np.array([2, 2]))
))
snuggs.eval("(- (read 1) (read 2))", ctx)
# array([3, 3])
Arithmetic (* + / -) and logical (< <= == != >= > & |) operators are
available. Members of the numpy module such as asarray(), mean(),
and where() are also available.
.. code-block:: python
snuggs.eval("(mean (asarray 1 2 4))")
# 2.3333333333333335
.. code-block:: python
snuggs.eval("(where (& tt tf) 1 0)",
tt=numpy.array([True, True]),
tf=numpy.array([True, False]))
# array([1, 0])
New in snuggs 1.1 are higher-order functions map and partial.
.. code-block:: python
snuggs.eval("((partial * 2) 2)")
# 4
snuggs.eval('(asarray (map (partial * 2) (asarray 1 2 3)))')
# array([2, 4, 6])
Snuggs makes simple calculator programs possible. None of the optimizations
of, e.g., numexpr <https://github.com/pydata/numexpr>__ (multithreading,
elimination of temporary data, etc) are currently available.
If you're looking to combine Numpy with a more complete Lisp, see
Hy <https://github.com/hylang/hy>__:
.. code-block:: clojure
=> (import numpy)
=> (* 2 (.asarray numpy [1 2 3]))
array([2, 4, 6])
FAQs
Snuggs are s-expressions for Numpy
We found that snuggs demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.
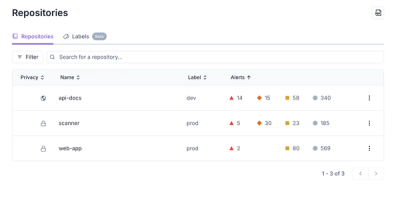
Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.

Security News
Slopsquatting is a new supply chain threat where AI-assisted code generators recommend hallucinated packages that attackers register and weaponize.