
Security News
VulnCon 2025: NVD Scraps Industry Consortium Plan, Raising Questions About Reform
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
Comprehensive EOF analysis in Python with xarray: A versatile, multidimensional, and scalable tool for advanced climate data analysis

| Versions |   |
|---|---|
| Build & Testing |  |
| Code Quality |   |
| Documentation | |
| Citation | |
| Licensing |  |
| User Engagement |  |
xeofs is a specialized Python package designed for dimensionality reduction in climate science, aimed at extracting meaningful patterns from large datasets. It provides eigenmethods such as Principal Component Analysis (EOF analysis) and several related variants. Seamlessly integrated with xarray and Dask, xeofs enables efficient handling and scalable computation of large, multi-dimensional datasets.
xarray objects, it applies dimensionality reduction to multi-dimensional data while maintaining data labels.Dask xarray objectsxr.DataArray or xr.DatasetNaN values within the dataTo install the package, use either of the following commands:
conda install -c conda-forge xeofs
or
pip install xeofs
In order to get started with xeofs, follow these simple steps:
Import the package
>>> import xarray as xr # for example data only
>>> import xeofs as xe
Load example data
>>> t2m = xr.tutorial.open_dataset("air_temperature")
>>> t2m_west = t2m.isel(lon=slice(None, 20))
>>> t2m_east = t2m.isel(lon=slice(21, None))
EOF analysis Initiate and fit the EOF/PCA model to the data
>>> eof = xe.single.EOF(n_modes=10)
>>> eof.fit(t2m, dim="time") # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
<xeofs.single.eof.EOF object at ...>
Now, you can access the model's EOF components and PC scores:
>>> comps = eof.components() # EOFs (spatial patterns)
>>> scores = eof.scores() # PCs (temporal patterns)
Varimax-rotated EOF analysis
Initiate and fit an EOFRotator class to the model to obtain a varimax-rotated EOF analysis
>>> rotator = xe.single.EOFRotator(n_modes=3)
>>> rotator.fit(eof) # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
<xeofs.single.eof_rotator.EOFRotator object at ...>
>>> rot_comps = rotator.components() # Rotated EOFs (spatial patterns)
>>> rot_scores = rotator.scores() # Rotated PCs (temporal patterns)
Maximum Covariance Analysis (MCA)
>>> mca = xe.cross.MCA(n_modes=10)
>>> mca.fit(t2m_west, t2m_east, dim="time") # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
<xeofs.cross.mca.MCA object at ...>
>>> comps1, comps2 = mca.components() # Singular vectors (spatial patterns)
>>> scores1, scores2 = mca.scores() # Expansion coefficients (temporal patterns)
Varimax-rotated MCA
>>> rotator = xe.cross.MCARotator(n_modes=10)
>>> rotator.fit(mca) # doctest: +ELLIPSIS
<xeofs.cross.mca_rotator.MCARotator object at ...>
>>> rot_comps = rotator.components() # Rotated singular vectors (spatial patterns)
>>> rot_scores = rotator.scores() # Rotated expansion coefficients (temporal patterns)
To further explore the capabilities of xeofs, check out the available documentation and examples.
For a full list of currently available methods, see the Reference API.
For a more comprehensive overview and usage examples, visit the documentation.
Contributions are highly welcomed and appreciated. If you're interested in improving xeofs or fixing issues, please read our Contributing Guide.
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
For questions or support, please open a Github issue.
When using xeofs, kindly remember to cite the original references of the methods employed in your work. Additionally, if xeofs is proving useful in your research, we'd appreciate if you could acknowledge its use with the following citation:
@article{rieger_xeofs_2024,
author = {Rieger, Niclas and Levang, Samuel J.},
doi = {10.21105/joss.06060},
journal = {Journal of Open Source Software},
month = jan,
number = {93},
pages = {6060},
title = {{xeofs: Comprehensive EOF analysis in Python with xarray}},
url = {https://joss.theoj.org/papers/10.21105/joss.06060},
volume = {9},
year = {2024}
}
FAQs
Comprehensive EOF analysis in Python with xarray: A versatile, multidimensional, and scalable tool for advanced climate data analysis
We found that xeofs demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
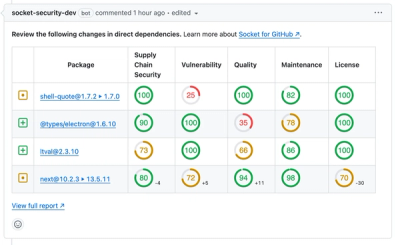
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.
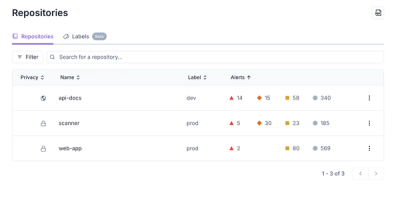
Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.