
Security News
VulnCon 2025: NVD Scraps Industry Consortium Plan, Raising Questions About Reform
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular
Advanced tools
Official ElasticEmail SDK. This API is based on the REST API architecture, allowing the user to easily manage their data with this resource-based approach.
To install the required dependencies and to build the typescript sources run:
npm install
npm run build
First build the package then run npm publish dist (don't forget to specify the dist folder!)
Navigate to the folder of your consuming project and run one of next commands.
published:
npm install @elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular@4.1.22 --save
without publishing (not recommended):
npm install PATH_TO_GENERATED_PACKAGE/dist.tgz --save
It's important to take the tgz file, otherwise you'll get trouble with links on windows
using npm link:
In PATH_TO_GENERATED_PACKAGE/dist:
npm link
In your project:
npm link @elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular
Note for Windows users: The Angular CLI has troubles to use linked npm packages. Please refer to this issue https://github.com/angular/angular-cli/issues/8284 for a solution / workaround. Published packages are not effected by this issue.
In your Angular project:
// without configuring providers
import { ApiModule } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
@NgModule({
imports: [
ApiModule,
// make sure to import the HttpClientModule in the AppModule only,
// see https://github.com/angular/angular/issues/20575
HttpClientModule
],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}
// configuring providers
import { ApiModule, Configuration, ConfigurationParameters } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
export function apiConfigFactory (): Configuration {
const params: ConfigurationParameters = {
// set configuration parameters here.
}
return new Configuration(params);
}
@NgModule({
imports: [ ApiModule.forRoot(apiConfigFactory) ],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
providers: [],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}
// configuring providers with an authentication service that manages your access tokens
import { ApiModule, Configuration } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
@NgModule({
imports: [ ApiModule ],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
providers: [
{
provide: Configuration,
useFactory: (authService: AuthService) => new Configuration(
{
basePath: environment.apiUrl,
accessToken: authService.getAccessToken.bind(authService)
}
),
deps: [AuthService],
multi: false
}
],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}
import { DefaultApi } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private apiGateway: DefaultApi) { }
}
Note: The ApiModule is restricted to being instantiated once app wide. This is to ensure that all services are treated as singletons.
In order to use multiple ApiModules generated from different OpenAPI files,
you can create an alias name when importing the modules
in order to avoid naming conflicts:
import { ApiModule } from 'my-api-path';
import { ApiModule as OtherApiModule } from 'my-other-api-path';
import { HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';
@NgModule({
imports: [
ApiModule,
OtherApiModule,
// make sure to import the HttpClientModule in the AppModule only,
// see https://github.com/angular/angular/issues/20575
HttpClientModule
]
})
export class AppModule {
}
If different than the generated base path, during app bootstrap, you can provide the base path to your service.
import { BASE_PATH } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
bootstrap(AppComponent, [
{ provide: BASE_PATH, useValue: 'https://your-web-service.com' },
]);
or
import { BASE_PATH } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
@NgModule({
imports: [],
declarations: [ AppComponent ],
providers: [ provide: BASE_PATH, useValue: 'https://your-web-service.com' ],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule {}
First extend your src/environments/*.ts files by adding the corresponding base path:
export const environment = {
production: false,
API_BASE_PATH: 'http://127.0.0.1:8080'
};
In the src/app/app.module.ts:
import { BASE_PATH } from '@elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular';
import { environment } from '../environments/environment';
@NgModule({
declarations: [
AppComponent
],
imports: [ ],
providers: [{ provide: BASE_PATH, useValue: environment.API_BASE_PATH }],
bootstrap: [ AppComponent ]
})
export class AppModule { }
Without further customization, only path-parameters of style 'simple' and Dates for format 'date-time' are encoded correctly.
Other styles (e.g. "matrix") are not that easy to encode and thus are best delegated to other libraries (e.g.: @honoluluhenk/http-param-expander).
To implement your own parameter encoding (or call another library),
pass an arrow-function or method-reference to the encodeParam property of the Configuration-object
(see General Usage above).
Example value for use in your Configuration-Provider:
new Configuration({
encodeParam: (param: Param) => myFancyParamEncoder(param),
})
FAQs
Official ElasticEmail SDK. This API is based on the REST API architecture, allowing the user to easily manage their data with this resource-based approach.
The npm package @elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular receives a total of 2 weekly downloads. As such, @elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that @elasticemail/elasticemail-client-ts-angular demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
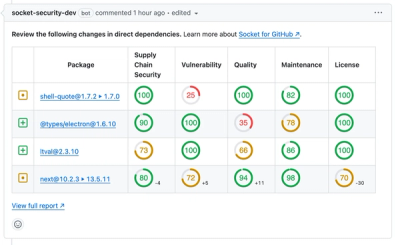
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.
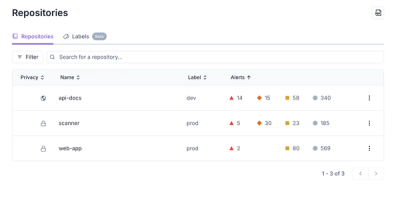
Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.