bird-oid









A 3D boid system with accompanying emergent behaviors. Implementation mostly based on Craig Reynolds paper Steering Behaviors For Autonomous Characters.



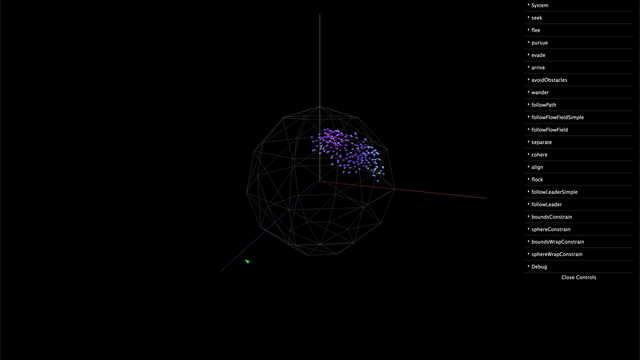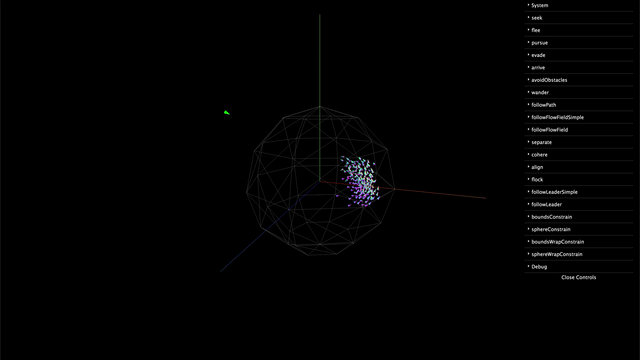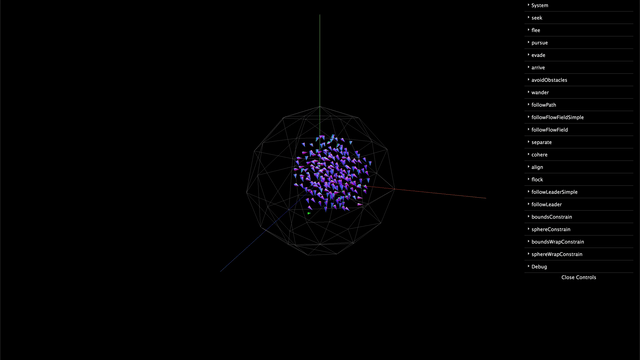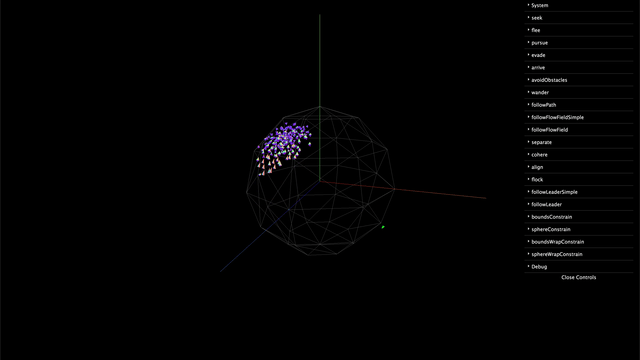
Installation
npm install bird-oid
Usage
import { System as BoidSystem, behaviors } from "bird-oid";
const BOIDS_COUNT = 100;
const WANDER_SPEED = 2;
const system = new BoidSystem({
maxSpeed: 0.3,
maxForce: 0.4,
});
const boidBehaviors = [
{
fn: behaviors.wander,
options: {
distance: system.scale * 0.04,
radius: system.scale * 0.3,
theta: 0,
phi: 0.3,
},
},
{
enabled: true,
fn: behaviors.boundsConstrain,
scale: 2,
},
{
enabled: false,
fn: behaviors.boundsWrapConstrain,
},
];
for (let i = 0; i < BOIDS_COUNT; i++) {
const boid = new Boid(boidBehaviors);
boid.position = system.getRandomPosition();
boid.velocity = [
Math.random() * 0.5 * system.maxSpeed,
Math.random() * 0.5 * system.maxSpeed,
Math.random() * 0.5 * system.maxSpeed,
];
system.addBoid(boid);
}
const frame = () => {
const dt = Math.min(0.1, myClock.getDelta());
boidBehaviors[0].options.theta +=
Math.random() * WANDER_SPEED - WANDER_SPEED * 0.5;
boidBehaviors[0].options.phi +=
Math.random() * WANDER_SPEED - WANDER_SPEED * 0.5;
system.update(dt);
requestAnimationFrame(frame);
};
requestAnimationFrame(() => {
frame();
});
API
Modules
- behaviors
Steering based on https://www.red3d.com/cwr/steer/gdc99/
Use these function as fn property of the BehaviorObject passed to a Boid.
Classes
- Boid
A data structure for a single Boid.
- Obstacle
Data structure used for obstacle avoidance behavior.
- Path
Data structure used for path following behavior.
- System
Handle common boids update and global state.
Typedefs
- SystemOptions :
Object
- Radians :
number
- BehaviorObject :
Object
- ApplyBehaviorObject :
Object
- BehaviorOptions :
Object
- BasicBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- ExtendedBasicBehaviorOptions :
BasicBehaviorOptions
- BasicWithRadiusBehaviorOptions :
BasicBehaviorOptions
- ObstacleBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- WanderBehaviorOptions :
Object
- FollowPathBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- FollowFlowFieldSimpleBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- FollowFlowFieldBehaviorOptions :
FollowFlowFieldSimpleBehaviorOptions
- FollowLeaderSimpleBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- FollowLeaderBehaviorOptions :
FollowLeaderSimpleBehaviorOptions
- GroupsBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- ConstraintBehaviorOptions :
BehaviorOptions
- BoundsConstraintBehaviorOptions :
ConstraintBehaviorOptions
- SphereConstraintBehaviorOptions :
ConstraintBehaviorOptions
- WrapConstraintBehaviorOptions :
Object
- BoundsWrapConstraintBehaviorOptions :
WrapConstraintBehaviorOptions
- SphereWrapConstraintBehaviorOptions :
WrapConstraintBehaviorOptions
behaviors
Steering based on https://www.red3d.com/cwr/steer/gdc99/
Use these function as fn property of the BehaviorObject passed to a Boid.
"Seek (or pursuit of a static target) acts to steer the character towards a specified position in global space."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.flee(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Flee is simply the inverse of seek and acts to steer the character so that its velocity is radially aligned away from the target. The desired velocity points in the opposite direction."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.pursue(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Pursuit is similar to seek except that the quarry (target) is another moving character. [...] The position of a character T units of time in the future (assuming it does not maneuver) can be obtained by scaling its velocity by T and adding that offset to its current position. Steering for pursuit is then simply the result of applying the seek steering behavior to the predicted target location."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.evade(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Evasion is analogous to pursuit, except that flee is used to steer away from the predicted future position of the target character."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.arrive(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Arrival behavior is identical to seek while the character is far from its target. But instead of moving through the target at full speed, this behavior causes the character to slow down as it approaches the target, eventually slowing to a stop coincident with the target"
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.avoidObstacles(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"The implementation of obstacle avoidance behavior described here will make a simplifying assumption that both the character and obstacle can be reasonably approximated as spheres, although the basic concept can be easily extend to more precise shape models. [...] It is convenient to consider the geometrical situation from the character’s local coordinate system. The goal of the behavior is to keep an imaginary cylinder of free space in front of the character. The cylinder lies along the character’s forward axis, has a diameter equal to the character’s bounding sphere, and extends from the character’s center for a distance based on the character’s speed and agility. An obstacle further than this distance away is not an immediate threat. The obstacle avoidance behavior considers each obstacle in turn (perhaps using a spatial portioning scheme to cull out distance obstacles) and determines if they intersect with the cylinder. By localizing the center of each spherical obstacle, the test for non-intersection with the cylinder is very fast. The local obstacle center is projected onto the side-up plane (by setting its forward coordinate to zero) if the 2D distance from that point to the local origin is greater than the sum of the radii of the obstacle and the character, then there is no potential collision. Similarly obstacles which are fully behind the character, or fully ahead of the cylinder, can be quickly rejected. For any remaining obstacles a line-sphere intersection calculation is performed. The obstacle which intersects the forward axis nearest the character is selected as the “most threatening.” Steering to avoid this obstacle is computed by negating the (lateral) side-up projection of the obstacle’s center.
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.wander(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"The steering force takes a “random walk” from one direction to another. This idea [...] is to constrain the steering force to the surface of a sphere located slightly ahead of the character. To produce the steering force for the next frame: a random displacement is added to the previous value, and the sum is constrained again to the sphere’s surface. The sphere’s radius [...] determines the maximum wandering “strength” and the magnitude of the random displacement [...] determines the wander “rate.”"
Note: Don't forget to update theta and phi angles: angle += Math.random() _ WANDER_SPEED - WANDER_SPEED _ 0.5;
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.followPath(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Path following behavior enables a character to steer along a predetermined path, such as a roadway, corridor or tunnel."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.followFlowFieldSimple(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"In flow field following behavior the character steers to align its motion with the local tangent of a flow field (also known as a force field or a vector field). [...] The future position of a character is estimated and the flow field is sampled at that location. This flow direction [...] is the “desired velocity” and the steering direction (vector S) is simply the difference between the current velocity (vector V) and the desired velocity."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.followFlowField(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.followLeaderSimple(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Leader following behavior causes one or more character to follow another moving character designated as the leader. Generally the followers want to stay near the leader, without crowding the leader, and taking care to stay out of the leader’s way (in case they happen to find them selves in front of the leader). In addition, if there is more than one follower, they want to avoid bumping each other. The implementation of leader following relies on arrival behavior (see above) a desire to move towards a point, slowing as it draws near. The arrival target is a point offset slightly behind the leader. (The offset distance might optionally increases with speed.) If a follower finds itself in a rectangular region in front of the leader, it will steer laterally away from the leader’s path before resuming arrival behavior. In addition the followers use separation behavior to prevent crowding each other."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.followLeader(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
Notes: next behaviour should be a separation
Kind: static method of behaviors
"To compute steering for separation, first a search is made to find other characters within the specified neighborhood. [...] For each nearby character, a repulsive force is computed by subtracting the positions of our character and the nearby character, normalizing, and then applying a 1/r weighting. (That is, the position offset vector is scaled by 1/r 2.) Note that 1/r is just a setting that has worked well, not a fundamental value. These repulsive forces for each nearby character are summed together to produce the overall steering force."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.cohere(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Cohesion steering behavior gives an character the ability to cohere with (approach and form a group with) other nearby characters. [...] Steering for cohesion can be computed by finding all characters in the local neighborhood (as described above for separation), computing the “average position” (or “center of gravity”) of the nearby characters. The steering force can applied in the direction of that “average position” (subtracting our character position from the average position, as in the original boids model), or it can be used as the target for seek steering behavior."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.align(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"Alignment steering behavior gives an character the ability to align itself with (that is, head in the same direction and/or speed as) other nearby characters [...]. Steering for alignment can be computed by finding all characters in the local neighborhood (as described above for separation), averaging together the velocity (or alternately, the unit forward vector) of the nearby characters. This average is the “desired velocity,” and so the steering vector is the difference between the average and our character’s current velocity (or alternately, its unit forward vector)."
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.flock(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
"[...] in addition to other applications, the separation, cohesion and alignment behaviors can be combined to produce the boids model of flocks, herds and schools"
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.boundsConstrain(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
Constraint in system bounds.
Kind: static method of behaviors
Constraint in sphere bounds.
Kind: static method of behaviors
behaviors.boundsWrapConstrain(options) ⇒ module:gl-matrix~vec3
Wrap to opposite bound (no velocity change).
Kind: static method of behaviors
Wrap to opposite bound (no velocity change).
Kind: static method of behaviors
Boid
A data structure for a single Boid.
Kind: global class
Properties
| position | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| velocity | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| acceleration | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| target | Array.<module:gl-matrix~vec3> |
| behavious | Array.<BehaviorObject> |
new Boid(behaviors)
boid.applyForce(force)
Add a force to the boid's acceleration vector. If you need mass, you can either use behaviors.scale or override.
Kind: instance method of Boid
| force | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
boid.applyBehaviors(applyOptions)
Compute all the behaviors specified in boid.behaviors and apply them via applyForce. Arguments usually come from the system and can be overridden via behavior.options.
Kind: instance method of Boid
boid.update(dt, maxSpeed)
Update a boid's position according to its current acceleration/velocity and reset acceleration. Usually called consecutively to boid.applyBehaviors.
Kind: instance method of Boid
Obstacle
Data structure used for obstacle avoidance behavior.
Kind: global class
new Obstacle(position, radius)
| position | module:gl-matrix~vec3 | The center of the obstacle. |
| radius | number | The radius of the sphere. |
Path
Data structure used for path following behavior.
Kind: global class
new Path(points, radius)
| points | Array.<module:gl-matrix~vec3> | An array of 3d points. |
| radius | number | |
System
Handle common boids update and global state.
Kind: global class
new System(options)
system.getRandomPosition() ⇒ Array.<number>
Get a position within the system's bounds.
Kind: instance method of System
system.addBoid(boid)
Push a new boid to the system.
Kind: instance method of System
system.update(dt)
Update all behaviours in the system.
Kind: instance method of System
SystemOptions : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| [scale] | number | 1 | A global scale for the system. |
| [maxSpeed] | number | scale | A maximum speed for the boids in the system. Can be tweaked individually via boid.maxSpeed. |
| [maxForce] | number | scale | A maximum force for each behavior of a boid. Can be tweaked individually via boid.maxForce or via behaviors.options.maxForce. |
| [center] | module:gl-matrix~vec3 | [0, 0, 0] | A center point for the system. |
| [bounds] | module:gl-matrix~vec3 | [scale, scale, scale] | Positives bounds x/y/z for the system expanding from the center point. |
Radians : number
Kind: global typedef
BehaviorObject : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| fn | function |
| enabled | boolean |
| scale | number |
| options | Object |
ApplyBehaviorObject : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| boids | Array.<Boid> |
| maxSpeed | number |
| [maxForce] | number |
| center | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| bounds | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
BehaviorOptions : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| position | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| velocity | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| maxSpeed | number |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| target | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| targetVelocity | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| obstacles | Array.<Obstacles> | |
| maxAvoidForce | number | |
| [fixedDistance] | boolean | false |
WanderBehaviorOptions : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| velocity | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| distance | number |
| maxSpeed | number |
| radius | number |
| theta | Radians |
| phi | Radians |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| path | Path | |
| [fixedDistance] | boolean | false |
FollowFlowFieldSimpleBehaviorOptions : BehaviorOptions
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| flowField | module:vector-field~FlowField |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| flowField | module:vector-field~FlowField | |
| [fixedDistance] | boolean | false |
FollowLeaderSimpleBehaviorOptions : BehaviorOptions
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| leader | Boid |
| distance | number |
| radius | number |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| [evadeScale] | number | 1 |
| [arriveScale] | number | 1 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| center | module:gl-matrix~vec3 | |
| maxDistance | number | |
| [fixedDistance] | boolean | false |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| bounds | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
WrapConstraintBehaviorOptions : Object
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| position | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
| center | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
| bounds | module:gl-matrix~vec3 |
Kind: global typedef
Properties
License
MIT. See license file.
















