
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
cmd.js
Advanced tools
Readme
Ever find yourself handling complex data structures in JavaScript? With cmd.js, one can assemble small blocks of logic, and easily pass data through them for processing.
Install with npm:
npm install cmd.js
var cmd = require('cmd.js');
// Enable all cmd modules
cmd.use('*');
// Test
cmd.log('Hello World');
<script src="src/cmd.js"></script>
<script src="build/cmd.lib.js"></script>
<script>
// Enable all cmd modules
cmd.use('*');
// Test
cmd.log('Hello World');
</script>
Goal: sort the users by increasing age, and display the name and id of each user.
var users = [
{name: 'John', id: 1, age: 37},
{name: 'Kimberly', id: 2, age: 35},
{name: 'Janine', id: 3, age: 33},
{name: 'Justin', id: 4, age: 31},
];
users.sort(function (a, b) {
return a.age > b.age;
});
users.forEach(function (user) {
console.log(user.name, user.id);
});
// The output:
// Justin 4
// Janine 3
// Kimberly 2
// John 1
Pretty simple, right? With cmd.js, it's even simpler:
// Enable all cmd modules
cmd.use('*');
var pluck = cmd.pluck;
var sortAndPrint = cmd.sort(pluck('age')).
and.logger(pluck('name'), pluck('id'));
sortAndPrint(users);
// The output:
// Justin 4
// Janine 3
// Kimberly 2
// John 1
The benefits of this style include reusability, clear logical flow, and less code in general. By chaining commands you create reusable logic isolated from specifc data variables.
Development dependencies can be installed with npm install or make install for convenience.
Testing is accomplished with mocha, and can be run with npm test or make test. There's also a handy make test-watch to see live test results during development.
This project is built with gulp. Make all changes/additions in src/lib/*.js while running make build-watch from the command line.
cmd.name(... args ...)(... vals ...);
Some commands do not accept args, and you are given the command with empty args already provided.
cmd.sum(... vals ...);
Arguments are automatically merged one level deep for maximum convenience. For example, you can provide an array of arguments or individual arguments, or any combination thereof. The following are all identical:
cmd.use('max');
cmd.max(1, 2, 3, 4, 5); // 5
cmd.max([1, 2, 3, 4, 5]); // 5
cmd.max(1, [2, 3], 4, 5); // 5
cmd.max([1], 2, [3, 4, 5]); // 5
cmd.max([1], [2], [3], [4], [5]); // 5
Because of this, if you absolutely need to work with an array as-is, pass it in like [[1, 2, 3]] to avoid automatic argument merging.
Most commands normally return an array of values. To get the first value not wrapped in an array instead, just use .raw immediately before passing in the values:
cmd.use('case');
cmd.case.upper.raw('hello world');
// "HELLO WORLD"
cmd.use('format');
cmd.format('my favorite number is {}').raw(100);
// "my favorite number is 100"
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
alert | [undefined, ...] | Causes a browser alert for each value passed in. Does nothing in a Node.js environment. |
The following example displays two alerts in sequence:
cmd.alert('Hello World!', 'Will Smith here.');
// two alerts displayed (only in browser)
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
case.lower | ['change string case', ...] | Convert strings to lower case. |
case.title | ['Change String Case', ...] | Convert strings to title case. |
case.upper | ['CHANGE STRING CASE', ...] | Convert strings to upper case. |
The following example converts strings to lowercase:
cmd.case.lower('Hello World!', 'Will Smith here.');
// ["hello world!", "will smith here."]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
clone | [mixed, ...] | Clone any JavaScript variable not containing a circular reference. |
The following example clones an object:
var answer = {data: 42};
var cloned = cmd.clone.raw(answer); // raw returns non-wrapped first response
[cloned === answer, cloned.data === answer.data];
// [false, true]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
compare | -1 or 0 or 1 | Compare is a unique command in that it only accepts 2 values. Any further values will be ignored. It is used internally for cmd.sort but available for custom sorting as well. |
The following examples compare two values. Compare defines a sort order for any two JavaScript types:
cmd.compare(8, 5);
// 3
cmd.compare(1000, 'a');
// -1
cmd.compare('boo', 'apple');
// 1
cmd.compare('hello', false);
// 1
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
equals | [true or false, ...] | Checks if each value passed in equals any of the given arguments. |
The following example checks for values that equal 50:
cmd.equals(30, 50)(100, 20, 50, 30);
// [false, false, true, true]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
exists | [true or false, ...] | Checks if each value passed in exists (not null or undefined). |
The following example checks the existence of the values. Only null and undefined count as not existing:
cmd.exists(null, undefined, false, '', 0, true);
// [false, false, true, true, true, true]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
extend | [{...}, ...] | Extends each value with each argument, in order. |
The following example adds the color red to each value passed in:
cmd.extend({color: 'red'})({item: 'wrench'}, {item: 'apple'});
// [{item: 'wrench', color: 'red'}, {item: 'apple', color: 'red'}]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
filter | [mixed, ...] | Filters out values based on arguments. |
The following example filters the values to only even numbers greater than 5:
cmd.filter(function (x) {
return x % 2 === 0;
}, function (x) {
return x > 5;
})(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10);
// [6, 8, 10]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
format | ['formatted string', ...] | Formats string arguments using positional {} targets. |
The following example formats two strings using positional targets:
cmd.format('I love {}pples, {}lueberries, and {}ake', '{} + {} = {}')('a', 'b', 'c');
// ["I love apples, blueberries, and cake", "a + b = c"]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
join | ['joined string', ...] | Joins values provided with arguments as glue. |
The following example joins the values using the glue provided in initial arguments:
cmd.join('-', '+')('a', 'b', 'c');
// ["a-b-c", "a+b+c"]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
log | [mixed, ...] | Logs values and passes them through unchanged. |
The following example logs each value to the console and returns the values:
cmd.log(1, 2, 3);
// 1
// 2
// 3
// [1, 2, 3]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
logger | [mixed, ...] | Logs values once per each argument and passes them through unchanged. |
The following example logs each value wrapped in a custom log format to the console and returns the values. If a string is passed it will use cmd.format to format the logs:
var withDate = function (x) {
return 'Log at ' + (new Date()) + ': ' + x;
};
cmd.logger(withDate, 'and the number is: {}')(1, 2, 3);
// Log at Sat Jan 31 2015 23:05:59 GMT-0800 (PST): 1 and the number is: 1
// Log at Sat Jan 31 2015 23:05:59 GMT-0800 (PST): 2 and the number is: 2
// Log at Sat Jan 31 2015 23:05:59 GMT-0800 (PST): 3 and the number is: 3
// [1, 2, 3]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
max | 100 | Returns the maximum of all given values. |
The following example returns the maximum value:
cmd.max(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 5
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
min | 100 | Returns the minimum of all given values. |
The following example returns the minimum value:
cmd.min(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 1
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
obj | [{ ... }, ...] | Zips up an object using arguments as keys and values as values. |
The following example builds an object with keys and repeated values. Note the [[wrapped array]] syntax to avoid spreading the array as arguments:
cmd.obj('name', 'age', 'city', 'interests')(
'Nate', 25, 'Los Angeles, CA', [['tech', 'javascript', 'node.js', 'space']]
);
// [{
// "name": "Nate",
// "age": 25,
// "city": "Los Angeles, CA",
// "interests": ["tech", "javascript", "node.js", "space"]
// }]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
pluck | [mixed, ...] | Surfaces data within a structure of objects or arrays, using arguments as keys. |
The following example plucks object properties:
var people = [{
name: 'Adam',
pet: {
type: 'bird',
name: 'Sherlock'
}
}, {
name: 'Shannon',
pet: {
type: 'snake',
name: 'Rosa'
}
}, {
name: 'Upgrayyed',
pet: {
type: 'dog',
name: 'Maxximus'
}
}];
cmd.pluck('pet', 'name')(people);
// ["Sherlock", "Rosa", "Maxximus"]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
product | 100 | Returns the product of all given values. |
The following example returns the product 1 * 2 * 3 * 4 * 5:
cmd.product(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 120
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
push.to | [mixed, ...] | Pushes provided values to each argument array. The use of .to avoids having to [[double wrap]] array arguments. |
The following example pushes to an array:
var people = [];
var add = cmd.push.to(people);
add({
name: 'Adam'
});
add({
name: 'Blake'
});
console.log(people);
// [{"name":"Adam"}, {"name":"Blake"}]
Push returns the value(s) passed in, so it can be used perfectly while chaining commands:
add.and.log({name: 'Charlie'});
// Object {name: "Charlie"}
people.length;
// 3
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
sort | [mixed, ...] | Sorts the array in custom order. |
sort.asc | [mixed, ...] | Sorts the array in ascending order. |
sort.desc | [mixed, ...] | Sorts the array in descending order. |
The following example sorts the values with various sort orders and parameters:
cmd.sort.asc('c', 'a', 'b', 3, 1, 2);
// [1, 2, 3, "a", "b", "c"]
cmd.sort.desc('c', 'a', 'b', 3, 1, 2);
// ["c", "b", "a", 3, 2, 1]
// Sort by type, leaving order preserved within a type
cmd.sort(function (x) {
return typeof x;
})('c', 'a', 'b', 3, 1, 2);
// [3, 1, 2, "c", "a", "b"]
// Sort objects by a key
cmd.sort(function (x) {
return x.price;
})(
{name: 'TV', price: 899.00},
{name: 'Car', price: 16999.00},
{name: 'Spoon', price: 1.29}
);
// [
// {name: "Spoon", price: 1.29},
// {name: "TV", price: 899},
// {name: "Car", price: 16999}
// ]
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
sum | 100 | Returns the sum of all given values. |
The following example returns the sum 1 + 2 + 3 + 4 + 5:
cmd.sum(1, 2, 3, 4, 5);
// 15
| name | return value | description |
|---|---|---|
switch | [mixed, ...] | Switches based on a matching when condition. |
The following example uses cmd.switch to choose an appropriate sentence:
var msgSwitch = cmd.switch(function (when, x) {
when(x > 5, 'You have lots of messages');
when(x === 5, 'You have five messages');
when(x > 1, 'You have a few messages');
when(x === 1, 'You have a message');
when(x === 0, 'You have no messages');
when(true, 'Unknown');
});
msgSwitch(0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 'x');
// ["You have no messages",
// "You have a message",
// "You have a few messages",
// "You have a few messages",
// "You have a few messages",
// "You have five messages",
// "You have lots of messages",
// "Unknown"]
FAQs
Unknown package
The npm package cmd.js receives a total of 2 weekly downloads. As such, cmd.js popularity was classified as not popular.
We found that cmd.js demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
Product
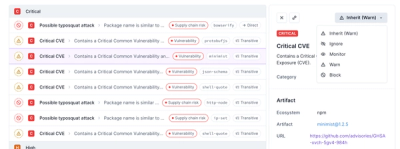
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.