
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
co
Advanced tools
Package description
The co npm package is a generator based flow-control utility for Node.js and the browser, making it easier to work with asynchronous JavaScript operations. It allows you to use generators to yield any function that returns a Promise. It can be used to simplify callback or promise-based code, especially in the context of async/await patterns.
Sequential Execution
This feature allows for sequential execution of asynchronous tasks. The code sample demonstrates how you can use co to run promises in sequence using a generator function, which yields a promise that resolves to true.
co(function* () {
var result = yield Promise.resolve(true);
return result;
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
}, function (err) {
console.error(err.stack);
});Error Handling
This feature demonstrates how co can be used for error handling in asynchronous operations. The code sample shows a generator function yielding a promise that gets rejected, and the error is caught and logged.
co(function* () {
try {
yield Promise.reject(new Error('Oops!'));
} catch (err) {
console.error(err.message);
}
});Parallel Execution
This feature showcases how co can handle parallel execution of promises. The code sample illustrates a generator function yielding an array of promises, which co runs in parallel, and then logs the array of results.
co(function* () {
var res = yield [
Promise.resolve(1),
Promise.resolve(2),
];
return res;
}).then(function (value) {
console.log(value);
});Bluebird is a fully featured promise library with focus on innovative features and performance. It provides utilities for working with promises including but not limited to parallel execution, which is similar to what co offers. However, Bluebird does not use generator functions.
Async is a utility module which provides straight-forward, powerful functions for working with asynchronous JavaScript. Although it does not use promises or generators in the same way as co, it offers similar functionalities in terms of controlling the flow of asynchronous operations.
Q is a promise library for JavaScript which provides a toolset for creating and composing asynchronous promises. It is similar to co in that it helps manage asynchronous operations, but it does not utilize generator functions for flow control.
Readme
Generator based flow-control goodness for nodejs and the browser, using thunks or promises, letting you write non-blocking code in a nice-ish way.
Currently you must use the --harmony-generators flag when
running node 0.11.x to get access to generators. Or use gnode to spawn your node instance.
However note that performance degrades quickly compared to 0.11.x.
Co is careful to relay any errors that occur back to the generator, including those
within the thunk, or from the thunk's callback. "Uncaught" exceptions in the generator
are passed to co()'s thunk.
Make sure to view the examples.
$ npm install co
View the wiki for libraries that work well with Co.
var co = require('co');
var thunkify = require('thunkify');
var request = require('request');
var get = thunkify(request.get);
co(function *(){
var a = yield get('http://google.com');
var b = yield get('http://yahoo.com');
var c = yield get('http://cloudup.com');
console.log(a[0].statusCode);
console.log(b[0].statusCode);
console.log(c[0].statusCode);
})()
co(function *(){
var a = get('http://google.com');
var b = get('http://yahoo.com');
var c = get('http://cloudup.com');
var res = yield [a, b, c];
console.log(res);
})()
// Error handling
co(function *(){
try {
var res = yield get('http://badhost.invalid');
console.log(res);
} catch(e) {
console.log(e.code) // ENOTFOUND
}
})()
The "yieldable" objects currently supported are:
To convert a regular node function that accepts a callback into one which returns a thunk you may want to use thunkify or similar.
While co supports promises, you may return "thunks" from your functions,
which otherwise behaves just like the traditional node-style callback
with a signature of: (err, result).
For example take fs.readFile, we all know the signature is:
fs.readFile(path, encoding, function(err, result){
});
To work with Co we need a function to return another function of the same signature:
fs.readFile(path, encoding)(function(err, result){
});
Which basically looks like this:
function read(path, encoding) {
return function(cb){
fs.readFile(path, encoding, cb);
}
}
or to execute immediately like this (see thunkify):
function read(path, encoding) {
// call fs.readFile immediately, store result later
return function(cb){
// cb(err, result) or when result ready
}
}
When co is invoked with a receiver it will propagate to most yieldables,
allowing you to alter this.
var ctx = {};
function foo() {
assert(this == ctx);
}
co(function *(){
assert(this == ctx);
yield foo;
}).call(ctx)
You also pass arguments through the generator:
co(function *(a){
assert(this == ctx);
assert('yay' == a);
yield foo;
}).call(ctx, 'yay');
Pass a generator fn and return a thunk. The thunk's signature is
(err, result), where result is the value passed to the return
statement.
var co = require('co');
var fs = require('fs');
function read(file) {
return function(fn){
fs.readFile(file, 'utf8', fn);
}
}
co(function *(){
var a = yield read('.gitignore');
var b = yield read('Makefile');
var c = yield read('package.json');
return [a, b, c];
})()
You may also yield Generator objects to support nesting:
var co = require('co');
var fs = require('fs');
function size(file) {
return function(fn){
fs.stat(file, function(err, stat){
if (err) return fn(err);
fn(null, stat.size);
});
}
}
function *foo(){
var a = yield size('.gitignore');
var b = yield size('Makefile');
var c = yield size('package.json');
return [a, b, c];
}
function *bar(){
var a = yield size('examples/parallel.js');
var b = yield size('examples/nested.js');
var c = yield size('examples/simple.js');
return [a, b, c];
}
co(function *(){
var results = yield [foo(), bar()];
console.log(results);
})()
Or if the generator functions do not require arguments, simply yield the function:
var thunkify = require('thunkify');
var request = require('superagent');
var get = thunkify(request.get);
function *results() {
var a = get('http://google.com')
var b = get('http://yahoo.com')
var c = get('http://ign.com')
return yield [a, b, c]
}
co(function *(){
// 3 concurrent requests at a time
var a = yield results;
var b = yield results;
console.log(a, b);
// 6 concurrent requests
console.log(yield [results, results]);
})()
If a thunk is written to execute immediately you may achieve parallelism
by simply yield-ing after the call. The following are equivalent if
each call kicks off execution immediately:
co(function *(){
var a = size('package.json');
var b = size('Readme.md');
var c = size('Makefile');
return [yield a, yield b, yield c];
})()
Or:
co(function *(){
var a = size('package.json');
var b = size('Readme.md');
var c = size('Makefile');
return yield [a, b, c];
})()
You can also pass arguments into the generator. The last argument, done, is
the callback function. Here's an example:
var exec = require('co-exec');
co(function *(cmd) {
var res = yield exec(cmd);
return res;
})('pwd', done);
By yielding an array of thunks you may "join" them all into a single thunk which executes them all concurrently, instead of in sequence. Note that the resulting array ordering is retained.
var co = require('co');
var fs = require('fs');
function size(file) {
return function(fn){
fs.stat(file, function(err, stat){
if (err) return fn(err);
fn(null, stat.size);
});
}
}
co(function *(){
var a = size('.gitignore');
var b = size('index.js');
var c = size('Makefile');
var res = yield [a, b, c];
console.log(res);
// => [ 13, 1687, 129 ]
})()
Nested arrays may also be expressed as simple nested arrays:
var a = [
get('http://google.com'),
get('http://yahoo.com'),
get('http://ign.com')
];
var b = [
get('http://google.com'),
get('http://yahoo.com'),
get('http://ign.com')
];
console.log(yield [a, b]);
Yielding an object behaves much like yielding an array, however recursion is supported:
co(function *(){
var user = yield {
name: {
first: get('name.first'),
last: get('name.last')
}
};
})()
Here is the sequential equivalent without yielding an object:
co(function *(){
var user = {
name: {
first: yield get('name.first'),
last: yield get('name.last')
}
};
})()
On my machine 30,000 sequential stat()s takes an avg of 570ms,
while the same number of sequential stat()s with co() takes
610ms, aka the overhead introduced by generators is extremely negligable.
MIT
FAQs
Unknown package
The npm package co receives a total of 13,353,124 weekly downloads. As such, co popularity was classified as popular.
We found that co demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 3 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
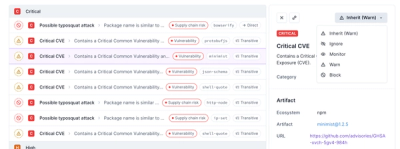
Product
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.