
Security News
tea.xyz Spam Plagues npm and RubyGems Package Registries
Tea.xyz, a crypto project aimed at rewarding open source contributions, is once again facing backlash due to an influx of spam packages flooding public package registries.
decimal.js
Advanced tools
Package description
The decimal.js npm package is a library for arbitrary-precision decimal arithmetic. It allows for high-precision decimal calculations in JavaScript, which is particularly useful when dealing with financial calculations, scientific computations, or any other use case that requires more precision than JavaScript's native Number type can provide.
Arithmetic Operations
Performing precise arithmetic operations like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division without the floating-point errors that can occur with JavaScript's native Number type.
{"addition": "new Decimal('0.1').plus('0.2').toString()", "subtraction": "new Decimal('0.3').minus('0.1').toString()", "multiplication": "new Decimal('2').times('3').toString()", "division": "new Decimal('1').dividedBy('3').toString()"}Comparison and Logical Operations
Comparing decimal numbers to determine equality, or whether one number is less than or greater than another. Also includes logical operations to check the sign of the numbers.
{"equals": "new Decimal('1.0').equals('1').toString()", "lessThan": "new Decimal('1').lessThan('2').toString()", "greaterThan": "new Decimal('2').greaterThan('1').toString()", "logicalAnd": "new Decimal('1').isPositive() && new Decimal('2').isPositive()"}Chaining Operations
Allows chaining of multiple arithmetic operations in a single statement, which can make complex calculations more readable and concise.
{"chaining": "new Decimal('1.5').plus('1').minus('0.5').times('2').dividedBy('2').toString()"}Configuration and Precision Control
Configuring the global settings of the library, such as the precision of calculations and the rounding mode to be used.
{"config": "Decimal.config({ precision: 5, rounding: 4 })"}bignumber.js is another arbitrary-precision decimal and non-decimal arithmetic library with similar functionality to decimal.js. It provides a similar API for arithmetic, comparison, and formatting operations. The main difference is in the internal representation and some API naming conventions.
big.js is a smaller and simpler library for arbitrary-precision arithmetic in JavaScript. It is less feature-rich than decimal.js and bignumber.js, but it is also smaller in size, which might be beneficial for some projects that require a lightweight solution.
mathjs is an extensive mathematics library that includes arbitrary-precision arithmetic as one of its many features. It offers a broader range of mathematical functions and utilities compared to decimal.js, which is focused solely on decimal arithmetic.
Changelog
10.4.3
toStringTag declaration for type compatibility.Readme
An arbitrary-precision Decimal type for JavaScript.
Number.prototype and Math objects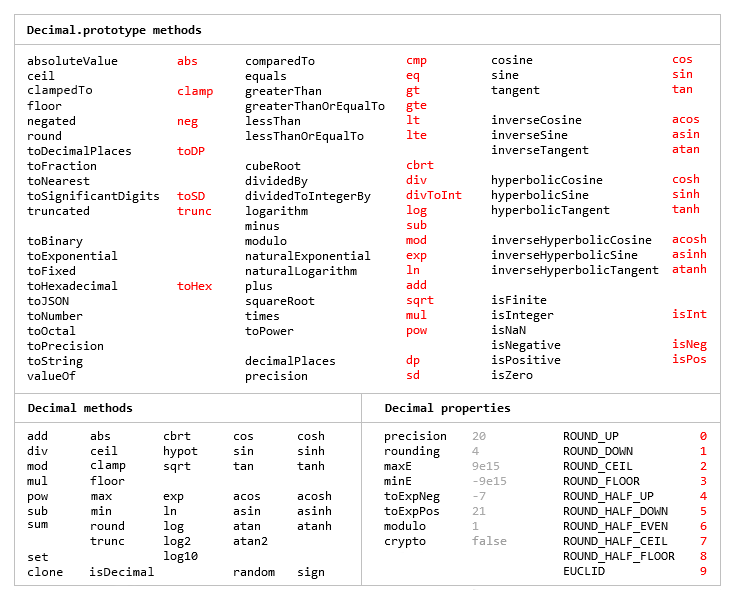
The library is similar to bignumber.js, but here precision is specified in terms of significant digits rather than decimal places, and all calculations are rounded to the precision (similar to Python's decimal module) rather than just those involving division.
This library also adds the trigonometric functions, among others, and supports non-integer powers, which makes it a significantly larger library than bignumber.js and the even smaller big.js.
For a lighter version of this library without the trigonometric functions see decimal.js-light.
The library is the single JavaScript file decimal.js or ES module decimal.mjs.
Browser:
<script src='path/to/decimal.js'></script>
<script type="module">
import Decimal from './path/to/decimal.mjs';
...
</script>
npm install decimal.js
const Decimal = require('decimal.js');
import Decimal from 'decimal.js';
import {Decimal} from 'decimal.js';
In all examples below, semicolons and toString calls are not shown.
If a commented-out value is in quotes it means toString has been called on the preceding expression.
The library exports a single constructor function, Decimal, which expects a single argument that is a number, string or Decimal instance.
x = new Decimal(123.4567)
y = new Decimal('123456.7e-3')
z = new Decimal(x)
x.equals(y) && y.equals(z) && x.equals(z) // true
If using values with more than a few digits, it is recommended to pass strings rather than numbers to avoid a potential loss of precision.
// Precision loss from using numeric literals with more than 15 significant digits.
new Decimal(1.0000000000000001) // '1'
new Decimal(88259496234518.57) // '88259496234518.56'
new Decimal(99999999999999999999) // '100000000000000000000'
// Precision loss from using numeric literals outside the range of Number values.
new Decimal(2e+308) // 'Infinity'
new Decimal(1e-324) // '0'
// Precision loss from the unexpected result of arithmetic with Number values.
new Decimal(0.7 + 0.1) // '0.7999999999999999'
As with JavaScript numbers, strings can contain underscores as separators to improve readability.
x = new Decimal('2_147_483_647')
String values in binary, hexadecimal or octal notation are also accepted if the appropriate prefix is included.
x = new Decimal('0xff.f') // '255.9375'
y = new Decimal('0b10101100') // '172'
z = x.plus(y) // '427.9375'
z.toBinary() // '0b110101011.1111'
z.toBinary(13) // '0b1.101010111111p+8'
// Using binary exponential notation to create a Decimal with the value of `Number.MAX_VALUE`.
x = new Decimal('0b1.1111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111111p+1023')
// '1.7976931348623157081e+308'
Decimal instances are immutable in the sense that they are not changed by their methods.
0.3 - 0.1 // 0.19999999999999998
x = new Decimal(0.3)
x.minus(0.1) // '0.2'
x // '0.3'
The methods that return a Decimal can be chained.
x.dividedBy(y).plus(z).times(9).floor()
x.times('1.23456780123456789e+9').plus(9876.5432321).dividedBy('4444562598.111772').ceil()
Many method names have a shorter alias.
x.squareRoot().dividedBy(y).toPower(3).equals(x.sqrt().div(y).pow(3)) // true
x.comparedTo(y.modulo(z).negated() === x.cmp(y.mod(z).neg()) // true
Most of the methods of JavaScript's Number.prototype and Math objects are replicated.
x = new Decimal(255.5)
x.toExponential(5) // '2.55500e+2'
x.toFixed(5) // '255.50000'
x.toPrecision(5) // '255.50'
Decimal.sqrt('6.98372465832e+9823') // '8.3568682281821340204e+4911'
Decimal.pow(2, 0.0979843) // '1.0702770511687781839'
// Using `toFixed()` to avoid exponential notation:
x = new Decimal('0.0000001')
x.toString() // '1e-7'
x.toFixed() // '0.0000001'
And there are isNaN and isFinite methods, as NaN and Infinity are valid Decimal values.
x = new Decimal(NaN) // 'NaN'
y = new Decimal(Infinity) // 'Infinity'
x.isNaN() && !y.isNaN() && !x.isFinite() && !y.isFinite() // true
There is also a toFraction method with an optional maximum denominator argument.
z = new Decimal(355)
pi = z.dividedBy(113) // '3.1415929204'
pi.toFraction() // [ '7853982301', '2500000000' ]
pi.toFraction(1000) // [ '355', '113' ]
All calculations are rounded according to the number of significant digits and rounding mode specified
by the precision and rounding properties of the Decimal constructor.
For advanced usage, multiple Decimal constructors can be created, each with their own independent configuration which applies to all Decimal numbers created from it.
// Set the precision and rounding of the default Decimal constructor
Decimal.set({ precision: 5, rounding: 4 })
// Create another Decimal constructor, optionally passing in a configuration object
Dec = Decimal.clone({ precision: 9, rounding: 1 })
x = new Decimal(5)
y = new Dec(5)
x.div(3) // '1.6667'
y.div(3) // '1.66666666'
The value of a Decimal is stored in a floating point format in terms of its digits, exponent and sign, but these properties should be considered read-only.
x = new Decimal(-12345.67);
x.d // [ 12345, 6700000 ] digits (base 10000000)
x.e // 4 exponent (base 10)
x.s // -1 sign
For further information see the API reference in the doc directory.
To run the tests using Node.js from the root directory:
npm test
Each separate test module can also be executed individually, for example:
node test/modules/toFraction
To run the tests in a browser, open test/test.html.
Two minification examples:
Using uglify-js to minify the decimal.js file:
npm install uglify-js -g
uglifyjs decimal.js --source-map url=decimal.min.js.map -c -m -o decimal.min.js
Using terser to minify the ES module version, decimal.mjs:
npm install terser -g
terser decimal.mjs --source-map url=decimal.min.mjs.map -c -m --toplevel -o decimal.min.mjs
import Decimal from './decimal.min.mjs';
FAQs
An arbitrary-precision Decimal type for JavaScript.
The npm package decimal.js receives a total of 13,365,100 weekly downloads. As such, decimal.js popularity was classified as popular.
We found that decimal.js demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Tea.xyz, a crypto project aimed at rewarding open source contributions, is once again facing backlash due to an influx of spam packages flooding public package registries.

Security News
As cyber threats become more autonomous, AI-powered defenses are crucial for businesses to stay ahead of attackers who can exploit software vulnerabilities at scale.

Security News
UnitedHealth Group disclosed that the ransomware attack on Change Healthcare compromised protected health information for millions in the U.S., with estimated costs to the company expected to reach $1 billion.