
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
faas-js-runtime
Advanced tools
Changelog
0.10.0 (2023-02-16)
Readme
This module provides a Node.js framework for executing a function that
exists in a user-provided directory path as an index.js file. The
directory may also contain an optional package.json file which can
be used to declare runtime dependencies for the function. You can also
provide a path to an arbitrary JavaScript file instead of a directory
path, allowing you to execute a single file as a function.
| Project Info | |
|---|---|
| License: | Apache-2.0 |
| Issue tracker: | https://github.com/nodeshift/faas-js-runtime/issues |
| Engines: | Node.js >= 14 |
The function is loaded and then invoked for incoming HTTP requests
at localhost:8080. The incoming request may be a
Cloud Event or
just a simple HTTP GET/POST request. The invoked user function can be
async but that is not required.
This module supports two different function signatures: HTTP or CloudEvents. In the type definitions below, we use TypeScript to express interfaces and types, but this module is usable from JavaScript as well.
The HTTP function signature is the simplest. It is invoked for every HTTP request that does not contain a CloudEvent.
interface HTTPFunction {
(context: Context, body?: IncomingBody): HTTPFunctionReturn;
}
Where the IncomingBody is either a string, a Buffer, a JavaScript object, or undefined, depending on what was supplied in the HTTP POST message body. The HTTTPFunctionReturn type is defined as:
type HTTPFunctionReturn = Promise<StructuredReturn> | StructuredReturn | ResponseBody | void;
Where the StructuredReturn is a JavaScript object with the following properties:
interface StructuredReturn {
statusCode?: number;
headers?: Record<string, string>;
body?: ResponseBody;
}
If the function returns a StructuredReturn object, then the statusCode and headers properties are used to construct the HTTP response. If the body property is present, it is used as the response body. If the function returns void or undefined, then the response body is empty.
The ResponseBody is either a string, a JavaScript object, or a Buffer. JavaScript objects will be serialized as JSON. Buffers will be sent as binary data.
CloudEvent functions are used in environments where the incoming HTTP request is a CloudEvent. The function signature is:
interface CloudEventFunction {
(context: Context, event: CloudEvent): CloudEventFunctionReturn;
}
Where the return type is defined as:
type CloudEventFunctionReturn = Promise<CloudEvent> | CloudEvent | HTTPFunctionReturn;
The function return type can be anything that a simple HTTP function can return or a CloudEvent. Whatever is returned, it will be sent back to the caller as a response.
The easiest way to get started is to use the CLI. You can call it with the path to any JavaScript file which has a default export that is a function. For example,
// index.js
function handle(context) {
const event = context.cloudevent;
// business logic
return {
statusCode: 200,
statusMessage: 'OK'
}
}
module.exports = handle;
Additionally, if your JavaScript file exports more than a single function,
an exported handle function will be invoked.
You can expose this function as an HTTP endpoint at localhost:8080
with the CLI.
npx faas-js-runtime ./index.js
Functions can be written and imported as ES modules with either the .mjs file extenstion or by adding the type property to the functions package.json and setting it to module.
// index.mjs
const handle = async function(context) => { ... };
// Export the function
export { handle };
If using the type property, the package.json might look something like this:
{
"name": "moduleName",
"type": "module"
}
In the current working directory, there is an index.js file like this.
const { start } = require('faas-js-runtime');
const options = {
// Pino is used as the logger implementation. Supported log levels are
// documented at this link:
// https://github.com/pinojs/pino/blob/master/docs/api.md#options
logLevel: 'info'
}
// The function directory is in ./function-dir
start(require(`${__dirname}/function-dir/`), server => {
// The server is now listening on localhost:8080
// and the function defined in `function-dir/index.js`
// will be invoked for each HTTP
// request to this endpoint.
console.log('Server listening');
// Whenever you want to shutdown the framework
server.close();
}, options);
In ./function-dir, there is an index.js file that looks
like this.
module.exports = async function myFunction(context) {
const ret = 'This is a test for Node.js functions. Success.';
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(_ => {
context.log.info('sending response to client')
resolve(ret);
}, 500);
});
};
You can use curl to POST to the endpoint:
$ curl -X POST -d 'hello=world' \
-H'Content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded' http://localhost:8080
You can use curl to POST JSON data to the endpoint:
$ curl -X POST -d '{"hello": "world"}' \
-H'Content-type: application/json' \
http://localhost:8080
You can use curl to POST an event to the endpoint:
$ curl -X POST -d '{"hello": "world"}' \
-H'Content-type: application/json' \
-H'Ce-id: 1' \
-H'Ce-source: cloud-event-example' \
-H'Ce-type: dev.knative.example' \
-H'Ce-specversion: 1.0' \
http://localhost:8080
You can see this in action by running node hack/run.js.
FAQs
Unknown package
We found that faas-js-runtime demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 0 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
Product
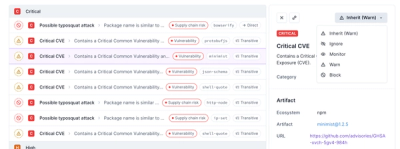
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.