
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
pem
Advanced tools
Package description
The 'pem' npm package is a tool for creating and managing PEM (Privacy Enhanced Mail) files, which are commonly used for SSL/TLS certificates and keys. It provides a variety of functionalities for generating, reading, and managing these files.
Generate SSL Certificates
This feature allows you to generate self-signed SSL certificates. The code sample demonstrates how to create a certificate that is valid for one day.
const pem = require('pem');
pem.createCertificate({ days: 1, selfSigned: true }, function (err, keys) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(keys);
});Read Certificate Information
This feature allows you to read and extract information from an existing certificate. The code sample shows how to read certificate information from a specified file path.
const pem = require('pem');
pem.readCertificateInfo('path/to/certificate.pem', function (err, info) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(info);
});Create Certificate Signing Request (CSR)
This feature allows you to create a Certificate Signing Request (CSR), which is used to request a certificate from a Certificate Authority (CA). The code sample demonstrates how to create a CSR with a specified common name.
const pem = require('pem');
pem.createCSR({ commonName: 'example.com' }, function (err, csr) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(csr);
});Create Private Key
This feature allows you to generate a private key. The code sample shows how to create a private key using the 'pem' package.
const pem = require('pem');
pem.createPrivateKey(function (err, key) {
if (err) {
throw err;
}
console.log(key);
});The 'node-forge' package is a comprehensive library for implementing various cryptographic functionalities in Node.js. It includes features for working with SSL/TLS, X.509 certificates, and more. Compared to 'pem', 'node-forge' offers a broader range of cryptographic tools but may require more in-depth knowledge to use effectively.
The 'openssl-wrapper' package is a Node.js wrapper for the OpenSSL command-line tool. It allows you to perform various cryptographic operations using OpenSSL commands. While 'openssl-wrapper' provides a wide range of functionalities similar to 'pem', it relies on having OpenSSL installed on the system and may be less user-friendly for those unfamiliar with OpenSSL commands.
The 'pkijs' package is a JavaScript library for Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) and X.509 certificates. It provides tools for creating, parsing, and validating certificates. Compared to 'pem', 'pkijs' is more focused on PKI and X.509 standards and offers more advanced features for working with certificates.
Changelog
Readme
Create private keys and certificates with node.js
Install with npm
npm install pem
Here are some examples for creating an SSL key/cert on the fly, and running an HTTPS server on port 443. 443 is the standard HTTPS port, but requires root permissions on most systems. To get around this, you could use a higher port number, like 4300, and use https://localhost:4300 to access your server.
var https = require('https')
var pem = require('pem')
pem.createCertificate({ days: 1, selfSigned: true }, function (err, keys) {
if (err) {
throw err
}
https.createServer({ key: keys.serviceKey, cert: keys.certificate }, function (req, res) {
res.end('o hai!')
}).listen(443)
})
var https = require('https')
var pem = require('pem')
var express = require('express')
pem.createCertificate({ days: 1, selfSigned: true }, function (err, keys) {
if (err) {
throw err
}
var app = express()
app.get('/', function (req, res) {
res.send('o hai!')
})
https.createServer({ key: keys.serviceKey, cert: keys.certificate }, app).listen(443)
})
Please have a look into the API documentation.
we had to clean up a bit
You can specify custom OpenSSL extensions using the config or extFile options for createCertificate (or using csrConfigFile with createCSR).
extFile and csrConfigFile should be paths to the extension files. While config will generate a temporary file from the supplied file contents.
If you specify config then the v3_req section of your config file will be used.
The following would be an example of a Certificate Authority extensions file:
[req]
req_extensions = v3_req
distinguished_name = req_distinguished_name
[req_distinguished_name]
commonName = Common Name
commonName_max = 64
[v3_req]
basicConstraints = critical,CA:TRUE
While the following would specify subjectAltNames in the resulting certificate:
[req]
req_extensions = v3_req
[ v3_req ]
basicConstraints = CA:FALSE
keyUsage = nonRepudiation, digitalSignature, keyEncipherment
subjectAltName = @alt_names
[alt_names]
DNS.1 = host1.example.com
DNS.2 = host2.example.com
DNS.3 = host3.example.com
Note that createCertificate and createCSR supports the altNames option which would be easier to use in most cases.
Warning: If you specify altNames the custom extensions file will not be passed to OpenSSL.
In some systems the openssl executable might not be available by the default name or it is not included in $PATH. In this case you can define the location of the executable yourself as a one time action after you have loaded the pem module:
var pem = require('pem')
pem.config({
pathOpenSSL: '/usr/local/bin/openssl'
})
// do something with the pem module
MIT
FAQs
Unknown package
The npm package pem receives a total of 195,682 weekly downloads. As such, pem popularity was classified as popular.
We found that pem demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
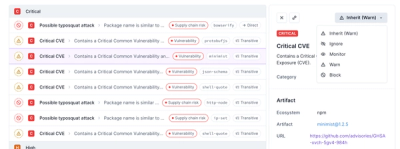
Product
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.