
Research
Security News
Quasar RAT Disguised as an npm Package for Detecting Vulnerabilities in Ethereum Smart Contracts
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.
redstone-evm-connector-exp
Advanced tools
A tool to inject RedStone data into EVM compatible smart contracts
The redstone-evm-connector module implements an alternative design of providing oracle data to smart contracts. Instead of constantly persisting data on EVM storage (by data providers), the information is brought on-chain only when needed (by end users). Until that moment data remains in the decentralised cache layer, which is powered by RedStone light cache gateways and streamr data broadcasting protocol. Data is transferred to the EVM by end users, who should attach signed data packages to their transaction calldata. The information integrity is verified on-chain through signature checking.
Try it directly in CodeSandbox: demo link
See a bunch of smart contract examples that use redstone-evm-connector in our dedicated repo with examples
Install redstone-evm-connector from NPM registry
# Using yarn
yarn add redstone-evm-connector
# Using NPM
npm install redstone-evm-connector
You need to apply a minium change to the source code to enable smart contract to access data. Your contract needs to extend one of our custom base contracts, which are located in the contracts/data-services folder.
We strongly recommend you to have some upgradability mechanism for your contracts (it can be based on multisig, DAO, or anything else). This way, you can quickly swtich to the latest trusted data providers in case of changes or problems with the current providers.
import "redstone-evm-connector/lib/contracts/data-services/AvalancheDataServiceConsumerBase.sol";
contract YourContractName is AvalancheDataServiceConsumerBase {
...
}
💡 Note: You can also override the following functions (do it on your own risk):
isTimestampValid(uint256 receivedTimestamp) returns (bool) - to enable custom logic of timestamp validationaggregateValues(uint256[] memory values) returns (uint256) - to enable custom logic of aggregating values from different providers (by default this function takes the median value)getAuthorisedSignerIndex(address _signerAddress) returns (uint256) function and uniqueSignersThreshold contract variable - to enable custom logic of signers authorisationAfter applying the mentioned change you will be able to access the data calling the local getOracleNumericValueFromTxMsg function. You should pass the data feed id converted to bytes32.
// Getting a single value
uint256 ethPrice = getOracleNumericValueFromTxMsg(bytes32("ETH"));
// Getting several values
bytes32[] memory dataFeedIds = new bytes32[](2);
dataFeedIds[0] = bytes32("ETH");
dataFeedIds[1] = bytes32("BTC");
uint256[] memory values = getOracleNumericValuesFromTxMsg(dataFeedIds);
uint256 ethPrice = values[0];
uint256 btcPrice = values[1];
You can see all available data feeds in our web app.
You should also update the code responsible for submitting transactions. If you're using ethers.js, we've prepared a dedicated library to make the transition seamless.
First, you need to import the wrapper code to your project
// Typescript
import { WrapperBuilder } from "redstone-evm-connector";
// Javascript
const { WrapperBuilder } = require("redstone-evm-connector");
Then you can wrap your ethers contract pointing to the selected redstone data service and requested data feeds.
const yourEthersContract = new ethers.Contract(address, abi, provider);
// Connecting all provider's prices (consumes more GAS)
const wrappedContract = WrapperBuilder
.wrap(yourEthersContract)
.usingDataService({
dataServiceId: "avalanche-main-data-service"
uniqueSignersCount: 10,
dataFeeds: ["ETH", "AVAX", "BTC"]
});
Now you can access any of the contract's methods in exactly the same way as interacting with the ethers-js code:
wrappedContract.executeYourMethod(arg1, arg2);
It's also possible to request pure bytes data. Take a look at bytes-many-data-feeds.test.ts to learn more.
Putting data directly into storage is the easiest to make information accessible to smart contracts. However, the convenience comes at a high price, as the storage access is the most costly operation in EVM (20k gas for 256bit word ~ $160k for 1Mb checked 30/08/2021) making it prohibitively expensive to use.
That's why, Redstone proposes a completely new storage-less approach.
At a top level, transferring data to an EVM environment requires packing an extra payload to a user's transaction and processing the message on-chain.
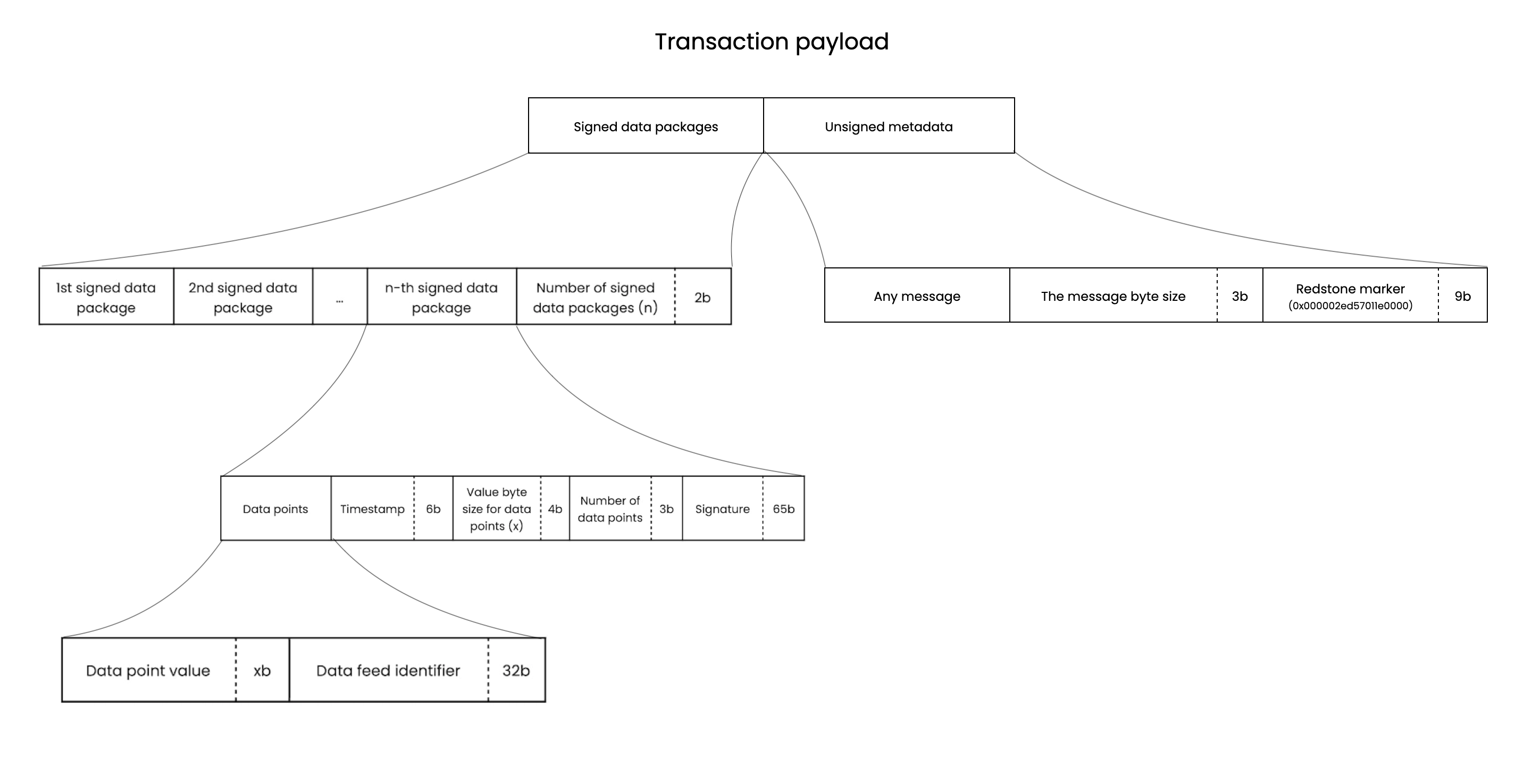
All of the steps are executed automatically by the ContractWrapper and transparent to the end-user
msg.dataThis logic is executed in the on-chain environment and we optimised the execution using a low-level assembly code to reduce gas consumption to the absolute minimum
To increase the security of the Redstone oracle system, we've created the on-chain aggregation mechanism. This mechanism adds an additional requirement of passing at least X signatures from different authorised data providers for a given data feed. The values of different providers are then aggregated before returning to a consumer contract (by default, we use median value calculation for aggregation). This way, even if some small subset of providers corrupt (e.g. 2 of 10), it should not significantly affect the aggregated value.
There are the following on-chain aggregation params in Redstone consumer base contract:
uniqueSignersThreshold valuegetAuthorisedSignerIndex functionaggregateValues function (for numeric values)aggregateByteValues function (for bytes arrays)We support 2 types of data to be received in contract:
uniqueSignersThreshold variable, unless you 100% sure about itYou can check the benchmarks script and reports in the benchmarks folder.
{
"1 data feed": {
"attaching to calldata": 1840,
"data extraction and validation": 10782
},
"2 data feeds": {
"attaching to calldata": 3380,
"data extraction and validation": 18657
},
"10 data feeds": {
"attaching to calldata": 15832,
"data extraction and validation": 95539
},
}
{
"1 data feed": {
"attaching to calldata": 15796,
"data extraction and validation": 72828
},
"2 data feeds": {
"attaching to calldata": 31256,
"data extraction and validation": 146223
},
"10 data feeds": {
"attaching to calldata": 156148,
"data extraction and validation": 872336
},
"20 data feeds": {
"attaching to calldata": 313340,
"data extraction and validation": 2127313
}
}
The codebase consists of a wrapper written in typescript which is responsible for packing the data and solidity smart contracts that extract the information. We encourage anyone to build and test the code and we welcome any issues with suggestions and pull requests.
yarn install
yarn test
Redstone EVM connector is an open-source and free software released under the MIT License.
FAQs
A tool to inject RedStone data into EVM compatible smart contracts
We found that redstone-evm-connector-exp demonstrated a not healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers uncover a malicious npm package posing as a tool for detecting vulnerabilities in Etherium smart contracts.

Security News
Research
A supply chain attack on Rspack's npm packages injected cryptomining malware, potentially impacting thousands of developers.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers discovered a malware campaign on npm delivering the Skuld infostealer via typosquatted packages, exposing sensitive data.