
Research
Security News
Malicious npm Package Typosquats react-login-page to Deploy Keylogger
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
ssh2
Advanced tools
Package description
The ssh2 npm package is a client and server module for SSH and SFTP written in pure JavaScript for node.js. It provides an interface to connect to and interact with SSH servers, allowing for the execution of commands, file transfers, local and remote port forwarding, and more.
Executing Commands on Remote Server
This code sample demonstrates how to execute a command (in this case, 'uptime') on a remote server using the ssh2 package.
const { Client } = require('ssh2');
const conn = new Client();
conn.on('ready', () => {
console.log('Client :: ready');
conn.exec('uptime', (err, stream) => {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('close', (code, signal) => {
console.log('Stream :: close :: code: ' + code + ', signal: ' + signal);
conn.end();
}).on('data', (data) => {
console.log('STDOUT: ' + data);
}).stderr.on('data', (data) => {
console.log('STDERR: ' + data);
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
privateKey: require('fs').readFileSync('/here/is/my/key')
});SFTP File Transfer
This code sample shows how to transfer a file from a local path to a remote path using SFTP with the ssh2 package.
const { Client } = require('ssh2');
const conn = new Client();
conn.on('ready', () => {
console.log('Client :: ready');
conn.sftp((err, sftp) => {
if (err) throw err;
sftp.fastPut(localPath, remotePath, {}, (err) => {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('File transferred successfully!');
conn.end();
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
privateKey: require('fs').readFileSync('/here/is/my/key')
});TCP Port Forwarding
This code sample illustrates how to set up TCP port forwarding from the local machine to a remote destination using the ssh2 package.
const { Client } = require('ssh2');
const conn = new Client();
conn.on('ready', () => {
console.log('Client :: ready');
conn.forwardOut('127.0.0.1', 12345, 'www.google.com', 80, (err, stream) => {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('close', () => {
console.log('TCP :: CLOSED');
conn.end();
}).on('data', (data) => {
console.log('TCP :: DATA: ' + data);
});
stream.end('GET / HTTP/1.1\r\nHost: www.google.com\r\nConnection: close\r\n\r\n');
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
privateKey: require('fs').readFileSync('/here/is/my/key')
});node-ssh is an SSH2 client module that provides a higher-level API for interacting with SSH servers. It simplifies tasks like executing commands and handling file transfers. Compared to ssh2, node-ssh is built on top of ssh2 and offers a more promise-based API, which can be easier to use for some developers.
simple-ssh is another SSH client for node.js that aims to provide a simpler and more intuitive API than ssh2. It offers a chainable API for executing multiple commands in sequence. While it may be easier for beginners, it is not as feature-rich as ssh2 and may not be suitable for more complex SSH interactions.
Readme
An SSH2 client module written in pure JavaScript for node.js.
Development/testing is done against OpenSSH (6.6 currently).
Upgrading from v0.2.x? See the list of changes (including backwards incompatibilities).
npm install ssh2
uptime on a server:var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.exec('uptime', function(err, stream) {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('exit', function(code, signal) {
console.log('Stream :: exit :: code: ' + code + ', signal: ' + signal);
}).on('close', function() {
console.log('Stream :: close');
conn.end();
}).on('data', function(data) {
console.log('STDOUT: ' + data);
}).stderr.on('data', function(data) {
console.log('STDERR: ' + data);
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
privateKey: require('fs').readFileSync('/here/is/my/key')
});
// example output:
// Connection :: ready
// STDOUT: 17:41:15 up 22 days, 18:09, 1 user, load average: 0.00, 0.01, 0.05
//
// Stream :: close
// Stream :: exit :: code: 0, signal: undefined
var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.shell('uptime', function(err, stream) {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('close', function() {
console.log('Stream :: close');
conn.end();
}).on('data', function(data) {
console.log('STDOUT: ' + data);
}).stderr.on('data', function(data) {
console.log('STDERR: ' + data);
});
stream.end('ls -l\nexit\n');
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
privateKey: require('fs').readFileSync('/here/is/my/key')
});
// example output:
// Connection :: ready
// STDOUT: Last login: Sun Jun 15 09:37:21 2014 from 192.168.100.100
//
// STDOUT: ls -l
// exit
//
// STDOUT: frylock@athf:~$ ls -l
//
// STDOUT: total 8
//
// STDOUT: drwxr-xr-x 2 frylock frylock 4096 Nov 18 2012 mydir
//
// STDOUT: -rw-r--r-- 1 frylock frylock 25 Apr 11 2013 test.txt
//
// STDOUT: frylock@athf:~$ exit
//
// STDOUT: logout
//
// Stream :: close
var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.forwardOut('192.168.100.102', 8000, '127.0.0.1', 80, function(err, stream) {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('close', function() {
console.log('TCP :: CLOSED');
conn.end();
}).on('data', function(data) {
console.log('TCP :: DATA: ' + data);
}).end([
'HEAD / HTTP/1.1',
'User-Agent: curl/7.27.0',
'Host: 127.0.0.1',
'Accept: */*',
'Connection: close',
'',
''
].join('\r\n'));
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
password: 'nodejsrules'
});
// example output:
// Connection :: ready
// TCP :: DATA: HTTP/1.1 200 OK
// Date: Thu, 15 Nov 2012 13:52:58 GMT
// Server: Apache/2.2.22 (Ubuntu)
// X-Powered-By: PHP/5.4.6-1ubuntu1
// Last-Modified: Thu, 01 Jan 1970 00:00:00 GMT
// Content-Encoding: gzip
// Vary: Accept-Encoding
// Connection: close
// Content-Type: text/html; charset=UTF-8
//
//
// TCP :: CLOSED
var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.forwardIn('127.0.0.1', 8000, function(err) {
if (err) throw err;
console.log('Listening for connections on server on port 8000!');
});
}).on('tcp connection', function(info, accept, reject) {
console.log('TCP :: INCOMING CONNECTION:');
console.dir(info);
accept().on('close', function() {
console.log('TCP :: CLOSED');
}).on('data', function(data) {
console.log('TCP :: DATA: ' + data);
}).end([
'HTTP/1.1 404 Not Found',
'Date: Thu, 15 Nov 2012 02:07:58 GMT',
'Server: ForwardedConnection',
'Content-Length: 0',
'Connection: close',
'',
''
].join('\r\n'));
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
password: 'nodejsrules'
});
// example output:
// Connection :: ready
// Listening for connections on server on port 8000!
// (.... then from another terminal on the server: `curl -I http://127.0.0.1:8000`)
// TCP :: INCOMING CONNECTION: { destIP: '127.0.0.1',
// destPort: 8000,
// srcIP: '127.0.0.1',
// srcPort: 41969 }
// TCP DATA: HEAD / HTTP/1.1
// User-Agent: curl/7.27.0
// Host: 127.0.0.1:8000
// Accept: */*
//
//
// TCP :: CLOSED
var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.sftp(function(err, sftp) {
if (err) throw err;
sftp.readdir('foo', function(err, list) {
if (err) throw err;
console.dir(list);
conn.end();
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.100.100',
port: 22,
username: 'frylock',
password: 'nodejsrules'
});
// example output:
// Connection :: ready
// [ { filename: 'test.txt',
// longname: '-rw-r--r-- 1 frylock frylock 12 Nov 18 11:05 test.txt',
// attrs:
// { size: 12,
// uid: 1000,
// gid: 1000,
// mode: 33188,
// atime: 1353254750,
// mtime: 1353254744 } },
// { filename: 'mydir',
// longname: 'drwxr-xr-x 2 frylock frylock 4096 Nov 18 15:03 mydir',
// attrs:
// { size: 1048576,
// uid: 1000,
// gid: 1000,
// mode: 16877,
// atime: 1353269007,
// mtime: 1353269007 } } ]
var Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn1 = new Connection(),
conn2 = new Connection();
conn1.on('ready', function() {
console.log('FIRST :: connection ready');
conn1.exec('nc 192.168.1.2 22', function(err, stream) {
if (err) {
console.log('FIRST :: exec error: ' + err);
return conn1.end();
}
conn2.connect({
sock: stream,
username: 'user2',
password: 'password2',
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.1.1',
username: 'user1',
password: 'password1',
});
conn2.on('ready', function() {
console.log('SECOND :: connection ready');
conn2.exec('uptime', function(err, stream) {
if (err) {
console.log('SECOND :: exec error: ' + err);
return conn1.end();
}
stream.on('end', function() {
conn1.end(); // close parent (and this) connection
}).on('data', function(data) {
console.log(data.toString());
});
});
});
var net = require('net'),
Connection = require('ssh2');
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('x11', function(info, accept, reject) {
var xserversock = new net.Socket();
xserversock.on('connect', function() {
var xclientsock = accept();
xclientsock.pipe(xserversock).pipe(xclientsock);
});
// connects to localhost:0.0
xserversock.connect(6000, 'localhost');
});
conn.on('ready', function() {
conn.exec('xeyes', { x11: true }, function(err, stream) {
if (err) throw err;
var code = 0;
stream.on('end', function() {
if (code !== 0)
console.log('Do you have X11 forwarding enabled on your SSH server?');
conn.end();
}).on('exit', function(exitcode) {
code = exitcode;
});
});
}).connect({
host: '192.168.1.1',
username: 'foo',
password: 'bar'
});
var socks = require('socksv5'),
Connection = require('ssh2');
var ssh_config = {
host: '192.168.100.1',
port: 22,
username: 'nodejs',
password: 'rules'
};
socks.createServer(function(info, accept, deny) {
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
conn.forwardOut(info.srcAddr,
info.srcPort,
info.dstAddr,
info.dstPort,
function(err, stream) {
if (err)
return deny();
var clientSocket;
if (clientSocket = accept(true)) {
stream.pipe(clientSocket).pipe(stream).on('close', function() {
conn.end();
});
} else
conn.end();
});
}).on('error', function(err) {
deny();
}).connect(ssh_config);
}).listen(1080, 'localhost', function() {
console.log('SOCKSv5 proxy server started on port 1080');
}).useAuth(socks.auth.None());
// test with cURL:
// curl -i --socks5 localhost:1080 google.com
var Connection = require('ssh2'),
xmlhello = '<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>'+
'<hello xmlns="urn:ietf:params:xml:ns:netconf:base:1.0">'+
' <capabilities>'+
' <capability>urn:ietf:params:netconf:base:1.0</capability>'+
' </capabilities>'+
'</hello>]]>]]>';
var conn = new Connection();
conn.on('ready', function() {
console.log('Connection :: ready');
conn.subsys('netconf', function(err, stream) {
if (err) throw err;
stream.on('data', function(data) {
console.log(data);
}).write(xmlhello);
});
}).connect({
host: '1.2.3.4',
port: 22,
username: 'blargh',
password: 'honk'
});
require('ssh2') returns a Connection constructor
banner(< string >message, < string >language) - A notice was sent by the server upon connection.
ready() - Authentication was successful.
tcp connection(< object >details, < function >accept, < function >reject) - An incoming forwarded TCP connection is being requested. Calling accept accepts the connection and returns a ChannelStream object. Calling reject rejects the connection and no further action is needed. details contains:
srcIP - string - The originating IP of the connection.
srcPort - integer - The originating port of the connection.
dstIP - string - The remote IP the connection was received on (given in earlier call to forwardIn()).
dstPort - integer - The remote port the connection was received on (given in earlier call to forwardIn()).
x11(< object >details, < function >accept, < function >reject) - An incoming X11 connection is being requested. Calling accept accepts the connection and returns a ChannelStream object. Calling reject rejects the connection and no further action is needed. details contains:
srcIP - string - The originating IP of the connection.
srcPort - integer - The originating port of the connection.
keyboard-interactive(< string >name, < string >instructions, < string >instructionsLang, < array >prompts, < function >finish) - The server is asking for replies to the given prompts for keyboard-interactive user authentication. name is generally what you'd use as a window title (for GUI apps). prompts is an array of { prompt: 'Password: ', echo: false } style objects (here echo indicates whether user input should be displayed on the screen). The answers for all prompts must be provided as an array of strings and passed to finish when you are ready to continue. Note: It's possible for the server to come back and ask more questions.
change password(< string >message, < string >language, < function >done) - If using password-based user authentication, the server has requested that the user's password be changed. Call done with the new password.
error(< Error >err) - An error occurred. A 'level' property indicates 'connection-socket' for socket-level errors and 'connection-ssh' for SSH disconnection messages. In the case of 'connection-ssh' messages, there may be a 'description' property that provides more detail.
end() - The socket was disconnected.
close(< boolean >hadError) - The socket was closed. hadError is set to true if this was due to error.
debug(< string >message) - If debug is set in the object passed to connect(), then this event will be emitted when the server sends debug messages. For OpenSSH, these usually are messages like "Pty allocation disabled.", "X11 forwarding disabled.", etc. when options are set for particular keys in ~/.ssh/authorized_keys.
(constructor)() - Creates and returns a new Connection instance.
connect(< object >config) - (void) - Attempts a connection to a server using the information given in config:
host - < string > - Hostname or IP address of the server. Default: 'localhost'
port - < integer > - Port number of the server. Default: 22
hostHash - < string > - 'md5' or 'sha1'. The host's key is hashed using this method and passed to the hostVerifier function. Default: (none)
hostVerifier - < function > - Function that is passed a string hex hash of the host's key for verification purposes. Return true to continue with the connection, false to reject and disconnect. Default: (none)
username - < string > - Username for authentication. Default: (none)
password - < string > - Password for password-based user authentication. Default: (none)
agent - < string > - Path to ssh-agent's UNIX socket for ssh-agent-based user authentication. Windows users: set to 'pageant' for authenticating with Pageant or (actual) path to a cygwin "UNIX socket." Default: (none)
privateKey - < mixed > - Buffer or string that contains a private key for key-based user authentication (OpenSSH format). Default: (none)
passphrase - < string > - For an encrypted private key, this is the passphrase used to decrypt it. Default: (none)
tryKeyboard - < boolean > - Try keyboard-interactive user authentication if primary user authentication method fails. Default: false
pingInterval - < integer > - How often (in milliseconds) to send SSH-level keepalive packets to the server. Default: 60000
readyTimeout - < integer > - How long (in milliseconds) to wait for the SSH handshake to complete. Default: 10000
sock - < ReadableStream > - A ReadableStream to use for communicating with the server instead of creating and using a new TCP connection (useful for connection hopping).
agentForward - < boolean > - Set to true to use OpenSSH agent forwarding ('auth-agent@openssh.com'). Default: false
Authentication method priorities: Password -> Private Key -> Agent (-> keyboard-interactive if tryKeyboard is true)
exec(< string >command[, < object >options], < function >callback) - (void) - Executes command on the server. Valid options properties are:
env - < object > - An environment to use for the execution of the command.
pty - < mixed > - Set to true to allocate a pseudo-tty with defaults, or an object containing specific pseudo-tty settings (see 'Pseudo-TTY settings'). Setting up a pseudo-tty can be useful when working with remote processes that expect input from an actual terminal (e.g. sudo's password prompt).
x11 - < mixed > - Set to true to use defaults below, a number to specify a specific screen number, or an object with the following valid properties:
single - < boolean > - Allow just a single connection? Default: false
screen - < number > - Screen number to use Default: 0
callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < ChannelStream >stream.
shell([[< object >window,] < object >options]< function >callback) - (void) - Starts an interactive shell session on the server, with optional window pseudo-tty settings (see 'Pseudo-TTY settings'). options supports the 'x11' option as described in exec(). callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < ChannelStream >stream.
forwardIn(< string >remoteAddr, < integer >remotePort, < function >callback) - (void) - Bind to remoteAddr on remotePort on the server and forward incoming connections. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < integer >port (port is the assigned port number if remotePort was 0). Here are some special values for remoteAddr and their associated binding behaviors:
'' - Connections are to be accepted on all protocol families supported by the server.
'0.0.0.0' - Listen on all IPv4 addresses.
'::' - Listen on all IPv6 addresses.
'localhost' - Listen on all protocol families supported by the server on loopback addresses only.
'127.0.0.1' and '::1' - Listen on the loopback interfaces for IPv4 and IPv6, respectively.
unforwardIn(< string >remoteAddr, < integer >remotePort, < function >callback) - (void) - Unbind remoteAddr on remotePort on the server and stop forwarding incoming connections. Until callback is called, more connections may still come in. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
forwardOut(< string >srcIP, < integer >srcPort, < string >dstIP, < integer >dstPort, < function >callback) - (void) - Open a connection with srcIP and srcPort as the originating address and port and dstIP and dstPort as the remote destination address and port. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < ChannelStream >stream.
sftp(< function >callback) - (void) - Starts an SFTP (protocol version 3) session. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < SFTP >sftpConnection.
subsys(< string >subsystem, < function >callback) - (void) - Invokes subsystem on the server. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < ChannelStream >stream.
end() - (void) - Disconnects the socket.
This is a normal streams2 Duplex Stream, with the following changes:
A boolean property 'allowHalfOpen' exists and behaves similarly to the property of the same name for net.Socket. When the stream's end() is called, if 'allowHalfOpen' is true, only EOF will be sent (the server can still send data if they have not already sent EOF). The default value for this property is true.
For shell():
For exec():
For shell() and exec():
The readable side represents stdout and the writable side represents stdin.
A stderr property that represents the stream of output from stderr.
signal(< string >signalName) - (void) - Sends a POSIX signal to the current process on the server. Valid signal names are: 'ABRT', 'ALRM', 'FPE', 'HUP', 'ILL', 'INT', 'KILL', 'PIPE', 'QUIT', 'SEGV', 'TERM', 'USR1', and 'USR2'. Also, from the RFC: "Some systems may not implement signals, in which case they SHOULD ignore this message." Note: If you are trying to send SIGINT and you find signal() doesn't work, try writing '\x03' to the exec/shell stream instead.
end() - (void) - Ends the SFTP session.
fastGet(< string >remotePath, < string >localPath[, < object >options], < function >callback) - (void) - Downloads a file at remotePath to localPath using parallel reads for faster throughput. options can have the following properties:
concurrency - integer - Number of concurrent reads Default: 25
chunkSize - integer - Size of each read in bytes Default: 32768
step - function(< integer >total_transferred, < integer >chunk, < integer >total) - Called every time a part of a file was transferred
callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
fastPut(< string >localPath, < string >remotePath[, < object >options], < function >callback) - (void) - Uploads a file from localPath to remotePath using parallel reads for faster throughput. options can have the following properties:
concurrency - integer - Number of concurrent reads Default: 25
chunkSize - integer - Size of each read in bytes Default: 32768
step - function(< integer >total_transferred, < integer >chunk, < integer >total) - Called every time a part of a file was transferred
callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
createReadStream(< string >path[, < object >options]) - ReadStream - Returns a new readable stream for path. options has the following defaults:
{ flags: 'r',
encoding: null,
handle: null,
mode: 0666,
autoClose: true
}
options can include start and end values to read a range of bytes from the file instead of the entire file. Both start and end are inclusive and start at 0. The encoding can be 'utf8', 'ascii', or 'base64'.
If autoClose is false, then the file handle won't be closed, even if there's an error. It is your responsiblity to close it and make sure there's no file handle leak. If autoClose is set to true (default behavior), on error or end the file handle will be closed automatically.
An example to read the last 10 bytes of a file which is 100 bytes long:
sftp.createReadStream('sample.txt', {start: 90, end: 99});
createWriteStream(< string >path[, < object >options]) - WriteStream - Returns a new writable stream for path. options has the following defaults:
{ flags: 'w',
encoding: null,
mode: 0666 }
options may also include a start option to allow writing data at some position past the beginning of the file. Modifying a file rather than replacing it may require a flags mode of 'r+' rather than the default mode 'w'.
If 'autoClose' is set to false and you pipe to this stream, this stream will not automatically close after there is no more data upstream -- allowing future pipes and/or manual writes.
open(< string >filename, < string >mode, [< ATTRS >attributes, ]< function >callback) - (void) - Opens a file filename for mode with optional attributes. mode is any of the modes supported by fs.open (except sync mode). callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < Buffer >handle.
close(< Buffer >handle, < function >callback) - (void) - Closes the resource associated with handle given by open() or opendir(). callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
read(< Buffer >handle, < Buffer >buffer, < integer >offset, < integer >length, < integer >position, < function >callback) - (void) - Reads length bytes from the resource associated with handle starting at position and stores the bytes in buffer starting at offset. callback has 4 parameters: < Error >err, < integer >bytesRead, < Buffer >buffer (offset adjusted), < integer >position.
write(< Buffer >handle, < Buffer >buffer, < integer >offset, < integer >length, < integer >position, < function >callback) - (void) - Writes length bytes from buffer starting at offset to the resource associated with handle starting at position. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
fstat(< Buffer >handle, < function >callback) - (void) - Retrieves attributes for the resource associated with handle. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < Stats >stats.
fsetstat(< Buffer >handle, < ATTRS >attributes, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the attributes defined in attributes for the resource associated with handle. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
futimes(< Buffer >handle, < mixed >atime, < mixed >mtime, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the access time and modified time for the resource associated with handle. atime and mtime can be Date instances or UNIX timestamps. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
fchown(< Buffer >handle, < integer >uid, < integer >gid, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the owner for the resource associated with handle. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
fchmod(< Buffer >handle, < mixed >mode, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the mode for the resource associated with handle. mode can be an integer or a string containing an octal number. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
opendir(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Opens a directory path. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < Buffer >handle.
readdir(< mixed >location, < function >callback) - (void) - Retrieves a directory listing. location can either be a Buffer containing a valid directory handle from opendir() or a string containing the path to a directory. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < mixed >list. list is an Array of { filename: 'foo', longname: '....', attrs: {...} } style objects (attrs is of type ATTR). If location is a directory handle, this function may need to be called multiple times until list is boolean false, which indicates that no more directory entries are available for that directory handle.
unlink(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Removes the file/symlink at path. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
rename(< string >srcPath, < string >destPath, < function >callback) - (void) - Renames/moves srcPath to destPath. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
mkdir(< string >path, [< ATTRS >attributes, ]< function >callback) - (void) - Creates a new directory path. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
rmdir(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Removes the directory at path. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
stat(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Retrieves attributes for path. callback has 2 parameter: < Error >err, < Stats >stats.
lstat(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Retrieves attributes for path. If path is a symlink, the link itself is stat'ed instead of the resource it refers to. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < Stats >stats.
setstat(< string >path, < ATTRS >attributes, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the attributes defined in attributes for path. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
utimes(< string >path, < mixed >atime, < mixed >mtime, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the access time and modified time for path. atime and mtime can be Date instances or UNIX timestamps. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
chown(< string >path, < integer >uid, < integer >gid, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the owner for path. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
chmod(< string >path, < mixed >mode, < function >callback) - (void) - Sets the mode for path. mode can be an integer or a string containing an octal number. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
readlink(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Retrieves the target for a symlink at path. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < string >target.
symlink(< string >targetPath, < string >linkPath, < function >callback) - (void) - Creates a symlink at linkPath to targetPath. callback has 1 parameter: < Error >err.
realpath(< string >path, < function >callback) - (void) - Resolves path to an absolute path. callback has 2 parameters: < Error >err, < string >absPath.
An object with the following valid properties:
mode - < integer > - Mode/permissions for the resource.
uid - < integer > - User ID of the resource.
gid - < integer > - Group ID of the resource.
size - < integer > - Resource size in bytes.
atime - < integer > - UNIX timestamp of the access time of the resource.
mtime - < integer > - UNIX timestamp of the modified time of the resource.
When supplying an ATTRS object to one of the SFTP methods:
atime and mtime can be either a Date instance or a UNIX timestamp.
mode can either be an integer or a string containing an octal number.
An object with the same attributes as an ATTRS object with the addition of the following methods:
stats.isDirectory()
stats.isFile()
stats.isBlockDevice()
stats.isCharacterDevice()
stats.isSymbolicLink()
stats.isFIFO()
stats.isSocket()
rows - < integer > - Number of rows Default: 24
cols - < integer > - Number of columns Default: 80
height - < integer > - Height in pixels Default: 480
width - < integer > - Width in pixels Default: 640
term - < string > - The value to use for $TERM Default: 'vt100'
rows and cols override width and height when rows and cols are non-zero.
Pixel dimensions refer to the drawable area of the window.
Zero dimension parameters are ignored.
FAQs
Unknown package
We found that ssh2 demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Research
Security News
Socket researchers unpack a typosquatting package with malicious code that logs keystrokes and exfiltrates sensitive data to a remote server.
Security News
The JavaScript community has launched the e18e initiative to improve ecosystem performance by cleaning up dependency trees, speeding up critical parts of the ecosystem, and documenting lighter alternatives to established tools.
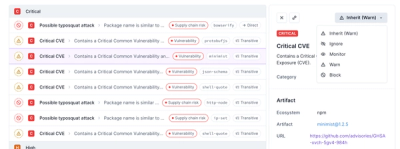
Product
Socket now supports four distinct alert actions instead of the previous two, and alert triaging allows users to override the actions taken for all individual alerts.