💻 Termost
Get the most of your terminal
✨ Features
Termost allows building command line tools in a minute thanks to its:
- Fluent syntax to express your CLI configurations with instructions such as:
- Shareable output between instructions
- Auto-generated help and version metadata
- TypeScript support to foster a type-safe API
- Built-in helpers to make stdin/stdout management a breeze (including exec, and message helpers...)
🚀 Quickstart
Install the library:
npm install termost
pnpm add termost
yarn add termost
Once you're done, you can play with the API:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { helpers, termost } from "termost";
import { name, version } from "../package.json" with { type: "json" };
type ProgramContext = {
globalFlag: string;
};
type DebugCommandContext = {
localFlag: string;
};
const program = termost<ProgramContext>({
name,
description: "CLI description",
version,
onException(error) {
console.error(`Error logic ${error.message}`);
},
onShutdown() {
console.log("Clean-up logic");
},
});
program.option({
key: "globalFlag",
name: { long: "global", short: "g" },
description:
"A global flag/option example accessible by all commands (key is used to persist the value into the context object)",
defaultValue:
"A default value can be set if no flag is provided by the user",
validate({ globalFlag }) {
if (globalFlag === "invalid") return new Error("Invalid input");
return undefined;
},
});
program
.command({
name: "build",
description:
"A custom command example runnable via `bin-name build` (command help available via `bin-name build --help`)",
})
.task({
label: "A label can be displayed to follow the task progress",
async handler() {
await fakeBuild();
},
});
program
.command<DebugCommandContext>({
name: "debug",
description: "A command to play with Termost capabilities",
})
.option({
key: "localFlag",
name: "local",
description: "A local flag accessible only by the `debug` command",
defaultValue: "local-value",
})
.task({
handler(context, argv) {
helpers.message(`Hello, I'm the ${argv.command} command`);
helpers.message(`Context value = ${JSON.stringify(context)}`);
helpers.message(`Argv value = ${JSON.stringify(argv)}`);
},
});
const fakeBuild = async () => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(resolve, 3000);
});
};
Depending on the command, the output will look like this (bin-name is the program name automatically retrieved from the package.json>name):
bin-name --help | 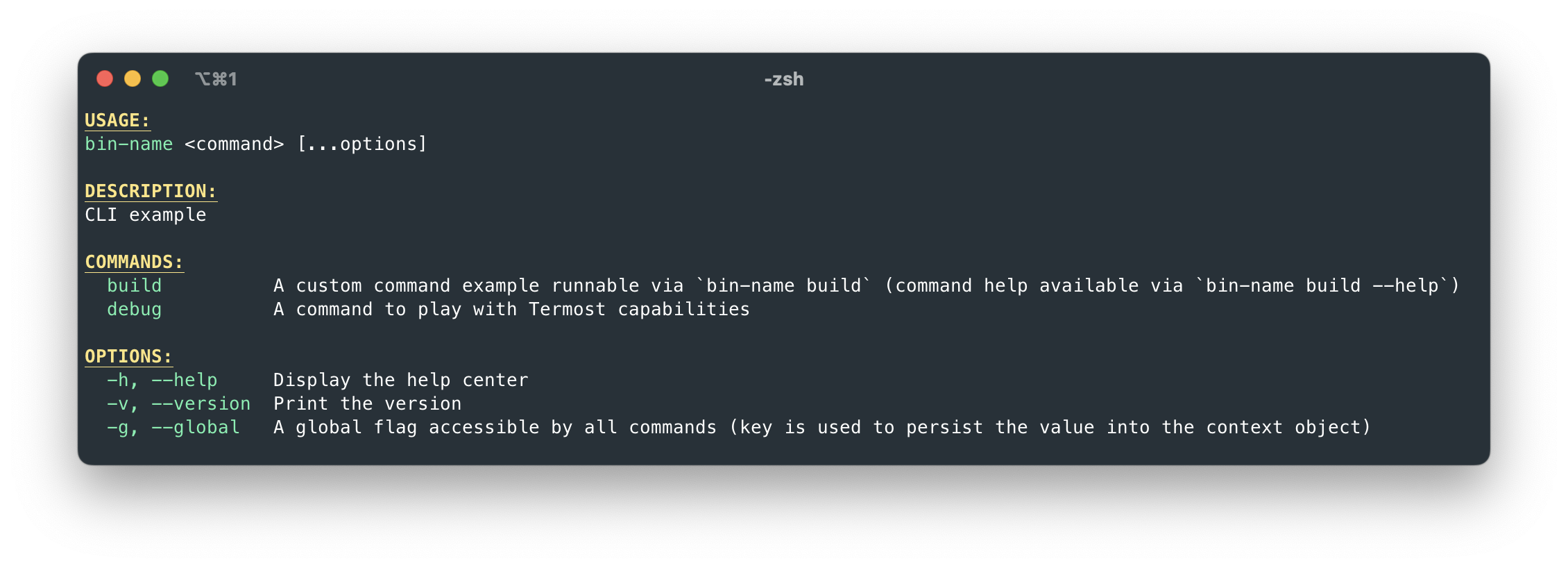 |
bin-name debug --help | 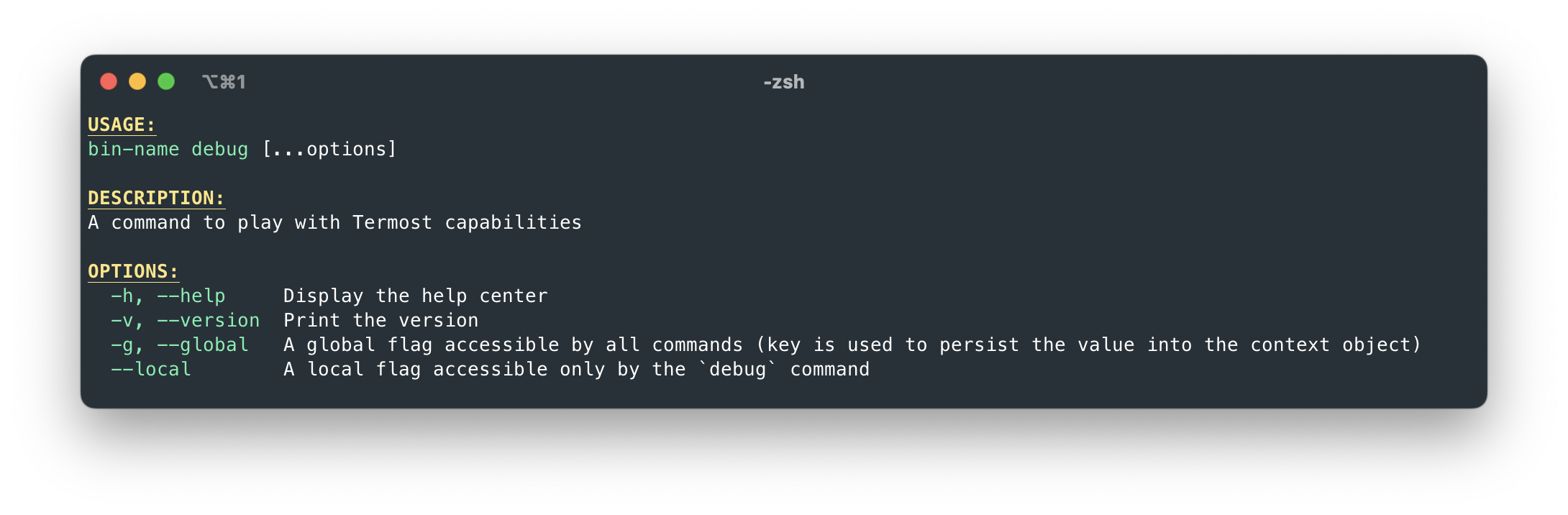 |
bin-name build | 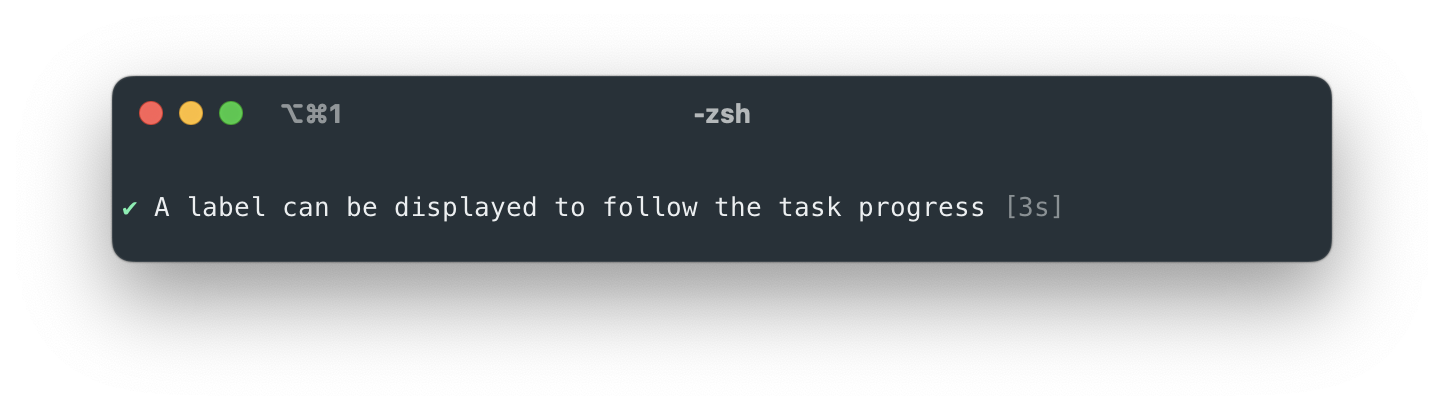 |
bin-name debug | 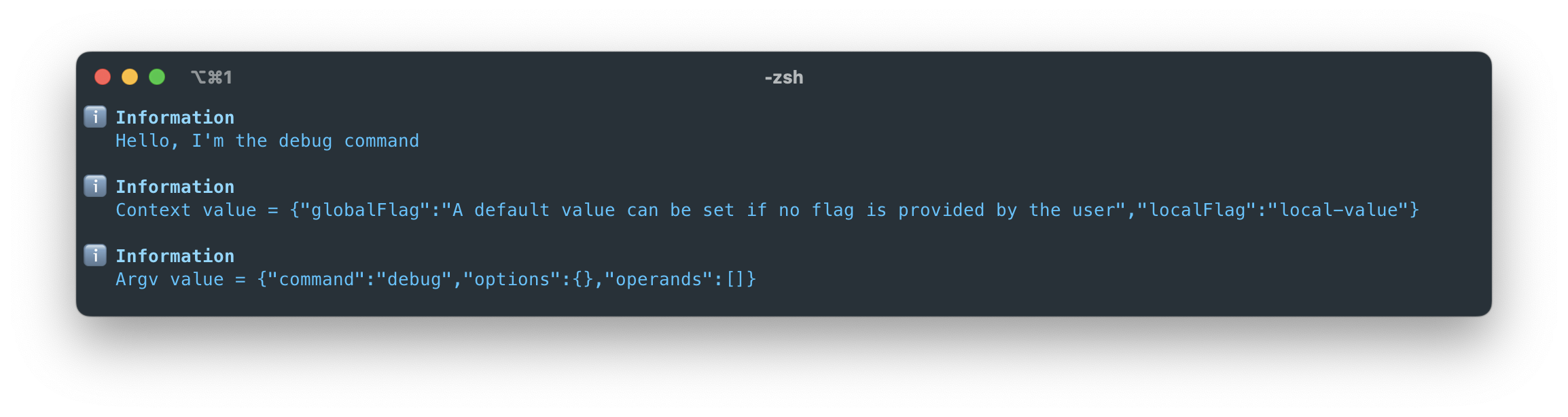 |
✍️ Usage
Here's an API overview:
command({ name, description })
The command API creates a new subcommand context.
Please note that the root command context is shared across subcommands but subcommand's contexts are scoped and not accessible between each other.
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { termost, helpers } from "termost";
import { name, version } from "../package.json" with { type: "json" };
const program = termost({
name,
description: "CLI description",
version,
});
program
.command({
name: "build",
description: "Transpile and bundle in production mode",
})
.task({
handler(context, argv) {
helpers.message(`👋 Hello, I'm the ${argv.command} command`);
},
});
program
.command({
name: "watch",
description: "Rebuild your assets on any code change",
})
.task({
handler(context, argv) {
helpers.message(`👋 Hello, I'm the ${argv.command} command`, {
type: "warning",
});
},
});
input({ key, label, type, skip, validate, ...typeParameters })
The input API creates an interactive prompt.
It supports several types:
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { termost, helpers } from "termost";
import { name, version } from "../package.json" with { type: "json" };
type ProgramContext = {
input1: "singleOption1" | "singleOption2";
input2: Array<"multipleOption1" | "multipleOption2">;
input3: boolean;
input4: string;
};
const program = termost<ProgramContext>({
name,
description: "CLI description",
version,
});
program
.input({
type: "select",
key: "input1",
label: "What is your single choice?",
options: ["singleOption1", "singleOption2"],
defaultValue: "singleOption2",
})
.input({
type: "multiselect",
key: "input2",
label: "What is your multiple choices?",
options: ["multipleOption1", "multipleOption2"],
defaultValue: ["multipleOption2"],
})
.input({
type: "confirm",
key: "input3",
label: "Are you sure to skip next input?",
defaultValue: false,
})
.input({
type: "text",
key: "input4",
label: (context) =>
`Dynamic input label generated from a contextual value: ${context.input1}`,
defaultValue: "Empty input",
skip(context) {
return Boolean(context.input3);
},
validate(context) {
if (context.input4 === "invalid") return new Error("Invalid input");
return undefined;
},
})
.task({
handler(context) {
helpers.message(JSON.stringify(context, null, 4));
},
});
option({ key, name, description, defaultValue, skip, validate })
The option API defines a contextual CLI option.
The option value can be accessed through its key property from the current context.
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { termost, helpers } from "termost";
import { name, version } from "../package.json" with { type: "json" };
type ProgramContext = {
optionWithAlias: number;
optionWithoutAlias: string;
};
const program = termost<ProgramContext>({
name,
description: "CLI description",
version,
});
program
.option({
key: "optionWithAlias",
name: { long: "shortOption", short: "s" },
description: "Useful CLI flag",
defaultValue: 0,
})
.option({
key: "optionWithoutAlias",
name: "longOption",
description: "Useful CLI flag",
defaultValue: "defaultValue",
validate(context) {
if (context.optionWithoutAlias === "invalid")
return new Error("Invalid input");
return undefined;
},
})
.task({
handler(context) {
helpers.message(JSON.stringify(context, null, 2));
},
});
task({ key, label, handler, skip, validate })
The task executes a handler (either a synchronous or an asynchronous one).
The output can be either:
- Displayed gradually if no
label is provided
- Displayed until the promise is fulfilled if a
label property is specified (in the meantime, a spinner with the label is showcased)
#!/usr/bin/env node
import { helpers, termost } from "../src";
import { name, version } from "../package.json" with { type: "json" };
type ProgramContext = {
computedFromOtherTaskValues: "big" | "small";
execOutput: string;
size: number;
};
const program = termost<ProgramContext>({
name,
description: "CLI description",
version,
});
program
.task({
key: "size",
label: "Task with returned value (persisted)",
async handler() {
return 45;
},
})
.task({
label: "Task with side-effect only (no persisted value)",
async handler() {
await wait(500);
},
})
.task({
key: "computedFromOtherTaskValues",
label: "Task can also access other persisted task values",
handler(context) {
if (context.size > 2000) {
return Promise.resolve("big");
}
return Promise.resolve("small");
},
validate(context) {
if (context.computedFromOtherTaskValues === "big")
return new Error("Invalid input");
return undefined;
},
})
.task({
key: "execOutput",
label: "Or even execute external commands thanks to its provided helpers",
handler() {
return helpers.exec("echo 'Hello from shell'");
},
})
.task({
label: "A task can be skipped as well",
async handler() {
await wait(2000);
return Promise.resolve("Super long task");
},
skip(context) {
const needOptimization = context.size > 2000;
return !needOptimization;
},
})
.task({
label: (context) =>
`A task can have a dynamic label generated from contextual values: ${context.computedFromOtherTaskValues}`,
async handler() {},
})
.task({
handler(context) {
helpers.message(
`If you don't specify a label, the handler is executed in "live mode" (the output is not hidden by the label and is displayed gradually).`,
{ label: "Label & console output" },
);
helpers.message(
`A task with a specified "key" can be retrieved here. Size = ${context.size}. If no "key" was specified the task returned value cannot be persisted across program instructions.`,
{ label: "Context management" },
);
},
})
.task({
handler(context) {
const content =
"The `message` helpers can be used to display task content in a nice way";
helpers.message(content, {
label: "Output formatting",
});
helpers.message(content, { type: "warning" });
helpers.message(content, { type: "error" });
helpers.message(content, { type: "success" });
helpers.message(content, {
type: "information",
label: "👋 You can also customize the label",
});
console.log(
helpers.format(
"\nYou can also have a total control on the formatting through the `format` helper.",
{
color: "white",
modifiers: ["italic", "strikethrough", "bold"],
},
),
);
console.info(JSON.stringify(context, null, 2));
},
});
const wait = (delay: number) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => setTimeout(resolve, delay));
};
🤩 Built with Termost
- Quickbundle The zero-configuration transpiler and bundler for the web.
💙 Acknowledgements
This project is built upon solid open-source foundations. We'd like to thank:
enquirer for managing input internalslistr2 for managing task internals
📖 License
MIT



