
Security News
Safari 18.4 Ships 3 New JavaScript Features from the TC39 Pipeline
Safari 18.4 adds support for Iterator Helpers and two other TC39 JavaScript features, bringing full cross-browser coverage to key parts of the ECMAScript spec.
aequitas is an open-source bias auditing and Fair ML toolkit for data scientists, machine learning researchers, and policymakers. The objective of this package is to provide an easy-to-use and transparent tool for auditing predictors, as well as experimenting with Fair ML methods in binary classification settings.
pip install aequitas
or
pip install git+https://github.com/dssg/aequitas.git
To perform a bias audit, you need a pandas DataFrame with the following format:
| label | score | sens_attr_1 | sens_attr_2 | ... | sens_attr_N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 0 | A | F | Y | |
| 1 | 0 | 1 | C | F | N | |
| 2 | 1 | 1 | B | T | N | |
| ... | ||||||
| N | 1 | 0 | E | T | Y |
where label is the target variable for your prediction task and score is the model output.
Only one sensitive attribute is required; all must be in Categorical format.
from aequitas import Audit
audit = Audit(df)
To obtain a summary of the bias audit, run:
# Select the fairness metric of interest for your dataset
audit.summary_plot(["tpr", "fpr", "pprev"])
We can also observe a single metric and sensitive attribute:
audit.disparity_plot(attribute="sens_attr_2", metrics=["fpr"])
To perform an experiment, a dataset is required. It must have a label column, a sensitive attribute column, and features.
from aequitas.flow import DefaultExperiment
experiment = DefaultExperiment(dataset, label="label", s="sensitive_attribute")
experiment.run()
Several aspects of an experiment (e.g., algorithms, number of runs, dataset splitting) can be configured individually.
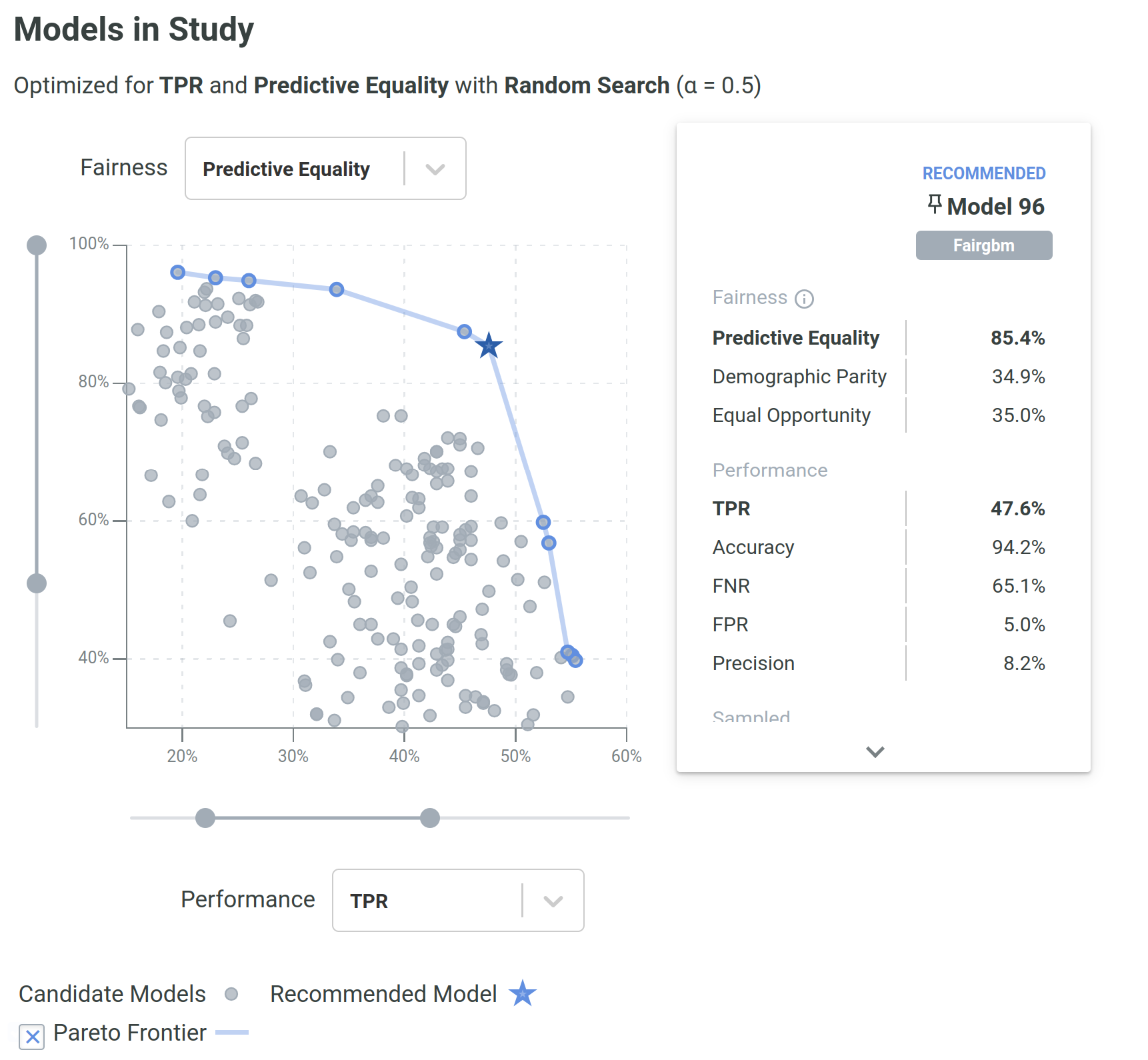
Assuming an aequitas.flow.Dataset, it is possible to train methods and use their functionality depending on the type of algorithm (pre-, in-, or post-processing).
For pre-processing methods:
from aequitas.flow.methods.preprocessing import PrevalenceSampling
sampler = PrevalenceSampling()
sampler.fit(dataset.train.X, dataset.train.y, dataset.train.s)
X_sample, y_sample, s_sample = sampler.transform(dataset.train.X, dataset.train.y, dataset.train.s)
for in-processing methods:
from aequitas.flow.methods.inprocessing import FairGBM
model = FairGBM()
model.fit(X_sample, y_sample, s_sample)
scores_val = model.predict_proba(dataset.validation.X, dataset.validation.y, dataset.validation.s)
scores_test = model.predict_proba(dataset.test.X, dataset.test.y, dataset.test.s)
for post-processing methods:
from aequitas.flow.methods.postprocessing import BalancedGroupThreshold
threshold = BalancedGroupThreshold("top_pct", 0.1, "fpr")
threshold.fit(dataset.validation.X, scores_val, dataset.validation.y, dataset.validation.s)
corrected_scores = threshold.transform(dataset.test.X, scores_test, dataset.test.s)
With this sequence, we would sample a dataset, train a FairGBM model, and then adjust the scores to have equal FPR per group (achieving Predictive Equality).
Experiment.We support a range of methods designed to address bias and discrimination in different stages of the ML pipeline.
| Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-processing | Data Repairer | Transforms the data distribution so that a given feature distribution is marginally independent of the sensitive attribute, s. |
| Label Flipping | Flips the labels of a fraction of the training data according to the Fair Ordering-Based Noise Correction method. | |
| Prevalence Sampling | Generates a training sample with controllable balanced prevalence for the groups in dataset, either by undersampling or oversampling. | |
| Unawareness | Removes features that are highly correlated with the sensitive attribute. | |
| Massaging | Flips selected labels to reduce prevalence disparity between groups. | |
| In-processing | FairGBM | Novel method where a boosting trees algorithm (LightGBM) is subject to pre-defined fairness constraints. |
| Fairlearn Classifier | Models from the Fairlearn reductions package. Possible parameterization for ExponentiatedGradient and GridSearch methods. | |
| Post-processing | Group Threshold | Adjusts the threshold per group to obtain a certain fairness criterion (e.g., all groups with 10% FPR) |
| Balanced Group Threshold | Adjusts the threshold per group to obtain a certain fairness criterion, while satisfying a global constraint (e.g., Demographic Parity with a global FPR of 10%) |
aequitas provides the value of confusion matrix metrics for each possible value of the sensitive attribute columns To calculate fairness metrics. The cells of the confusion metrics are:
| Cell | Symbol | Description |
|---|---|---|
| False Positive | $FP_g$ | The number of entities of the group with $\hat{Y}=1$ and $Y=0$ |
| False Negative | $FN_g$ | The number of entities of the group with $\hat{Y}=0$ and $Y=1$ |
| True Positive | $TP_g$ | The number of entities of the group with $\hat{Y}=1$ and $Y=1$ |
| True Negative | $TN_g$ | The number of entities of the group with $\hat{Y}=0$ and $Y=0$ |
From these, we calculate several metrics:
| Metric | Formula | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | $Acc_g = \cfrac{TP_g + TN_g}{|g|}$ | The fraction of correctly predicted entities withing the group. |
| True Positive Rate | $TPR_g = \cfrac{TP_g}{TP_g + FN_g}$ | The fraction of true positives within the label positive entities of a group. |
| True Negative Rate | $TNR_g = \cfrac{TN_g}{TN_g + FP_g}$ | The fraction of true negatives within the label negative entities of a group. |
| False Negative Rate | $FNR_g = \cfrac{FN_g}{TP_g + FN_g}$ | The fraction of false negatives within the label positive entities of a group. |
| False Positive Rate | $FPR_g = \cfrac{FP_g}{TN_g + FP_g}$ | The fraction of false positives within the label negative entities of a group. |
| Precision | $Precision_g = \cfrac{TP_g}{TP_g + FP_g}$ | The fraction of true positives within the predicted positive entities of a group. |
| Negative Predictive Value | $NPV_g = \cfrac{TN_g}{TN_g + FN_g}$ | The fraction of true negatives within the predicted negative entities of a group. |
| False Discovery Rate | $FDR_g = \cfrac{FP_g}{TP_g + FP_g}$ | The fraction of false positives within the predicted positive entities of a group. |
| False Omission Rate | $FOR_g = \cfrac{FN_g}{TN_g + FN_g}$ | The fraction of false negatives within the predicted negative entities of a group. |
| Predicted Positive | $PP_g = TP_g + FP_g$ | The number of entities within a group where the decision is positive, i.e., $\hat{Y}=1$. |
| Total Predictive Positive | $K = \sum PP_{g(a_i)}$ | The total number of entities predicted positive across groups defined by $A$ |
| Predicted Negative | $PN_g = TN_g + FN_g$ | The number of entities within a group where the decision is negative, i.e., $\hat{Y}=0$ |
| Predicted Prevalence | $Pprev_g=\cfrac{PP_g}{|g|}=P(\hat{Y}=1 | A=a_i)$ | The fraction of entities within a group which were predicted as positive. |
| Predicted Positive Rate | $PPR_g = \cfrac{PP_g}{K} = P(A=A_i | \hat{Y}=1)$ | The fraction of the entities predicted as positive that belong to a certain group. |
These are implemented in the Group class. With the Bias class, several fairness metrics can be derived by different combinations of ratios of these metrics.
| Notebook | Description |
|---|---|
| Audit a Model's Predictions | Check how to do an in-depth bias audit with the COMPAS example notebook. |
| Correct a Model's Predictions | Create a dataframe to audit a specific model, and correct the predictions with group-specific thresholds in the Model correction notebook. |
| Train a Model with Fairness Considerations | Experiment with your own dataset or methods and check the results of a Fair ML experiment. |
You can find the toolkit documentation here.
For more examples of the python library and a deep dive into concepts of fairness in ML, see our Tutorial presented on KDD and AAAI. Visit also the Aequitas project website.
If you use Aequitas in a scientific publication, we would appreciate citations to the following paper:
Pedro Saleiro, Benedict Kuester, Abby Stevens, Ari Anisfeld, Loren Hinkson, Jesse London, Rayid Ghani, Aequitas: A Bias and Fairness Audit Toolkit, arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.05577 (2018). (PDF)
@article{2018aequitas,
title={Aequitas: A Bias and Fairness Audit Toolkit},
author={Saleiro, Pedro and Kuester, Benedict and Stevens, Abby and Anisfeld, Ari and Hinkson, Loren and London, Jesse and Ghani, Rayid}, journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.05577}, year={2018}}
FAQs
The bias and fairness audit toolkit.
We found that aequitas demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 2 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
Safari 18.4 adds support for Iterator Helpers and two other TC39 JavaScript features, bringing full cross-browser coverage to key parts of the ECMAScript spec.

Research
Security News
The Socket Research Team investigates a malicious Python package that enables automated credit card fraud on WooCommerce stores by abusing real checkout and payment flows.

Security News
Python has adopted a standardized lock file format to improve reproducibility, security, and tool interoperability across the packaging ecosystem.