Product
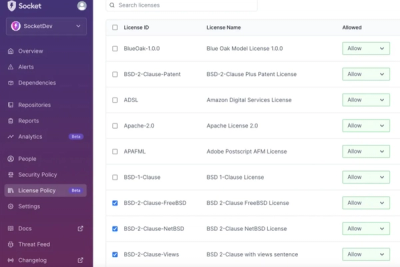
Introducing License Enforcement in Socket
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
This package provides helpers for writing tests.
.. contents:: Table of Contents
FTWIntegrationTesting layer
The ``FTWIntegrationTesting`` is an opinionated extension of Plone's
default integration testing layer.
The primary goal is to be able to run ``ftw.testbrowser``\s traversal
driver with integration testing.
**Database isolation and transactions**
The Plone default integration testing layer does support transactions:
when changes are committed in tests, no isolation is provided
and the committed changes will apear in the next layer.
- We isolate between tests by making a savepoint in the test setup and
rolling back to the savepoint in test tear down.
- With a transaction interceptor we make sure that no code in the test
can commit or abort a transaction. Transactional behavior is simulated
by using savepoints.
**Usage example:**
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import FTWIntegrationTesting
from plone.app.testing import PLONE_FIXTURE
from plone.app.testing import PloneSandboxLayer
class TestingLayer(PloneSandboxLayer):
defaultBases = (PLONE_FIXTURE,)
TESTING_FIXTURE = TestingLayer()
INTEGRATION_TESTING = FTWIntegrationTesting(
bases=(TESTING_FIXTURE,),
name='my.package:integration')
FTWIntegrationTestCase
~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~
The integration test case is an test case base class providing sane defaults
and practical helpers for testing Plone addons with an ``FTWIntegrationTesting``
testing layer.
You may make your own base class in your package, setting the default testing
layer and extending the behavior and helpers for your needs.
**Usage example:**
.. code:: python
# my/package/tests/test_case.py
from ftw.testing import FTWIntegrationTestCase
from my.package.testing import INTEGRATION_TESTING
class IntegrationTestCase(FTWIntegrationTestCase):
layer = INTEGRATION_TESTING
MockTestCase
------------
``ftw.testing`` provides an advanced MockTestCase with support for registering
Zope components (utilities, adapters, subscription adapters and event handlers)
from mocks and tearing down the global component registry during test tear-down.
Some functionality was formerly provided by plone.mocktestcase, which is no
longer maintained. Thus it has been copied over into this package.
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import MockTestCase
The following methods are available:
``self.create_dummy(**kw)``
Return a dummy object that is *not* a mock object, just a dumb object
with whatever attributes or methods you pass as keyword arguments.
To make a dummy method, pass a function object or a lambda, e.g.
self.create_dummy(id="foo", absolute_url=lambda:'http://example.org/foo')
``self.mock_utility(mock, provides, name=u"")```
Register the given mock object as a global utility providing the given
interface, with the given name (defaults to the unnamed default utility).
``self.mock_adapter(mock, provides, adapts, name=u"")```
Register the given mock object as a global adapter providing the given
interface and adapting the given interfaces, with the given name
(defaults to the unnamed default adapter).
``self.mock_subscription_adapter(mock, provides, adapts)``
Register the given mock object as a global subscription adapter providing
the given interface and adapting the given interfaces.
``self.mock_handler(mock, adapts)``
Register the given mock object as a global event subscriber for the
given event types.
``self.mock_tool(mock, name)``
Create a getToolByName() mock (using 'replace' mode) and configure it so
that code calling getToolByName(context, name) obtains the given mock
object. Can be used multiple times: the getToolByName() mock is created
lazily the first time this method is called in any one test fixture.
``self.providing_mock(interfaces, *args, **kwargs)``
Creates a mock which provides ``interfaces``.
``self.mock_interface(interface, provides=None, *args, **kwargs)``
Creates a mock object implementing ``interface``. The mock does not
only provide ``interface``, but also use it as specification and
asserts that the mocked methods do exist on the interface.
``self.stub(*args, **kwargs)``
Creates a stub. It acts like a mock but has no assertions.
``self.providing_stub(interfaces, *args, **kwargs)``
Creates a stub which provides ``interfaces``.
``self.stub_interface(interface, provides=None, *args, **kwargs)``
Does the same as ``mock_interface``, but disables counting of expected
method calls and attribute access. See "Mocking vs. stubbing" below.
``self.set_parent(context, parent_context)``
Stubs the ``context`` so that its acquisition parent is ``parent_context``.
Expects at least context to be a mock or a stub. Returns the ``context``.
``self.stub_request(interfaces=[], stub_response=True, content_type='text/html', status=200)``
Returns a request stub which can be used for rendering templates. With the
``stub_response`` option, you can define if the request should stub a
response by itself. The other optional arguments:
``content_type``: Defines the expected output content type of the response.
``status``: Defines the expected status code of the response.
``self.stub_response(request=None, content_type='text/html', status=200))``
Returns a stub response with some headers and options. When a ``request``
is given the response is also added to the given request.
The other optional arguments:
``content_type``: Defines the expected output content type of the response.
``status``: Defines the expected status code of the response.
Component registry layer
------------------------
The ``MockTestCase`` is able to mock components (adapters, utilities). It
cleans up the component registry after every test.
But when we use a ZCML layer, loading the ZCML of the package it should use
the same component registry for all tests on the same layer. The
``ComponentRegistryLayer`` is a layer superclass for sharing the component
registry and speeding up tests.
Usage:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.layer import ComponentRegistryLayer
class ZCMLLayer(ComponentRegistryLayer):
def setUp(self):
super(ZCMLLayer, self).setUp()
import my.package
self.load_zcml_file('configure.zcml', my.package)
ZCML_LAYER = ZCMLLayer()
Be aware that ``ComponentRegistryLayer`` is a base class for creating your
own layer (by subclassing ``ComponentRegistryLayer``) and is not usable with
``defaultBases`` directly. This allows us to use the functions
``load_zcml_file`` and ``load_zcml_string``.
Mailing test helper
-------------------
The Mailing helper object mocks the mailhost and captures sent emails.
The emails can then be easily used for assertions.
Usage:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.mailing import Mailing
import transaction
class MyTest(TestCase):
layer = MY_FUNCTIONAL_TESTING
def setUp(self):
Mailing(self.layer['portal']).set_up()
transaction.commit()
def tearDown(self):
Mailing(self.layer['portal']).tear_down()
def test_mail_stuff(self):
portal = self.layer['portal']
do_send_email()
mail = Mailing(portal).pop()
self.assertEquals('Subject: ...', mail)
Freezing datetime.now()
-----------------------
When testing code which depends on the current time, it is necessary to set
the current time to a specific time. The ``freeze`` context manager makes that
really easy:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import freeze
from datetime import datetime
with freeze(datetime(2014, 5, 7, 12, 30)):
# test code
The ``freeze`` context manager patches the `datetime` module, the `time` module
and supports the Zope `DateTime` module. It removes the patches when exiting
the context manager.
**Updating the freezed time**
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import freeze
from datetime import datetime
with freeze(datetime(2014, 5, 7, 12, 30)) as clock:
# its 2014, 5, 7, 12, 30
clock.forward(days=2)
# its 2014, 5, 9, 12, 30
clock.backward(minutes=15)
# its 2014, 5, 9, 12, 15
It is possible to ignore modules, so that all calls to date / time functions from
this module are responded with the real current values instead of the frozen ones:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import freeze
from datetime import datetime
with freeze(datetime(2014, 5, 7, 12, 30), ignore_modules=['my.package.realtime']):
pass
You can use the
`timedelta arguments`(https://docs.python.org/2/library/datetime.html#datetime.timedelta)_
for ``forward`` and ``backward``.
Static UUIDS
------------
When asserting UUIDs it can be annoying that they change at each test run.
The ``staticuid`` decorator helps to fix that by using static uuids which
are prefixed and counted within a scope, usually a test case:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import staticuid
from plone.app.testing import PLONE_INTEGRATION_TESTING
from unittest import TestCase
class MyTest(TestCase):
layer = PLONE_INTEGRATION_TESTING
@staticuid()
def test_all_the_things(self):
doc = self.portal.get(self.portal.invokeFactory('Document', 'the-document'))
self.assertEquals('testallthethings0000000000000001', IUUID(doc))
@staticuid('MyUIDS')
def test_a_prefix_can_be_set(self):
doc = self.portal.get(self.portal.invokeFactory('Document', 'the-document'))
self.assertEquals('MyUIDS00000000000000000000000001', IUUID(doc))
Generic Setup uninstall test
----------------------------
``ftw.testing`` provides a test superclass for testing uninstall profiles.
The test makes a Generic Setup snapshot before installing the package, then
installs and uninstalls the package, creates another snapshot and diffs it.
The package is installed without installing its dependencies, because it
should not include uninstalling dependencies in the uninstall profile.
Appropriate testing layer setup is included and the test runs on a seperate
layer which should not interfere with other tests.
Simple example:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.genericsetup import GenericSetupUninstallMixin
from ftw.testing.genericsetup import apply_generic_setup_layer
from unittest import TestCase
@apply_generic_setup_layer
class TestGenericSetupUninstall(TestCase, GenericSetupUninstallMixin):
package = 'my.package'
The ``my.package`` is expected to have a Generic Setup profile
``profile-my.package:default`` for installing the package and a
``profile-my.package:uninstall`` for uninstalling the package.
It is expected to use ``z3c.autoinclude`` entry points for loading
its ZCML.
The options are configured as class variables:
**package**
The dotted name of the package as string, which is used for things such
as guessing the Generic Setup profile names. This is mandatory.
**autoinclude** (``True``)
This makes the testing fixture load ZCML using the ``z3c.autoinclude``
entry points registered for the target ``plone``.
**additional_zcml_packages** (``()``)
Use this if needed ZCML is not loaded using the ``autoinclude`` option,
e.g. when you need to load testing zcml. Pass in an iterable of
dottednames of packages, which contain a ``configure.zcml``.
**additional_products** (``()``)
A list of additional Zope products to install.
**install_profile_name** (``default``)
The Generic Setup install profile name postfix.
**skip_files** (``()``)
An iterable of Generic Setup files (e.g. ``("viewlets.xml",)``) to be
ignored in the diff. This is sometimes necessary, because not all
components can and should be uninstalled properly. For example viewlet
orders cannot be removed using Generic Setup - but this is not a problem
they do no longer take effect when the viewlets / viewlet managers are
no longer registered.
Full example:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.genericsetup import GenericSetupUninstallMixin
from ftw.testing.genericsetup import apply_generic_setup_layer
from unittest import TestCase
@apply_generic_setup_layer
class TestGenericSetupUninstall(TestCase, GenericSetupUninstallMixin):
package = 'my.package'
autoinclude = False
additional_zcml_packages = ('my.package', 'my.package.tests')
additional_products = ('another.package', )
install_profile_name = 'default'
skip_files = ('viewlets.xml', 'rolemap.xml')
Disabling quickinstaller snapshots
----------------------------------
Quickinstaller normally makes a complete Generic Setup (GS) snapshot
before and after installing each GS profile, in order to be able to
uninstall the profile afterwards.
In tests we usually don't need this feature and want to disable it to
speed up tests.
The ``ftw.testing.quickinstaller`` module provides a patcher for
replacing the quickinstaller event handlers to skip creating snapshots.
Usually we want to do this early (when loading ``testing.py``), so that
all the tests are speeding up.
However, some tests which involve quickinstaller rely on having the
snapshots made (see previous section about uninstall tests).
Therefore the snapshot patcher object provides context managers for
temporarily enabling / disabling the snapshot feature.
Usage:
Disable snapshots early, so that everything is fast. Usually this is
done in the ``testing.py`` in module scope, so that it happens already
when the testrunner imports the tests:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.quickinstaller import snapshots
from plone.app.testing import PloneSandboxLayer
snapshots.disable()
class MyPackageLayer(PloneSandboxLayer):
...
When testing quickinstaller snapshot related things, such as uninstalling,
the snapshots can be re-enabled for a context manager or in general:
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing.quickinstaller import snapshots
snapshots.disable()
# snapshotting is now disabled
with snapshots.enabled():
# snapshotting is enabled only within this block
snapshots.enable()
# snapshotting is now enabled
with snapshots.disabled():
# snapshotting is disabled only within this block
Transaction interceptor
-----------------------
The ``TransactionInterceptor`` patches Zope's transaction manager in
order to prevent code from interacting with the transaction.
This can be used for example for making sure that no tests commit transactions
when they are running on an integration testing layer.
The interceptor needs to be installed manually with ``install()`` and removed
at the end with ``uninstall()``. It is the users responsibility to ensure
proper uninstallation.
When the interceptor is installed, it is not yet active and passes through all
calls.
The intercepting begins with ``intercept()`` and ends when ``clear()`` is
called.
.. code:: python
from ftw.testing import TransactionInterceptor
interceptor = TransactionInterceptor().install()
try:
interceptor.intercept(interceptor.BEGIN | interceptor.COMMIT
| interceptor.ABORT)
# ...
interceptor.clear()
transaction.abort()
finally:
interceptor.uninstall()
Testing Layers
--------------
Component registry isolation layer
plone.app.testing's default testing layers (such as PLONE_FIXTURE) do not
isolate the component registry for each test.
ftw.testing's COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION testing layer isolates the
component registry for each test, provides a stacked ZCML configuration context
and provides the methods load_zcml_string and load_zcml_file for loading
ZCML.
Example:
.. code:: python
# testing.py
from ftw.testing.layer import COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION
from plone.app.testing import IntegrationTesting
from plone.app.testing import PloneSandboxLayer
from zope.configuration import xmlconfig
class MyPackageLayer(PloneSandboxLayer):
defaultBases = (COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION,)
def setUpZope(self, app, configurationContext):
import my.package
xmlconfig.file('configure.zcml', ftw.package,
context=configurationContext)
MY_PACKAGE_FIXTURE = MyPackageLayer()
MY_PACKAGE_INTEGRATION = IntegrationTesting(
bases=(MY_PACKAGE_FIXTURE,
COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION),
name='my.package:integration')
# ----------------------------
# test_*.py
from unittest import TestCase
class TestSomething(TestCase):
layer = MY_PACKAGE_INTEGRATION
def test(self):
self.layer['load_zcml_string']('<configure>...</configure>')
Temp directory layer
The ``TEMP_DIRECTORY`` testing layer creates an empty temp directory for
each test and removes it recursively on tear down.
The path to the directory can be accessed with the ``temp_directory`` key.
Usage example:
.. code:: python
from unittest import TestCase
from ftw.testing.layer import TEMP_DIRECTORY
class TestSomething(TestCase):
layer = TEMP_DIRECTORY
def test(self):
path = self.layer['temp_directory']
Console script testing layer
The console script layer helps testing console scripts. On layer setup it creates and executes an isolated buildout with the package under development, which creates all console scripts of this package. This makes it easy to test console scripts by really executing them.
Usage example:
.. code:: python
# testing.py
from ftw.testing.layer import ConsoleScriptLayer
CONSOLE_SCRIPT_TESTING = ConsoleScriptLayer('my.package')
# test_*.py
from my.package.testing import CONSOLE_SCRIPT_TESTING
from unittest import TestCase
class TestConsoleScripts(TestCase):
layer = CONSOLE_SCRIPT_TESTING
def test_executing_command(self):
exitcode, output = self.layer['execute_script']('my-command args')
self.assertEqual('something\n', output)
Be aware that the dependency zc.recipe.egg is required for building the
console scripts. You may put the dependency into your tests extras require.
Upgrading from ftw.testing 1.x to 2.0
``mocker`` has been replaced in favor of ``unittest.mock``.
This is a `breaking` change and may require amending existing tests based on
``MockTestCase``.
With ``mocker`` expectations were recorded in `record` mode while using the
mock in tests was done in `replay` mode. This is no longer the case with
``unittest.mock``. Here's a simple example how expectations can be adopted:
.. code:: python
# Mocking with mocker
mock = self.mocker.mock() # mocker.Mock
self.expect(mock.lock()).result('already locked')
self.replay()
self.assertEqual(mock.lock(), 'already locked')
.. code:: python
# Mocking with unittest.mock
mock = self.mock() # unittest.mock.Mock
mock.lock.return_value = 'already locked'
self.assertEqual(mock.lock(), 'already locked')
Compatibility
-------------
Runs with `Plone <http://www.plone.org/>`_ `4.3`, `5.1` and `5.2`.
Links
-----
- Github: https://github.com/4teamwork/ftw.testing
- Issues: https://github.com/4teamwork/ftw.testing/issues
- Pypi: http://pypi.python.org/pypi/ftw.testing
- Continuous integration: https://jenkins.4teamwork.ch/search?q=ftw.testing
Copyright
---------
This package is copyright by `4teamwork <http://www.4teamwork.ch/>`_.
``ftw.testing`` is licensed under GNU General Public License, version 2.
.. _plone.mocktestcase: http://pypi.python.org/pypi/plone.mocktestcase
.. _Splinter: https://pypi.python.org/pypi/splinter
Changelog
=========
2.0.7 (2022-12-23)
------------------
- Make freezer's "ignore_modules" more robust.
[phgross]
2.0.6 (2020-05-28)
------------------
- Significantly optimize freezer's "ignore_modules" by avoiding retrieving the
complete call stack.
[buchi]
2.0.5 (2019-12-17)
------------------
- Stop quickinstall_uninstallation test from being skipped on Plone 5.1 [djowett-ftw]
- restore diffs for uninstall tests after removing unittest2 [djowett-ftw]
2.0.4 (2019-12-04)
------------------
- Add missing getToolByName default argument [Nachtalb]
2.0.3 (2019-11-22)
------------------
- Fix pickling of datetime while time is frozen. [buchi]
2.0.2 (2019-11-19)
------------------
- Fix super call to mock_tool. [buchi]
2.0.1 (2019-11-19)
------------------
- Fix component registry tear down in MockTestCase. [buchi]
- Rename FrozenDateTime class to FrozenDatetime to workaround poor check for
Zope's DateTime in plone.event. [buchi]
2.0.0 (2019-11-11)
------------------
- Add support for Plone 5.2 and Python 3. [buchi]
- No longer base on plone.mocktestcase as it's not compatible with Python 3 and
replace mocker with unittest.mock. This is a *breaking* change and may
require amending existing tests based on ``MockTestCase``.
[buchi]
- Reimplement freezer without forbiddenfruit and mocker. [buchi]
1.20.1 (2019-04-04)
-------------------
- Optimize "ignore_modules" to avoid unneeded stack inspections. [Rotonen]
1.20.0 (2019-01-25)
-------------------
- Add "ignore_modules" support to freezer. [jone]
1.19.2 (2018-11-05)
-------------------
- Fix in timezone aware freezing for Zope DateTime. [njohner]
1.19.1 (2018-10-23)
-------------------
- Fix invalid reST in README.rst [Nachtalb]
1.19.0 (2018-10-15)
-------------------
- Drop support for plone 4.2. [jone]
- Fix bug with getting a timezone aware "now". [njohner]
1.18.0 (2018-07-12)
-------------------
- Extend ``staticuid`` to also be a context manager. [jone]
- Also freeze ``datetime.utcnow()``. [Rotonen]
1.17.0 (2017-10-02)
-------------------
- Add ``FTWIntegrationTesting`` and ``FTWIntegrationTestCase``. [jone]
1.16.0 (2017-08-08)
-------------------
- Support Plone 5.1 for ConsoleScriptLayer. [jone]
1.15.2 (2017-07-18)
-------------------
- Freezer: keep timezone info when moving clock forward / backward. [jone]
- Freezer: Fix DST-bug in today() and time(). [jone]
1.15.1 (2017-07-04)
-------------------
- Fix savepoint simulation to cleanup savepoints. [jone]
1.15.0 (2017-07-03)
-------------------
- Add savepoint simulation to transaction interceptor. [jone]
1.14.0 (2017-06-23)
-------------------
- Do not require "Plone" egg. [jone]
1.13.0 (2017-06-20)
-------------------
- Add transaction interceptor. [jone]
1.12.0 (2017-06-19)
-------------------
- Support Plone 5.1 [mathias.leimgruber, jone]
- Remove splinter browser. Use ftw.testbrowser instead. [mathias.leimgruber, jone]
- Drop Plone 4.1 support. [jone]
1.11.0 (2016-03-31)
-------------------
- Freezer: reimplement "now" patching with forbiddenfruit.
This fixes problems with pickling and comparison of frozen datetime objects.
[jone]
1.10.3 (2015-10-11)
-------------------
- Freezer: disable freezing while committing to database for preventing pickling errors.
[jone]
- Freezer bugfix: replace datetime instances when leaving freeze context manager.
[jone]
1.10.2 (2015-07-30)
-------------------
- Added timezone(`tz`) support for "freeze".
[phgross]
1.10.1 (2015-07-27)
-------------------
- Use "now" as default of "freeze".
[jone]
1.10.0 (2015-05-18)
-------------------
- Update the freezed time with ``forward`` and ``backward``.
[jone]
1.9.1 (2015-05-15)
------------------
- Fix site hook within ``staticuid`` decorated methods.
[jone]
1.9.0 (2015-05-15)
------------------
- Add ``staticuid`` decorator for having static uids.
[jone]
1.8.1 (2015-01-05)
------------------
- Declare missing dependency to p.a.testing
required by the COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION layer.
[jone]
1.8.0 (2014-12-31)
------------------
- Implement console script testing layer.
[jone]
- Implement TEMP_DIRECTORY testing layer.
[jone]
- Implement COMPONENT_REGISTRY_ISOLATION layer.
[jone]
1.7.0 (2014-09-30)
------------------
- Add patcher for disabling quickinstaller snappshotting in tests.
[jone]
1.6.4 (2014-05-01)
------------------
- Generic Setup uninstall test: Add a second test that uses Portal Setup for
uninstallation. This makes sure that Portal Setup uninstallation behaves the same as
quickinstaller uninstallation.
[deif]
1.6.3 (2014-04-30)
------------------
- Generic Setup uninstall test: Remove is_product option, since we
require an uninstall external method which requires the package
to be a product anyway.
[jone]
- Generic Setup uninstall test: test that there is an uninstall external method.
Uninstall external methods are still necessary today for properly uninstalling
a package.
[jone]
1.6.2 (2014-04-30)
------------------
- Generic Setup test: use quickinstaller for uninstalling.
[jone]
1.6.1 (2014-04-29)
------------------
- Also install profile dependencies before creating a snapshot.
[deif]
1.6.0 (2014-04-29)
------------------
- Implement Generic Setup uninstall base test.
[jone]
1.5.2 (2014-02-09)
------------------
- Fix ``isinstance`` calls of freezed time in ``freeze`` context manager.
[jone]
1.5.1 (2014-02-08)
------------------
- Implement ``freeze`` context manager for freezing the time.
[jone]
1.5.0 (2013-09-24)
------------------
- AT form page object: add schemata helper methods for testing visible
schematas and fields.
[jone]
1.4 (2013-08-26)
----------------
- Add custom mailhost class, remembering the sender and recipient
of each email separately.
[deif]
- Deprecate @javascript because Selenium with PhantomJS is too unstable.
Removes tests and documentation, the @javascript decorator still works
for now but needs to be imported from ftw.testing.browser.
[jone]
- Page objects: add a Plone.visit(obj) function.
[jone]
- Fix a rare bug where the MockMailHost message list has been replaced by
another instance.
[jone, deif]
1.3.1 (2013-05-24)
------------------
- Move ``Mailing`` helper class to its own module ``mailing``.
[deif]
1.3 (2013-05-03)
----------------
- Drop official Plone 4.0 support.
[jone]
- Component registry layer: use isolated ZCML layers.
When using the same layer instances it may conflict with integration or
functional testing layers.
[jone]
- Add splinter integration and Plone page objects.
[jone]
- onegov.ch approved: add badge to readme.
[jone]
- MockTestCase: Support Products.PloneHotfix20121106 patch when mocking getToolByName.
[jone]
- MockTestCase: add checks that setUp is called correctly.
[jone]
1.2 (2012-05-22)
----------------
- Add ``stub_reponse`` method to ``MockTestCase`` and adjust the
``stub_request`` method accordant.
[phgross]
- Made providing interfaces configurable for the ``stub_request`` method.
[phgross]
- Let the stub_request method also stub the getStatus of the response.
[phgross]
- Add ``stub_request`` method to ``MockTestCase``.
[jone]
- No longer tear down the component registry in mock test case. Use the
ComponentRegistryLayer.
[jone]
- Add ``ComponentRegistryLayer`` base class.
[jone]
- Add ``mock_interface`` and ``stub_interface`` methods to MockTestCase, creating
a mock and using the interface as spec.
[jone]
- Accept also interfaces directly rather than lists of interfaces when
creating mocks or stubs which provides the interfaces.
[jone]
1.1 (2011-11-16)
----------------
- Patch mock_tool: do not count, so that it can be used multiple times.
[jone]
1.0 (2011-10-12)
----------------
- Initial release
FAQs
Provides some testing helpers and an advanced MockTestCase.
We found that ftw.testing demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 12 open source maintainers collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Product
Ensure open-source compliance with Socket’s License Enforcement Beta. Set up your License Policy and secure your software!
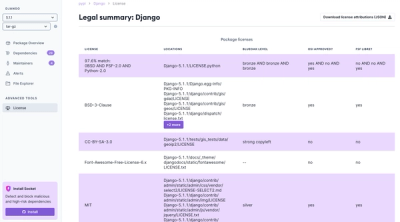
Product
We're launching a new set of license analysis and compliance features for analyzing, managing, and complying with licenses across a range of supported languages and ecosystems.
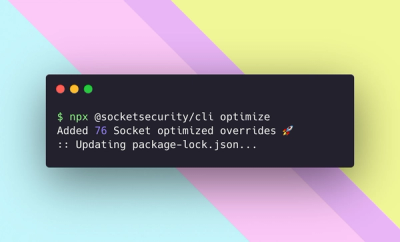
Product
We're excited to introduce Socket Optimize, a powerful CLI command to secure open source dependencies with tested, optimized package overrides.