
Security News
VulnCon 2025: NVD Scraps Industry Consortium Plan, Raising Questions About Reform
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
Labelatory - the powerful and the greatest tool for label management across repositories on different git systems.
Labelatory is a web application for synchronization of labels among repositories stored on diffenrent git services.
To use the Labelatory application you have to do the following steps:
pip install labelatory
export FLASK_APP=labelatory
export LABELATORY_CONFIG=<PATH TO YOUR credentials_conf.cfg>
flask run
It is recommenden to use ngrok or another similar program to make Labelatory be able to process webhooks events from your repositories.
The application allows to manage labels (create, update and delete) for given services and repositries according to API of the services.
Work with API runs in asynchronous manner.
The application is built with Flask framework and uses webhooks cofigured for labels events. Once some action with some label in managable repository is performed, the application reacts on this event and checks whether the label conforms to configuration. If it does not conform, the application reverts this label.
Web interface displays current preferences for services and repositories that were read by the application from the configuration file.
User can change these preferences at his own discretion - customize already defined labels, add new label, add new repository for service.
Adding support for a new service is provided with implementing the interface for comunnication with git service according to API documentation of the new service.
User can save his customized preferences to local configuration file.
Credentials cofiguration file is stored locally and contains data for accessing the services and defines, where the label configuration file is stored.
Credentials cofiguration file example:
[config]
type = <TYPE>
repo = github_username/github_config_repo
[service:github]
token = <GITHUB_TOKEN>
secret = <GITHUB_WEBHOOK_SECRET>
[service:gitlab]
host = <HOST>
token = <GITLAB_TOKEN>
secret = <GITLAB_WEBHOOK_SECRET>
Labels settings are stored in configuration files. The example of such a file is below:
[repo:github]
github_username/github_repo_1 = true
github_username/github_repo_2 = false
[repo:gitlab]
gitlab_username/gitlab_repo_1 = true
gitlab_username/gitlab_repo_2 = false
[label:bug]
color = #123456
description = Indicates an unexpected problem or unintended behavior
FAQs
Labelatory - the powerful and the greatest tool for label management across repositories on different git systems.
We found that labelatory demonstrated a healthy version release cadence and project activity because the last version was released less than a year ago. It has 1 open source maintainer collaborating on the project.
Did you know?

Socket for GitHub automatically highlights issues in each pull request and monitors the health of all your open source dependencies. Discover the contents of your packages and block harmful activity before you install or update your dependencies.

Security News
At VulnCon 2025, NIST scrapped its NVD consortium plans, admitted it can't keep up with CVEs, and outlined automation efforts amid a mounting backlog.
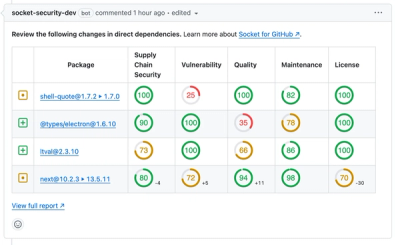
Product
We redesigned our GitHub PR comments to deliver clear, actionable security insights without adding noise to your workflow.
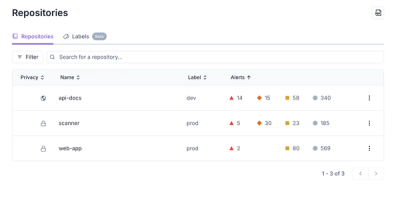
Product
Our redesigned Repositories page adds alert severity, filtering, and tabs for faster triage and clearer insights across all your projects.